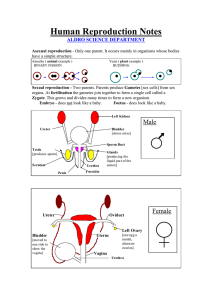
Reproduction 2 weeks Essential questions: - How do different animals (including humans) create children? What are the parts of the human reproductive system? How can technology help to solve problems around reproduction? How can we interpret and present information in diagrams? Vocabulary: - asexual reproduction sexual reproduction meiosis mitosis infertility in-vitro fertilisation Developing baby - gamete fertilisation zygote blastocyst embryo foetus Females - ovulation menstruation pregnancy gestation umbilical cord ovum / ova ovary fallopian tube / oviduct uterus cervix vagina Males - sperm testis / testes epididymis vans deferens / sperm duct prostate gland urethra penis semen ejaculation Goals: - Outline the process of reproduction in humans Identify parts of the male and female reproductive systems Explain how technology can help to solve reproductive problems Interpret and present information in diagrams End product: - Summary diagrams: Venn diagram of male and female reproductive organs, flow charts of human reproduction and baby development, graph of hormone levels during menstruation cycle Checklist: 1. Unit outline, brainstorm, discussion of essential questions (identify existing understandings) 2. Asexual and sexual reproduction: advantages and disadvantages - Binary fission in bacteria graphing exercise - Briefly compare mitosis and meiosis 3. Human reproduction - The amazing sperm race - Parts of each system - Menstrual cycle - Flow chart of events from gamete production onwards 4. Issues around reproduction - Infertility and solutions including IVF - Sexually transmitted diseases and contraception - Pregnancy difficulties and solutions - Extension: diseases of the reproductive systems like cysts and cancers Year 9 Science Topic: Reproduction Big questions: How do different animals (including humans) create children? What are the parts of the human reproductive system? How can technology help to solve problems around reproduction? How can we interpret and present information in diagrams? Class assessment task: Create summary diagrams: a Venn diagram of male and female reproductive organs, a flow charts of human reproduction and one on baby development, a graph of hormone levels during menstruation cycle. Vocabulary: - asexual reproduction: process of producing offspring (children) without sex - sexual reproduction: process of producing offspring through sex, with a male and a female parent - meiosis: cell division that halves the number of chromosomes in a cell, producing gametes - mitosis: cell division that makes new cells with the same number of chromosomes as the original - infertility: the inability to have children - in-vitro fertilisation: a medical process where a sperm fertilises an egg outside of the body Developing baby - gamete: a male or female sex cell with half the normal number of chromosomes (male = sperm, female = ovum) that combines with another sex cell to create a zygote - fertilisation: the process where a male and female sex cell fuse together to form a zygote - zygote: the first cell of a new baby, produced by fertilisation of an egg by a sperm - embryo: a group of cells formed from the zygote and developing into different body organs - foetus: individual in the uterus after eight weeks of development Females - ovum / ova: the female sex cell created by meiosis in the ovaries (before a female is born) - ovary: the organ that stores and releases ova as they mature - fallopian tube / oviduct: tube that carries ova from ovary to uterus, where fertilisation occurs - uterus: the hollow space in which a baby develops - cervix: a muscular ring around the base of the uterus that keeps the baby from coming out - vagina: a muscular tube connecting the uterus to the outside - ovulation: the process where a female releases an egg so it can be fertilised - menstruation: the process where the uterine lining is shed if the egg is not fertilised (a period) - pregnancy: the state of carrying a developing child in the womb (uterus) - gestation: the period of time of child developing from conception to birth - umbilical cord: links the placenta to the foetus for the exchange of nutrients and gases - placenta: a structure that gives nutrients and oxygen to the developing baby and removes wastes Males - sperm: male sex cell created by meiosis in the testes (continuously throughout lifetime) - testis / testes: the organ in which sperm are created - scrotum: the sac in which the testes are held, keeps them away from the body so they are cooler - epididymis: coiled tubes at the back of the testes where sperm is stored - vans deferens / sperm duct: tubes that carry sperm from the epididymis to the urethra - prostate gland: gland that adds nourishing seminal fluid to sperm to help keep it alive - urethra: tube in the middle of the penis, carries sperm outside of the body - penis: fleshy tissue surrounding the urethra, used for delivery of semen from male to female - semen: mixture of sperm and seminal fluid - ejaculation: release of sperm from the penis