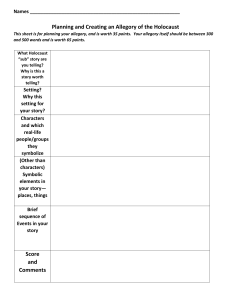
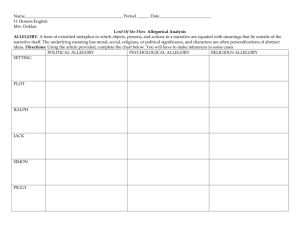
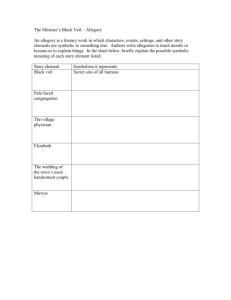
Allegory, Fable, Parable & Myth Learning Goal • To recognise that many stories are not literal, rather they use symbols to share their message. • To identify some of the different types of symbolic storytelling. Stories • Throughout history, stories have been told as a way of teaching lessons. • Many stories use symbols and simple characters to make the message more easily understood by the receivers. • Story types include: allegory, fable, parable and myths. Even many of the Indigenous dreaming stories share important morals and messages. Allegory • An allegory is a narrative (story) in which characters and action represent concepts different to their literal meaning in the story. • In an allegory, people, things and actions represent an idea or generalisation about life. • Allegories often have a strong moral lesson. • Examples: The Chronicles of Narnia, The Giver, Dr Seuss’ The Sneetches. Allegory Fables • A fable is a short story, often featuring animals that speak and act like human beings. • Their purpose is to teach the reader a lesson about life. • Features simple characters and plot. • Examples: The Hare and the Tortoise, The Boy who Cried Wolf, The Lion and the Mouse. • Many fables are credited to Aesop: a slave and a story teller in ancient Greece. Fables Parables • A brief and succinct (to-the-point) story that illustrate a moral or religious lesson. • While fables use animals, parables generally feature human characters. • Examples: Biblical: The Parable of the Good Samaritan, The Parable of the Lost Sheep. Buddhist: All is Vanity. Parables Myths • Myths are narratives (stories) often associated with religion, philosophy and various races and cultures. • They embody the social and cultural values of the time they were written. • Examples: Thor and the Valkyrie, Cyclops, Hades, Anubis. Myths