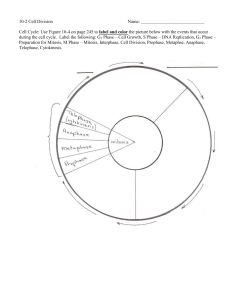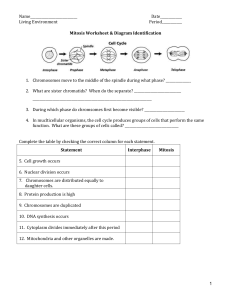
3.CELL DIVISION: MITOSIS Grade 10 Life Science Miss L Klein Terminology 1.Benign 3.Centromere 5.Chromosome 7.Chromatids 9.Malignant 11.Tumour 2.Cancer 4.Cell cycle 6.Cytokinesis 8.Karyokinesis 10.Mitosis Importance of Mitosis ◦Growth: new cells are formed for growth ◦ Reproduction: allows unicellular organisms to produce asexually ◦Repair: replaces and repairs damaged cells The cell cycle ◦The cell cycle starts when the cell forms and ends when the cell matures and division takes place. ◦The cell cycle has three parts. 1.Interphase: cell growth 2.Mitosis: cell division 3.Cytokinesis: cytoplasm divides into two parts at the end of cell division. Mitosis ◦It is the process of cell division where a parent cell divides into 2 daughter cells ◦Two division processes are important in mitosis: ◦Karyokinesis and cytokinesis Mitosis has four phases. 1. PROPHASE 2. METAPHASE 3. ANAPHASE 4. TELOPHASE ◦Before the cell divides, all the DNA is replicated (DNA replication) ◦Once DNA replication takes place, each chromosome appears as two chromatids, which are held together by a centromere. 1. Prophase ◦Chromosomes coil up ◦Nuclear envelope disappears ◦Spindle fibres form 2. Metaphase ◦Chromosomes line up in middle of cell ◦Spindle fibres connect to chromosomes 3. Anaphase ◦Chromosome copies divide ◦Spindle fibres pull chromosomes to opposite poles 4. Telophase ◦Chromosomes uncoil ◦Nuclear envelopes form ◦2 new nuclei are formed ◦Spindle fibres disappear Cytokinesis ◦It is the division of the rest of the cell (cytoplasm and organelles) after the nucleus divides ◦In animal cells the cytoplasm pinches in ◦In plant cells a cell plate is formed ◦After mitosis and cytokinesis the cell returns to Interphase to continue to grow and perform regular cell ativities. UNCONTROLLED CELL DIVISION (CANCER) ◦The cell cycle is controlled by signals and the body cells divide between 20 to 50 times, then get old and die. ◦However, some cells ignore the signals and carry on dividing to form a mass of cells which become cancerous. ◦They cause different cancers depending on where they are. ◦Cancer is dangerous because it can spread and attack healthy organs Different Kinds of Cancers ◦1. Carcinomas: skin or epithelium cancer lining organs, glands and skin ◦2. Sarcomas: bone, cartilage and muscle ◦3. Leukaemia: blood and lymphatic and immune system Causes of Cancer ◦Cancer is uncontrolled cell growth. ◦Different types are caused by different factors called carcinogens. ◦These could be: ◦ Inherited ◦ Smoking ◦ Processed foods ◦ Viruses -Radiation -Hormonal imbalances -Pollutants and pesticides Two Types of Tumours ◦Benign tumour: cell masses that stay at one site; does not spread ◦Malignant tumour: cancerous cells can leave the first site and invade other organs and tissue in a process called metastasis. Treatment of Cancer 1.Surgery: 2.Chemotherapy 3.Radiation