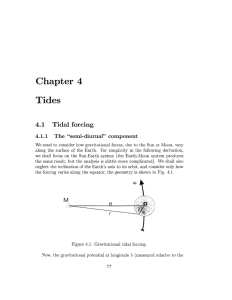
Marine Science: Test Review Posters = Students will work in their desk groups (no more than 4 people) to create a poster review of the material covered for this unit. Paper will be available by the front board in my room. The posters should include the following information in three sections: Waves: 1. Draw and label the parts of a water wave. 2. Define what a wave is and what influences waves. a. Wave = a disturbance that moves through or over the surface of water b. Caused by wind 3. Identify the typical causes of ocean waves. a. Undersea earthquakes & volcanic eruptions b. gravitational pull of sun & moon 4. How do waves effect the ocean physically? a. Cause the mixing of water temperatures & salinity b. Shapes the coastline as they hit it 5. How do waves effect the ocean biologically? a. Mix oxygen into water b. Mix nutrients from deep water to shallow 6. Describe the differences between chop, swell & tsunami a. Chop = small waves with a short wavelength and high frequency b. Swell = long wavelength and long time between (open ocean) c. Tsunami = high wave height in shallow water; caused by undersea earthquakes; low height in open ocean Tides: 1. Define what a tide is and what influences tides. a. Tides = rhythmic (comes in cycles) rise & fall of oceans b. Influenced by gravitational pull of sun & moon; depth of water; type of shoreline 2. Identify the typical causes of ocean tides. a. Caused by rotation of earth on axis b. Pull of sun & moon’s gravity on the earth 3. How do tides effect the ocean physically? a. Raise & lower water levels along coastlines b. Mix water vertically and horizontally on a cyclic basis 4. How do tides effect the ocean biologically? a. Mixes nutrients in the water b. Causes some areas to have wet & dry cycles c. Triggers breeding cycle in some species 5. Describe the differences between spring & neap tides. a. Spring tide happens when the sun, moon & earth are all in one line in space. Causes higher tides 2x a month. b. Neap tide happens when the moon is at a right angle to the sun in space (relative to the earth). Causes lower tides 2x a month. 6. Describe the differences between high, low and slack tides. a. High tide = rising, incoming tide, flow b. Low tide = receding, outgoing tide, ebb c. Slack tide = vertical movement stops Climate & Weather: 1. Define Weather a. The temperature and precipitation on a daily, short term, local basis b. Highly variable 2. Define Climate a. Temperature and precipitation patterns over a long term, large geographic area b. Generally stable in the terms of 100 – 1000 year cycles 3. Describe radiant energy and what 4 factors influence it. a. Radiant energy is the amount of energy reaching the earth from the sun b. Influenced by i. Angle of insolation ii. Cloud cover iii. Pollution in the air iv. Levels of greenhouse gases in the air (carbon dioxide, water vapor, nitrogen) 4. Know the three main climate zones and some of their characteristics a. Polar = 60-90 degrees Latitude; cold year-long; dry; average precipitation less than 10 inches b. Temperate = 30-60 degrees Latitude; 4 full seasons a year; variable climate north to south; 24-48 inches of precipitation yearly; average temps from 5-20 degrees celcius 5. Understand the factors that affect temperature and precipitation in a climate zone a. Latitude = how close to the equator or the poles an area is b. Altitude = elevation above sea level; higher altitude has colder and drier air c. Presence of Ocean currents near by = cold or warm water currents will cool or warm the air and land near them; also can change the amount of rainfall an area gets d. Prevailing winds = winds that are warmer or cooler e. High mountain ranges = block wind and air currents 6. Be able to explain how land breezes and sea breezes form a. Sea breezes form when the land heats up more quickly than the ocean. Heat over the land causes air to rise, pulling cooler air off the oceans. b. Land breezes form when the land cools off more quickly than the ocean. Heat over the ocean causes air to rise, pulling cooler air off the land. c. 7. Be able to explain maritime and continental climates a. Maritime = near oceans and large lakes have more precipitation and generally a more stable weather pattern and climate b. Continental = inland, less frequent precipitation; more extremes of weather and climate; really cold to really hot; really dry to very wet