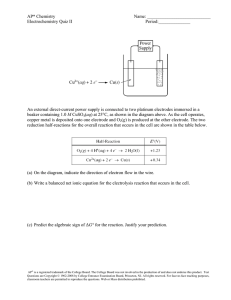
Analytical Chemistry Exam Questions
advertisement

Question 1 When potassium iodide reacts with lead(II) nitrate, a yellow precipitate (PbI2) is produced. If 0.78 g of lead(II) iodide was produced, how many grams of lead(II) nitrate was used? You may assume the reaction yield was 100%, and an excess of potassium iodide was used. A. B. C. D. E. 0.78 g 1.6 g 0.46 g 0.56 g Not enough information is given. Question 2 If 4.94 grams of KOH is dissolved in water to make a final volume of 2.0 L, what is the molarity of the solution? A. B. C. D. E. 0.088 M 0.044 M 2.5 M 0.025 M 0.18 M Question 3 If 21.3 g of glucose (C6H12O6) is dissolved in 5.00 L of deionized water, what is the molality of the solution? (The density of water is 1.00 g/mL.) A. B. C. D. E. 0.0237 m 0.592 m 0.118 m 4.26 m 0.00426 m Question 4 Which of the following is the equivalent of 4.3 ppm sodium ion (Na+) concentration? A. B. C. D. E. 0.0043 ppb 0.043 ppb 430 ppb 4300 ppb None of the above Question 5 How many milliliters of a 0.100 M potassium permanganate stock solution would be needed to make 100 mL of 0.0250 M potassium permanganate? A. B. C. D. E. 10.0 mL 4.00 mL 40.00 mL 2.50 mL 25.0 mL Question 6 The concentration of a solution is known to be 0.101 M. A student determines the concentration to be 0.088 M, 0.087 M, and 0.089 M for each titration performed. Which of the following best describes these results? A. B. C. D. E. The results are accurate but not precise. The results are precise but not accurate The results are neither accurate nor precise. The results are both accurate and precise. The results are not enough information is given to determine accuracy or precision. Question 7 Concentrated hydrochloric acid is 12 M and has a density of 1.18 g/mL. What is the weight percent (% w/w) of concentrated HCl? A. B. C. D. E. 14% 5.1% 12% 98% 37% Question 8 A stock solution of sodium acetate is 1.0 M. To make Solution A, 2.00 mL of the stock solution is transferred and diluted to a total volume of 100 mL. Solution B is made by transferring 5.0 mL of Solution A and diluting it to a total volume of 250 mL. Solution C is made by transferring 1.0 mL of Solution B and diluting it to a total volume of 25 mL. What is the concentration of solution C? A. B. C. D. E. 1.6 µM 16 µM 1.6 mM 0.16 mM None of the above Question 9 The equation for a normal calibration curve for the detection of iron(II) is determined experimentally to be: S = 12.93 M - 1 * C + 0.0017. Analysis of a sample with unknown concentration gives an absorbance reading of 0.106. What is the concentration of iron(II) in the unknown? A. B. C. D. E. 1.37 M 6.50 mM 9.90 mM 8.06 mM 8.83 mM Question 10 When performing calculations for standard additions, which of the following must be true? A. The volume of the standard added must be added with the volume of the sample used to give a new sample volume. B. The volume of the standard added is subtracted from the total volume of the sample used. C. The volume of the standard added can be ignored, because it is so small. D. The volume of the standard added can be ignored, because volumes are not used in the calculations. E. The volume of the standard added can be ignored, because it is part of the blank correction. E. Question 11 Which of the following statements about the sensitivity of an analytical method is true? A. B. C. D. E. A. The sensitivity of an analytical method is the same as its detection limit. B. The sensitivity of an analytical method is a measure of ability to determine whether slight differences in experimental results are significant. C. The sensitivity of an analytical method is the smallest amount of analyte that the instrument is able to measure. The law of gravity Question 15 Coprecipitates (inclusions, occlusions, and surface adsorbates) are a common problem in gravimetric analysis, but can be controlled by which of the following? Carefully controlling the solution conditions Reprecipitation of the solid Digestion of the precipitate Thoroughly washing and drying the filtrate All of the above Question 16 Volatilization gravimetry would be most useful in determining which of the following? D. The sensitivity of an analytical method is the response of the instrument to human error. E. None of the above A. B. C. D. E. Question 12 Which of the following statements is true of the detection limit of an instrument? Question 17 Which of the following statements about the equivalence point of an acid-base titration is true? A. The detection limit of an instrument is the same as its sensitivity. B. The detection limit of an instrument is a measure of ability to determine whether slight differences in experimental results are significant. C. The detection limit of an instrument is the smallest amount of analyte that the instrument is able to measure. A. The equivalence point of an acid-base titration is the same as the indicator endpoint. B. The equivalence point of an acid-base titration is the point where there is an equivalent amount of titrant and titrand. C. The equivalence point of an acid-base titration is where the pH = 7.0 (neutral). D. The equivalence point of an acid-base titration is where the entire volume of the buret has been used. E. The equivalence point of an acid-base titration is the average value of the dissociation constants. D. The detection limit of an instrument is the ability of the instrument to respond to an error. E. None of the above Question 13 Fill in the blank. Precipitation, volatilization, and particulation are all types of ____________________. A. B. C. D. E. Electrochemical analysis methods Gravimetric analysis methods Tritrimetric analysis methods Spectroscopic analysis methods Photochemical analysis methods Question 14 Fill in the blank. Gravimetric analysis relies heavily on the principle of __________________. A. B. C. D. Conservation of energy Conservation of mass Constant compostition Definite proportions The amount of silver in a solution of silver nitrate The acidity of a water sample The amount of water in eposom salts All of the above None of the above Question 18 What is the stoichiometry of EDTA with metal ions? A. It is 1:6, because EDTA is a hexaprotic weak acid with six distinct acid dissociation values. B. It is 1:4, because EDTA has four binding sites upon loss of the four carboxylic acid protons. C. It is 1:2, because EDTA has two binding sites upon loss of the two ammonium protons. D. It is 1:1, because EDTA forms a cage-like structure around the metal ion. E. It is dependent on the metal ion present. Question 19 A 58.3 mg sample containing Sn2+ is dissolved in 1.0 M HCl. If 23.6 mL of 0.010 M Tl3+ was required to titrate to endpoint, what is the mass percent (w/w%) of tin in the original sample? A. 48% B. C. D. E. 28% 24% 40% 14% C. σ → π* D. n → π* Question 20 A 0.357 g sample contains only lead(II) iodide and sodium iodide in 100 mL of distilled water. Titration to the Fajan's end point requires 22.37 mL of 0.050 M silver nitrate. What is the mass percent (w/w%) of lead(II) iodide in the sample? A. B. C. D. E. 18% 36% 1.6% 53% 47% Question 21 Which variable in Beer's law represents how well a chemical species absorbs light at a given wavelength? A. B. C. D. E. c - concentration ε - molar absorptivity coefficient A - absorbance b - path length of the sample λ - wavelength Question 22 According to Beer's Law, what happens to the absorbance reading if the concentration of the solution is halved? A. B. C. D. E. The absorbance will double. The absorbance will quadruple. The absorbance will be halved. The absorbance will be quartered. There is no way to tell, because concentration and absorbance are not a linear relationship. Question 23 Why must solutions with high concentrations be diluted prior to analysis via Beer's Law? A. The relationship between absorbance and concentration is not linear at high concentrations. B. The detector will reach its detection threshhold. C. The photon source is too weak to provide accurate results. D. The molar absorptivity of a compound is dependent on its concentration. E. There is no need to work with dilute concentrations; any concentration will work. Question 24 Which of the following transitions is NOT possible in UV-Vis absorption? A. σ → σ* B. σ → n Question 25 Which of the following typically exhibits the largest molar absorptivities? A. B. C. D. E. σ → σ* absorbances σ → n absorbances σ* → π* absorbances π → π* absorbances Metal to ligand charge transfer (MLCT) absorbances Question 26 Which of the following is the correct order in which light passes through a UV-Vis spectrometer? A. B. C. D. E. Detector, sample, source, monochromator Source, monochromator, sample, detector Source, sample, monochromator, detector Monochromator, source, sample, detector Sample, source, monochromator, detector Question 27 What is the purpose of a monochromator? A. B. C. D. E. To remove stray light from the room To serve as a polychromatic light source To interpret the photon signal into a digital readout To allow only light of a certain wavelength to pass from the source to the sample To focus light from the sample onto the detector Question 28 The regression line from a plot of absorbance vs. concentration yields: A = 2.31 c + 0.002. If the absorbance of an unknown is measured to be 0.124, what is the concentration of the analyte? A. B. C. D. E. 0.29 M 0.053 M 1.86 M 0.093 M 2.43 M Question 29 The method of continuous variations, also known as Job's method, uses the intersection of the ligand-line and the metal-line to determine which of the following? A. The concentration at which the detector can no longer respond to the signal B. The mole ratio between the metal and ligand in a complex C. The maximum intensity of source photons transmitted D. The number of dimeric molecules formed E. The oxidation number of the metal Question 30 Ultraviolet and visible radiationaffect which of the following? A. B. C. D. E. Core electrons Valence electrons Nuclear spin Molecular vibrations Molecular rotations Question 31 Infrared radiation affects which of the following? A. B. C. D. E. Core electrons Valence electrons Molecular vibrations Molecular rotations Nuclear spin Question 32 Complete the sentence. All of the following are used to describe the bending modes in infrared spectroscopy, EXCEPT: A. B. C. D. E. In-plane rocking. In-plane scissoring. Assymetric stretching. Out-of-plane twisting. Out-of-plane wagging. Question 33 What is the advantage of using a silver chloride sample cell rather than a sodium chloride sample cell for IR spectroscopy? A. Aquesous samples can be measured; AgCl is not water soluble. B. There is no advantage. C. Silver chloride does not absorb IR radiation. D. Silver chloride is translucent. E. Sodium chloride is less expensive. Question 34 In order for a compound to be IR active, it must undergo which of the following? A. B. C. D. E. A change in polarizability A change in dipole moment Emission of an electron Transfer of an electon Metal-ligand charge transfer Question 35 Complete the sentence. All of the following are infrared sources, EXCEPT: A. B. C. D. The Nernst glower. The Globar source. An incandescent wire. A pyroelectric glower. Question 36 Complete the sentence. All of the following are detectors used in infrared spectroscopy, EXCEPT: A. B. C. D. A charge-coupled diode. A thermocouple. A pyroelectric detector. A photoelectric detector. Question 37 Fill in the blank. NMR affects a molecule's ________________. A. B. C. D. E. Nuclear spin Valence electrons Core electrons Molecular vibrations Molecular rotations Question 38 In 1H-NMR spectroscopy, if a CH2 neighbors a CH3, the hydrogen nuclei of the CH3 will appear as which of the following? A. B. C. D. E. A doublet, with a peak integration of 2 A doublet, with a peak integration of 3 A triplet, with a peak integration of 2 A triplet, with a peak integration of 3 A single peak, with an integration of 5 Question 39 Where does spin-lattice relaxation occur? A. It occurs between neighboring nuclei with identical frequencies but different quantum states via energy transfer. B. It occurs between the excited nuclei and nuclei within the sample matrix. C. It occurs between atoms in the same molecule. D. It occurs between the nuclei of the sample and the signal source. E. All of the above Question 40 The value of the chemical shift in NMR spectroscopy is directly related to which of the following? A. B. C. D. E. The amount of shielding The applied magnetic field The identity of the reference sample The electronegativity of the nucleus All of the above Question 41 Fluorescence occurs as a result of which of the following? A. Relaxation from a singlet excited state to a singlet ground state B. Relaxation from a triplet excited state to a singlet ground state C. Nonradiative (vibrational) relaxation D. Intersystem crossing (isc) E. All of the above Question 42 Phosphorescence occurs as a result of which of the following? A. Relaxation from a singlet excited state to the singlet ground state B. From a triplet excited state to the singlet ground state C. Intersystem crossing (isc) D. Nonradiative (vibrational) relaxation E. All of the above Question 43 Why are flourescence and phosphorescence measured at a 90 degree angle to the source? spectra A. To ensure that incident (source) photons are not observed B. Because the sample cell is darkened on two adjacent sides C. Because the monochromator directs the light at a 90 degree angle D. Because the process of fluorescence and phosphorescence are too intense to observe directly E. To make the overall instrument smaller Question 44 Complete the sentence. Fluorescence and phosphorescence can be used for detection of all of the following, EXCEPT: A. B. C. D. E. Vitamins. Environmental pollutants. Uncomplexed metal ions. Pharmaceuticals. Aromatic amino acids. Question 45 A fluorescence quantum yield of 0.93 would suggest that most excited state molecules are doing which of the following? A. Returning to the ground state by fluorescence B. Returning to the ground state by non-radiative decay C. Returning to the ground state by intersystem crossing D. Remaining in the excited state past the experimental timeframe E. None of the above Question 46 Why are photomultiplier tubes often used in fluorescence spectroscopy? A. Because the photon sources are too weak to vibrationally excite the samples B. Because sample cells are small C. Because they supply a reference signal D. Because fluorescence intensities are usually low E. None of the above Question 47 Why is fluorescence spectroscopy often carried out in a liquid nitrogen environment? A. Phosphorescence is more likely to occur at low temperatures in a viscous medium. B. Phosphorescent molecules tend to also have explosive properties. C. The monochromator slows down the radiation before it hits the sample. D. The detector requires lower temperatures for operation. E. The source radiation can overheat and destroy the analyte. Question 48 How does turbidimetry differ from nephelometry? A. Turbidimerty measures the decrease in transmittance of incident radiation; nephelometry measures the intensity of scattered radiation. B. Nephelometry measures the decrease in transmittance of incident radiation; turbidimetry measures the intensity of scattered radiation. C. Nephelometry measures the total metal ion, or inorganic, content; turbidimetry measures total organic content. E. Turbidimetry measures the total metal ion, or inorganic, content; nephelometry measures total organic content. F. The terms are synonymous; there is no difference. Question 49 Turbidimetry and nephelometry are analytical methods based on which of the following? A. B. C. D. E. Light scattering Photon emission Photon absorption Nuclear repulsion Paramagnetism Question 50 What is the advantage of an inductively coupled plasma source rather than a flame? A. B. C. Better atomization and a higher population of excited states Lower operating temperatures and less expensive replacement costs Minimization of scattering and ionization of analytes D. E. All of the above None of the above Question 51 Atomic absorption spectroscopy results are highly reproducible but have low sensitivity and efficiency. This is due to which of the following? A. The small amount of analyte that actually reaches the flame B. The high temperatures of analysis often destroy the atoms C. The amount of dilution due to mixing with large volumes of combustion gases D. A and B only E. A and C only Question 52 Fill in the blank. The relationship between the analyte concentration and the intensity of measured radiation from thermal excitation methods, such as a flame or plasma, is ________________. A. B. C. D. E. Linear B. Exponential Parabolic Polynomial Asymptopic Question 53 Flame atomic absorption measures absorption of radiation of analytes in which phase? A. B. C. D. E. Solid phase Liquid (neat) phase Gas phase Aquesous phase Plasma phase Question 54 Why is a hollow cathode tube lamp necessary in atomic absorption? A. Because cathode lamps are cheaper to operate and maintain B. Because continuous spectrum lamps do not emit at the proper intensity C. Because the width of an atom's absorption band is narrow D. Because continuous spectrum lamps cause ionization of the molecules E. All of the above Question 55 Fill in the blank. Background correction in flame atomic absorption spectroscopy can minimize the effect of ___________________. A. Ionization of the analyte B. Scattering and absorption by the matrix of the analyte C. Reactions between the analyte and matrix D. Non-volatilization of the analyte Question 56 Chemical interferences in atomic absorption that cannot be accounted for using a background correction, but can be minimized, include which of the following? A. B. C. D. E. Nonvolatilization of the analyte Ionization of the analyte Absorption or scattering of radiation by the matrix All of the above A and B only Question 57 Which of the following are forms of radiationless deactivation of an excited state? A. B. C. D. E. Intersystem crossing Internal conversion External conversion Vibrational relaxation All of the above Question 58 When does intersystem crossing occur? A. When a molecule transfers to a higher vibrational energy level of a lower energy electronic state with a different spin B. When a molecule moves to a lower vibrational energy level in the same electronic state C. When a molecule transfers to a higher vibrational energy level of a lower energy electronic state with the same spin D. energy is emitted as a photon from a singlet or triplet spin state E. When energy is passed to the solvent or to another component of the sample's matrix Question 59 Fill in the blank. The lowest vibrational energy level of the lowest electronic singlet state (S0) is referred to as the ___________________. A. B. C. D. E. Ground state Zero state Newtonian state Bohring state Non-excited state Question 60 Whether an electron is in the triplet state or singlet state depends on which of the following? A. B. C. D. E. Its spin-pairing with the ground state The amount of radiation it was exposed to Its ability to undergo radiationless decay Its initial energy level before absorption Its availability to become excited Question 61 In a chromatographic analysis of an unknown mixture, compound A has a retention time of 5.56 minutes and a baseline width of 0.87, and compound B has a retention time of 6.32 minutes and a baseline width of 0.53 minutes. Are these peaks resolved, and what is the resolution between the two peaks? A. B. C. D. E. Yes, 0.54 No, 0.54 Yes, 1.09 No, 1.09 There is not enough information given to determine resolution. Question 62 The "void peak" in a chromatogram corresponds to which of the following? A. Components that had no interaction with the stationary phase B. The peak that arises from poor selection of a stationary phase C. The peak that arises from the mobile phase only D. Components that had no interaction with the mobile phase E. All peaks after the first peak in the chromatogram Question 63 If a compound has a retention time of 5.30 minutes with a baseline width of 0.64 minutes on a 2.0 m silica gel column, what is the average height of a theoretical plate? A. B. C. D. E. 1.8 mm/plate 15 mm/plate 29 mm/plate 0.24 mm/plate 2.7 mm/plate Question 64 Which of the following statements about columns containing more theoretical plates is true? A. Columns containing more theoretical plates make separations imposssible. B. Columns containing more theoretical plates take a long time to perform separations. C. Columns containing more theoretical plates are better suited to separate a complex mixture. D. Columns containing more theoretical plates interact irreversibly with the analyte. E. Columns containing more theoretical plates lend themselves to component mixing. Question 65 "Tailing" of a chromatographic peak is a result of which of the following? A. Interactions of the solute with the stationary phase B. Overloading the column with sample C. Interactions between the stationary and mobile phases D. Too many theoretical plates E. Small theoretical plate heights Question 66 "Fronting" of a chromatographic peak is a result of which of the following? A. Interactions between the stationary and mobile phase B. Overloading the column with sample C. Interactions of the solute with the stationary phase D. Small theoretical plate heights Question 67 Band broadening in column chromatography is a result of which of the following? A. B. C. D. E. Mass transfer in the stationary phase Mass transfer in the mobile phase Longitudinal diffusion Variations in path lengths (Eddy diffusion) All of the above Question 68 Complete the sentence. All of the following are common carrier gases from gas chromatography, EXCEPT: A. B. C. D. E. Oxygen. Nitrogen. Helium. Argon. Carbon dioxide. Question 69 When using gas chromatography, how is optimum column efficiency obtained? A. When the samples are injected slowly and in large quantities B. When the samples are injected slowly and in small quantities C. When the samples are injected quickly and in large quantities E. When the samples are injected quickly and in small quantities F. None of the above Question 70 What is the most common support material for a packed GC column? A. B. C. D. E. Silica gel Alumina Fused silica Glass Diatomaceous earth Question 71 WCOT, SCOT, PLOT, and FSOT are all types of which of the following? A. B. C. D. E. Open tubular GC columns Capillary GC columns Packed GC columns Both A and B Both A and C Question 72 Which of the following GC detectors would most likely allow recovery of a sample after analysis? A. B. C. D. E. Flame ionization detector (FID) Thermal conductivity detector (TCD) Flame photometric detector (FPD) Hall electrolytic conductivity detector Nitrogen-phosphorus detector Question 73 Which of the following GC detectors would be least affected by the carrier gas? A. B. C. D. E. Thermal conductivity detector (TCD) Electron capture detector (ECD) Photoionization detector (PID) Flame photometric detector (FPD) None of these detectors would be affected by the carrier gas. Question 74 In size exclusion chromatography, what happens to the larger particles? A. They elude first, before smaller particles. B. They are broken down into smaller particles. C. They become oxidized as they move through the column. G. They remain on the column longer than smaller particles. H. They bind permanently to the stationary phase. Question 75 Fill in the blank. Ion exchange chromatography is best suited to separate ___________________. A. Hydrophilic molecules B. C. D. E. Hydrophobic molecules Mixed metal sulfides and oxides Large molecules, such as DNA and RNA Cations and anions Question 76 Which of the following statements about the mobile phase in Supercritical fluid chromatography (SFC) is false? A. It requires lower pressures than those needed for HPLC. B. It gives better resolution than GC. C. It has densities similar to a liquid. D. Its mobile phase has the viscosity properties of a gas. E. It has solvent properties of a liquid. Question 77 The stationary phase in ion exchange chromatography is a cross-linked polymer resin with covalently attached functional groups. Which of the following is NOT a typical functional group used for IEC? A. B. C. D. E. Sulfonic acid (-SO3-) Carboxylic acid (-COO-) Quarternary amine (-CH2N(CH3)3+) Amine (-NH3+) Hydroxyl (-OH-) Question 78 Reversed-phase chromatography refers to which of the following? A. A stationary phase and mobile phase of similar polarities B. A nonpolar stationary phase and a nonpolar mobile phase C. A polar stationary phase and a nonpolar mobile phase D. A nonpolar stationary phase and a polar mobile phase E. A polar stationary phase and a polar mobile phase Question 79 Which of the following would elute first when using capillary zone electrophoresis? A. B. C. D. E. Ca2+ CH3NH3+ ClHCOOCH3COO- Question 80 How are separations by electrophoresis carried out? A. Via applying an electric current B. Via saponification of the analyte C. Via polymerization of the analyte D. Via oxidation reactions at stationary phase sites E. Via reduction reactions at stationary phase sites Question 81 Fill in the blank. Cd wire used to measure the concentration of cadmium ion is an example of a _______________________. A. B. C. D. E. Metallic electrode of the second kind Metallic electrode of the first kind Saturated calomel electrode Reference electrode Silver/silver chloride electrode Question 82 Fill in the blank. Ag wire used to measure the concentration of Br- ion is an example of a ______________________. a. b. c. d. e. Saturated calomel electrode Metallic electrode of the first kind Metallic electrode of the second kind Silver/silver chloride electrode Reference electrode Question 83 What is the process of the loss of an electron called? A. B. C. D. E. Oxidation Reduction Transference Sublimation Neutralization Question 84 What is the process of the gain of an electron called? A. B. C. D. E. Oxidation Reduction Sublimation Transference Neutralization Question 85 Which of the following is a substrate that is oxidized? A. B. C. D. E. Cationic species Anionic species Neutral species Reducing agent Oxidizing agent Question 86 Which of the following is a substrate that is reduced? A. B. C. D. Oxidizing agent Reducing agent Cationic species Anionic species E. Neutral species Question 87 What is the purpose of the salt bridge in a galvanic (voltaic) cell? A. B. C. D. E. To complete the electrochemical circuit To provide free electrons for redox processes To provide a site for oxidative reduction To serve as a working electrode To serve as a reference electrode Question 88 If a redox couple is at equilibrium in an electrochemical cell, then which of the following statements about the current and potential is most accurate? A. The current is zero, and the potential is given by the Nernst equation. B. The current and potential are both zero. C. The current is negative, and the potential is zero. D. The current is positive, and the potential is zero. E. The potential is zero, and the current is given by the Nernst equation. Question 89 Complete the sentence. The basic setups for electrochemical measurement include all of the following, EXCEPT: A. B. C. D. E. Measure the potential at zero current. Measure the potential while controlling the current. Measure the potential and current simultaneously. Measure the current while controlling the potential. All of the above Question 90 Which of the following is a static (i = 0) electrochemical technique? A. B. C. D. E. Potentiometry Controlled-current coulometry Controlled-potential coulometry Cyclic voltammetry Amperometry Question 91 Where does the reduction reaction occur? A. B. C. D. E. At the anode At the cathode Within the potentiometer Within the salt bridge Within the bulk solution Question 92 Where does the oxidation reaction occur? A. Within the potentiometer B. C. D. E. Within the salt bridge At the anode At the cathode Within the bulk solution Question 93 The use of the Nerst equation to calculate potentials is really a simplistic model. Which of the following does it ignore? A. B. C. D. E. Matrix effects Temperature effects Junction potentials All of the above None of the above Question 94 Fill in the blank. The potential that develops at the interface of two solutions due to differences in concentrations and ionic mobility is called the _________________ potential. A. B. C. D. E. Osmotic Bridging Coulombic Reference Junction Question 95 Which of the following statements about the standard hydrogen electrode, the calomel electrode, and the silver/silver chloride electrode is true? A. These electrodes combine to make a complete electrochemical cell. B. These electrodes are typically used as reference electrodes. C. These electrodes are typically used as working (indicator) electrodes. D. These electrodes are examples of membrane electrodes. E. These electrodes have the same electrochemical potential. Question 96 A pH meter is an example of which type of membrane electrode? A. B. C. D. E. Glass ion selective electrode Potentiometric biosensor (enzyme electrode) Solid-state ion selective electrode Liquid-based ion selective electrode Gas-sensing electrode Question 97 In a cyclic voltammogram, the peak current(i) is directly related to which of the following? A. The concentration of anayte B. The surface area of the working electrode C. The number of electrons involved in the redox process D. The diffusion coefficient of the electroactive species E. All of the above Question 98 One electrochemical technique involves first depositing an analyte on the surface of an electrode, then using an applied current to remove the analyte via a reduction or oxidation reaction. What is this method called? A. B. C. D. E. Hydrodynamic voltammetry Stripping voltammetry Amperometry Polarography Cyclic voltammetry Question 99 Which of the following is NOT a variable in voltammetric methods? A. B. C. D. E. Type of working electrode How the potential is applied The inclusion of convection How the current is applied All of the above Question 100 Fill in the blank. Coulometric techniques result in a plot of ____________________. A. B. C. D. E. Current versus time Electrochemical potential versus time Current versus electrochemical potential Current only Potential only ANSWER KEY 1. D 2. B 3. A 4. D 5. E 6. B 7. E 8. B 9. D 10. A 11. B 12. C 13. B 14. B 15. E 16. C 17. B 18. D 19. A 20. D 21. B 22. C 23. A 24. C 25. E 26. B 27. D 28. B 29. B 30. B 31. C 32. C 33. A 34. B 35. D 36. A 37. A 38. D 39. B 40. E 41. A 42. B 43. A 44. C 45. A 46. D 47. A 48. A 49. A 50. A 51. E 52. A 53. C 54. C 55. B 56. E 57. E 58. A 59. A 60. A 61. C 62. A 63. A 64. C 65. A 66. B 67. E 68. A 69. D 70. E 71. D 72. B 73. D 74. A 75. E 76. B 77. E 78. D 79. A 80. A 81. B 82. C 83. A 84. B 85. D 86. A 87. A 88. A 89. C 90. A 91. B 92. C 93. D 94. E 95. B 96. A 97. E 98. B 99. D 100. A