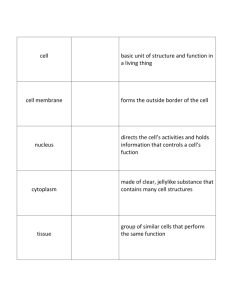
Organization of the Body Unit 1 ● Anatomy and Physiology is the study of the human body ● Anatomy -- concerned with the structure of the part (of the body) ○ e.g. the stomach is a J-shaped, pouch-like organ, the stomach wall has thick folds, which disappear as the stomach expands to increase its capacity. ● Physiology-- concerned with the function of the part (of the body) ○ e.g. the stomach temporarily stores food, secretes digestive juices, and passes on partially digested food to the small intestine. Atom Molecule (atoms join to form) Macromolecules (molecules join to form) Organelles--tiny structures in cells that perform cellular function Cell Tissue--composed of similar types of cells and perform a specific function Organ--composed of several types of tissue and performs a particular function within an organ system Organ System--organs work together to provide a specific need for the body. Organism Anatomical terms: Used to describe location of body parts, regions of the body and imaginary planes. Anterior: front Posterior: back Anatomical terms are only useful if everyone has the same position of the body in mind. All anatomical terms have a reference point called the anatomical position--standing erect, with face forward, arms at sides, and palms and toes directed forward. Superior: above or toward head Inferior: below or toward feet Medial: divide body through nose. Then closer to that imaginary midline Lateral: divide body through nose. Then farther away from imaginary midline Proximal: part is closer to point of attachment (trunk) Distal: part is farther from point of attachment (trunk) Superficial (external): part located near the surface Deep (internal): part located away from the surface Central: part situated at the center of the body or an organ. Peripheral: part is situated away from the center of the body or an organ. ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● The windpipe is anterior to the trachea. The heart is posterior to the rib cage. The face is superior to the neck. The navel is inferior to the chin. The bridge of the nose is medial to the eyes. The eyes are lateral to the nose. The elbow is proximal to the hand. The hand is distal to the elbow. The skin is superficial to the muscles. The intestines are deep to the spine. The central nervous system is located along the main axis of the body. The peripheral nervous system is located outside the central nervous system. Regions of the body