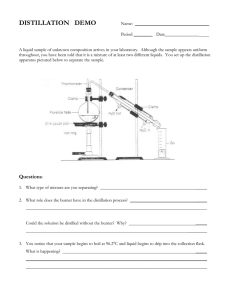
Name ___________________________________________ Section ___________ Date ___________________ Experiment # 5 PURIFICATION OF WATER OBJECTIVE: To be able to purify water. MATERIALS: Watch glass (3) Distilling flask Adaptor Erlenmeyer flask (100mL) Dropper River water Alum solution Fine soil particles Iron ring Condenser Graduated cylinder wire gauze distilled water phenolphthalein iron stand (2) filter paper iron clamp funnel rubber tubings funnel stand cork with hole(2) beaker (100mL) NH4OH (conc.) NH4OH (dilute) IMPURITIES OF WATER: Water may have suspended or dissolved impurities. The dissolved impurities may be volatile or nonvolatile. Water that contains dissolved calcium and magnesium is called hard water. The process of removing the hardness of water is called water softening. Water that is free from calcium and magnesium salts is called soft water. Place the following on three separate watch glasses (WG) and evaporate them to dryness over a water bath (Fig. 5-a). WG #1: 1 mL of distilled water WG #2: 1 mL of river water WG #3: 1 mL of distilled water to which 1 drop of concentrated NH4OH has been added. Which watch glasses had residue? The residue are the non-volatile impurities of the water and they may be dissolved mineral salts and suspended impurities such dust/soil and bacteria. as ___________________________________________ Fig 5-a. Apparatus set-up for water bath evaporation How is an impurity such as ammonia dissolved in water classified? ___________________________________________________________________________________ Name another example of a similar kind of impurity of water. 1 ___________________________________________________________________________________ PURIFICATION OF WATER: a) Elimination of Suspended Solids Place 10.0 mL of water containing fine soil particles in suspension in a test tube. Add 1.0 mL of alum solution. Set aside for a few minutes. Compare the water at the upper part with that at the lower part of the test tube. Filter and compare the filtrate with another 10.0 mL sample of the water that has not been treated with alum. ____________________________________________________________________________________ What is the role of ______________________________________________ alum in water purification? ____________________________________________________________________________________ Explain how alum _______________________________________________________________ does it. ____________________________________________________________________________________ b) Distill 25.0 mL river water, using the set-up shown on Fig.5-b. Collect 5 mL of the distillate. Compare it with the original water as to smell, taste and clarity. ____________________________________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________________________________ Add a drop of ammonium hydroxide to the water and continue distilling. Add a drop of phenolphthalein to the distillate. Is ammonia removed by distillation? ____________________________________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________________________________ Are volatile impurities removed from the water by distillation? Explain why. ____________________________________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________________________________ What kind of impurities are removed from the water by simple distillation? How does this experiment prove your answer? ____________________________________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________________________________ 2 What is distillation? ___________________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________________________________ Fig. 5-b. Distillation Set-Up 3