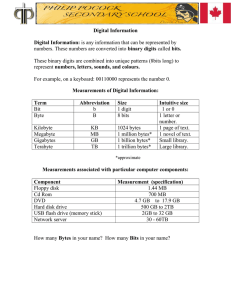
Exploring Computer Science: Mr Kapptie Unit: Basics Turn In List: 1. Bits & Bytes & Data (this file) “I will demonstrate an understanding of how digital information is stored on computers.” Title: Bits, Bytes and Digital Data Content Objectives: Students will explore the world of digital information and be able to convert bits and bytes to decimal and hexadecimal. Key Terms: Base 2 number system. It uses 0s and 1s. (a way of counting with only two digits). Binary Bit is the smallest unit of digital information – groups establish our bit system. Bit and Bit Systems 8 bits of data is one byte. Byte Kilo = 1,000 bytes, mega = 1,000,000 bytes, Giga = 1,000,000,000 bytes, Tera = 1,000,000,000,000 bytes A base sixteen number system, it uses 0-9 and A-F Kilo, Mega, Giga, Tera Hexadecimal Base 2: binary, base 8: octal, base 10: decimal, base 16: hex Base 2, 8, 10, 16 Gives instruction to the OS of what to do with that file. File and File Extension Organization unit on an OS Folder/Directory Reveals the location of a file on the computer Path Application Terms: Windows Explorer or Finder File Attributes - Properties or Get Info Size Attributes Created, Modified and Other File Attributes File Compression File manager Meta data Always measured in bytes. System information Save space or group files in one zip Assignment: Counting in Base 2, Base 10 and Base 16 number systems. Fill in the blanks: Decimal Hex 0 1 2 0 1 2 Binary 0000 0001 0010 4 5 3 3 4 5 0011 0100 0101 7 8 9 6 6 7 8 9 0110 0111 1000 1001 10 A 11 B 12 C 1010 1011 1100 13 D 1101 14 E 15 F 1110 1111 Using the following binary tool as a visual aid, see if you can decode the following values… Record all binary values in 8 bits. Exploring Computer Science: Mr Kapptie 1 Kilobyte (KB) = 1 Megabyte (MB) = 1 Gigabyte (GB) = 1 Terabyte (TB) = Decimal 1,000 Bytes 1,000,000 Bytes 1,000,000,000 Bytes 1,000,000,000,000 Bytes Binary Decimal Binary 92 = 01011100 12 = 00001100 173 = 10101101 9 = 00001001 53 = 00110101 122 = 01111010 95 = 01011111 232 = 11101000 154 = 10011010 111 = 01101111 255 = 11111111 98 = 01100010 10 = 00001010 85 = 01010101 27 = 00011011 297 = 000100101001 Binary Hex Hex Binary CA = 11001010 10 = 00010000 AD = 10101101 3F = 00111111 19 = 00011001 2A = 00101010 83 = 10000011 2B = 00101011 33 = 00110011 1F = 00011111 FF = 11111111 F8 = 11111000 E2 = 11100010 99 = 10011001 1B = 00011011 9F = 10011111 1. List all of the numbers and letters used in the hexadecimal system? 0-9 and A-F 2. How many unique and individual numbers do we use in our English (base 10) number system? 10 unique numbers: 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, and 9. Exploring Computer Science: Mr Kapptie 3. Using the article on “How CD’s Work” explain in your own words how information is read from a CD. There is an indentation on a flat surface and the light flashes up back into itself if the surface is flat and it reflects to the side if it is indented, giving a computer the ability to interpret binary code. 4. What do we call a computer’s language that is made up of 1’s and 0’s? Binary code. 5. What are the possible values of one bit? 1 or 0 6. EIGHT bits = 1 byte 7. 128 MB= 128,000 KB 8. 256 KB= 256,000 bytes 9. 512 MB= .512 GB 10. Your phone/music player = 8 GB – CONVERT to Megabytes 8,000 MB 11. Using the ASCII table, provide the following information for your first name: Your First Name: Letter A Hex 41 Binary 01000001 Notes: l 6c 01101100 e 65 01100101 c 63 01100011