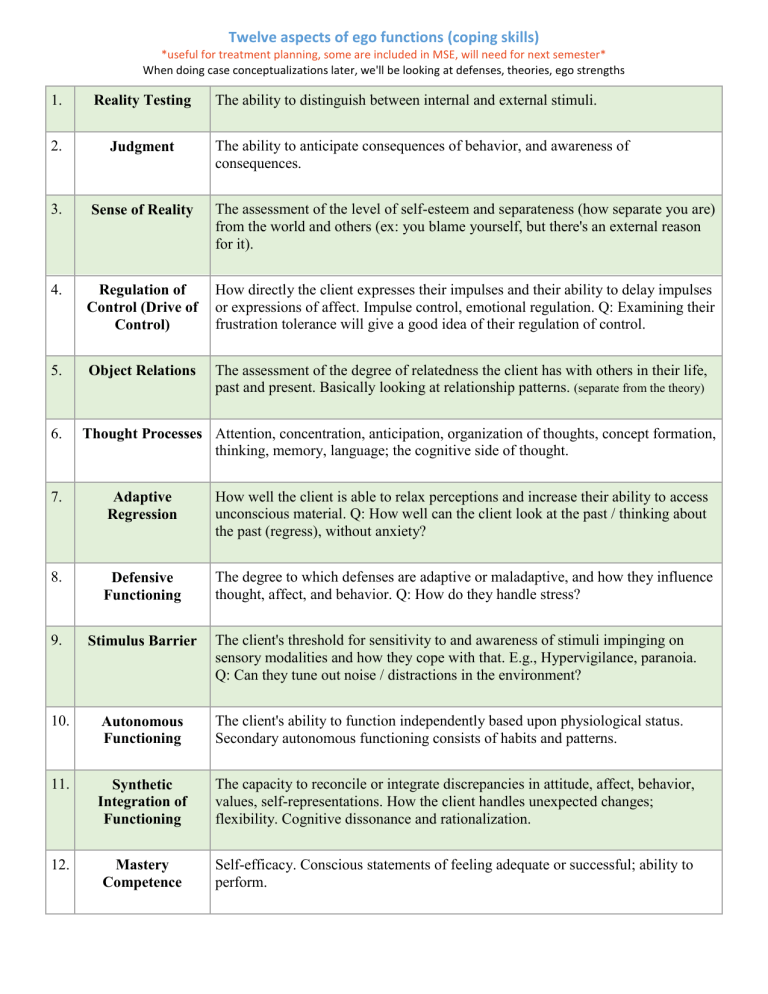
Twelve aspects of ego functions (coping skills) *useful for treatment planning, some are included in MSE, will need for next semester* When doing case conceptualizations later, we'll be looking at defenses, theories, ego strengths 1. Reality Testing 2. Judgment 3. Sense of Reality The assessment of the level of self-esteem and separateness (how separate you are) from the world and others (ex: you blame yourself, but there's an external reason for it). 4. Regulation of Control (Drive of Control) How directly the client expresses their impulses and their ability to delay impulses or expressions of affect. Impulse control, emotional regulation. Q: Examining their frustration tolerance will give a good idea of their regulation of control. 5. Object Relations The assessment of the degree of relatedness the client has with others in their life, past and present. Basically looking at relationship patterns. (separate from the theory) 6. The ability to distinguish between internal and external stimuli. The ability to anticipate consequences of behavior, and awareness of consequences. Thought Processes Attention, concentration, anticipation, organization of thoughts, concept formation, thinking, memory, language; the cognitive side of thought. 7. Adaptive Regression How well the client is able to relax perceptions and increase their ability to access unconscious material. Q: How well can the client look at the past / thinking about the past (regress), without anxiety? 8. Defensive Functioning The degree to which defenses are adaptive or maladaptive, and how they influence thought, affect, and behavior. Q: How do they handle stress? 9. Stimulus Barrier 10. Autonomous Functioning The client's ability to function independently based upon physiological status. Secondary autonomous functioning consists of habits and patterns. 11. Synthetic Integration of Functioning The capacity to reconcile or integrate discrepancies in attitude, affect, behavior, values, self-representations. How the client handles unexpected changes; flexibility. Cognitive dissonance and rationalization. 12. Mastery Competence Self-efficacy. Conscious statements of feeling adequate or successful; ability to perform. The client's threshold for sensitivity to and awareness of stimuli impinging on sensory modalities and how they cope with that. E.g., Hypervigilance, paranoia. Q: Can they tune out noise / distractions in the environment? Definition: "psychological techniques to protect ourselves from anxiety, stress, and conflict, and to maintain self-esteem." We all have them and use them; they don't develop out of trauma, only anxiety. The healthier the person, the less reliant they are upon defense mechanisms. Pathology occurs when you use the same defenses but they aren't helpful. Defense Mechanism Description Example Repression Involuntary exclusion from conscious awareness of conflictual or painful impulses, thoughts, or memories (aka motivated forgetting) so you don't have to deal with it. Battered child has no memory before age 7. Projection Attributing your feelings/impulses/characteristics, things you don't like about yourself, onto someone else instead of acknowledging they're yours. [part of transference] Woman represses her own sexual hunger and dismisses all men as sex fiends. Introjection (internalization) Assimilation of characteristics of an object into yourself. Can occur as part of or during a trauma. Man envies his boss so he adopts his politics and tastes. Client will say they did something to cause the trauma, abandoned because "I'm not good enough." Displacement Affect originally focused on one target is transferred to another innocuous target. [part of transference] Kid gets in trouble at school, comes home and gets mad at parents. Symbolization An object or act represents a complex group of objects or "Sometimes a cigar isn't just a acts which may create conflict or unacceptable feelings in the cigar…" person. The symbol stands for some repressed desire. Soldier in Vietnam War has internal "Representation of affect-laden person, thing, or thought in conflict. When asked why he the form of another person, thing, or thought that has some participated in the war, he responds, similarity of association." "I did it for the flag." Conversion Somatization Deflection Anxiety, stress, conflict, is transformed and expressed through physical symptoms involving portions of the body that are supplied by sensory or motor nerves. Usually impacts a major body part that is sensory or used for motor function. This and somatization are the only two considered to be pathological. Actual example: During the Vietnam War, women were out in the rice fields collecting rice. As they were walking back, the village was bombed. All of the women went blind; but had nothing wrong with their eyes. Expression of conflict by production of physical symptoms Child is afraid of being bullied at involving illness and pain, sometimes symbolic of the conflict. school, develops a stomachache before school. Person draws attention away from the real source of anxiety or conflict by distracting or confusing actions, statements, etc. Group therapy, person deflects by moving attention onto another participant instead of talking about themselves. Isolation Denial Acting Out Dissociation Person separates or closes off from others. Could be physically and/or emotionally. May push people away and engage in seclusion and solitude. "I'm upset, leave me alone." Failure to recognize external reality; refusing to believe information that's anxiety producing. Patient with malignant tumor insists she does not have cancer. Engaging in actions rather than reflecting on internal feelings or the real reason for the anxiety/stress conflict. Where the person loses track of time and/or person and instead find another representation of the self in order to continue in the moment. A child who has been sexually abused may create an imaginary friend who takes the abuse, so they won't have to. Intellectualization Avoid unacceptable or difficult emotions by focusing on the intellectual aspects. Overuse of reasoning or logic to avoid awareness of feelings and impulses. Adolescent talks at great length about social issues to avoid confronting his own aggressive impulses. Parent passes away, child focuses on the planning of the funeral instead of the thoughts and feelings. Idealization Overestimation of positive qualities and underestimation of limitations of a desired object. Widower is unable to recall any of the things he ever resented about his wife. Regression Return to an earlier, less mature stage of behavior, usually associated with the person's most fixated stage. Transference is a regressive phenomena because it's transferred from the past. Five-year-old boy begins wetting his bed again when sibling is born. Rationalization Elaboration of socially acceptable reasons to justify behavior, rather than to expose the true motive. Splitting Having an attitude about the self and others that is black and white; perceiving of things as all good or all bad. Substitution An unobtainable goal or object is replaced by one that can be achieved. Sublimation Partial gratification of an impulse by altering the aim or object to make it socially more acceptable Man channels aggressive urges into athletic competition. Reaction formation Reversal of an impulse to its opposite Jealous older sister becomes very protective and affectionate toward infant sibling. Affiliation Turning to other people for support. Aim Inhibition Avoidance Help-Rejecting Complaining Accepting partial gratification of an impulse. Accepts a modified form of their original goal so there's a change in focus. Settling for being just friends. Refusal to deal with or encounter unpleasant objects or situations. The individual complains or makes repetitious requests for help that disguise covert feelings or hostility or reproach toward others. The negative feelings then expressed by rejecting the suggestions/advice/help that others offer. Compartmentalizing Process of separating parts of the self from awareness of other parts and behaving as if one had separate sets of values. Compensation Overachieving in one area to compensate for failures in another. Omnipotence Dealing with conflict by feeling or acting as if he or she possesses special powers or abilities and is superior to others. Fantasy When used as a defense mechanism, the person is channeling unobtainable desires into imagination. Fan-fiction. Altruism Satisfying internal needs by helping others. Volunteering for homeless shelter helps man recognize his situation isn't so bad. Humor Pointing out the funny or ironic aspects of a situation in order to deal with it. Often self-deprecating humor or poking at someone else's inadequacy. Self-Assertion (Assertiveness) Person deals with conflicts by expressing their feelings and thoughts directly, in a way that is not coercive or manipulative. Passive-Aggression Indirectly express anger and instead of vocally expressing displeasure, they remain quiet. Undoing Person engages in behavior to make up for an undesirable behavior. Resistance Person feels uncomfortable with the situation and they engage in opposition. Client is reluctant to participate in therapy. Even though they're miserable, it's the comfort of familiarity. Suppression Conscious exclusion from awareness of painful impulses, thoughts, or memories "I choose not to think about that." Isolation (of affect) Repression of affect away from a thought, or a thought away from its affect Medical student dissects cadaver without any feelings about death. Identification Modeling of one's self on another person or group, but with less intensity and completeness than with introjection Conscious emulation of an admired public figure; early life- parents. Identification with the aggressor Incorporation of aspects of another person who is perceived as serious threat or cause of frustration Boy in Oedipal stages assumes characteristics of his father. Self-destructive thoughts or actions replace aggression toward other objects Woman blocks anxiety over fight with husband by getting into minor auto accident. Action in anticipation of being acted upon Patient misses therapy session just before therapist's announced vacation. Turning (aggression) against the self Turning passive into active