Ecology Guided Notes: Ecosystems, Biomes, and Relationships
advertisement

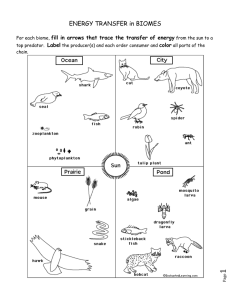
Ecology Guided Notes To be used with Ecology PowerPoint Name:_______________________ Ecology: the study of how living things ___________ of with their physical environment Ecological Organization An organism is living thing Anything that possesses all of the ________________ of _________ Species: a group of __________ that can mate & produce a _________ offspring Population: all the members of a __________ that live in one place at one time. How many zebras are apart of the population?______ Community: a collection of ________________ populations in an area Ecosystem: includes all of the organisms & the non-living environment. True or False Community members must interact to maintain balance. Biosphere: the portion of the earth where all life exists. A 13 mile band that surrounds earth. 6-7 miles into the ________________ & 6-7 miles deep into the __________ Put the Order of Ecological Organization from smallest to largest: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. __________________ __________________ __________________ __________________ __________________ What does an ecosystem need to be self-sustaining? 1. A constant source of ___________ is supplied. 2. Living things use this energy and convert into _________ molecules 3. A cycling of materials between organisms and their environment Resources Organisms with similar needs may compete with each other for resources like: 1. ________________________ 2. ________________________ 3. _______________________ 4. ________________________ Limiting Factor: anything that makes it more difficult for a species to live, grow, or reproduce in its environment Acclimation: when organisms _____________ to change Range of Tolerance: the ability of an organism to withstand __________ in their environment. Abiotic and Biotic Factors Abiotic Factors: _____________ factors which affect the ability of organisms to survive and reproduce What are three examples of abiotic factors? 1. ________________________ 3. ________________________ 2. ________________________ 4. ________________________ What abiotic factors limit vegetation at higher altitudes? 1. ______________________ 3. ____________________ 2. ________________________ 4. _______________________ Biotic Factors: ______ factors which affect the ability of organisms to survive & reproduce Examples: other organisms - ____________, food source Can an abiotic factor such as RAIN affect many biotic factors? Rain - ________ - ________ - _________ Nutritional Relationships Define Autotroph: organisms that synthesize their own __________ from inorganic molecules Define Heterotroph: ____ ______ synthesize their own food and are dependent on other organisms for their food Types of Heterotrophs Saprophyte: include those heterotrophic plants, fungi, and bacteria which live on __________ matter (a.k.a. decomposers or detritivores) Herbivores: _____________- eating animals Omnivores: consumes both ____________ & _______________ Carnivores: _____________- eating animals Types of Carnivores ______________: animals which kill and consume their other animals (prey) __________: animals which are killed by predators A _________________________ is an animal that feeds on other animals that they have not killed. A good example of this would be a ___________, ____________ & _____________. Symbiotic Relationships Symbiosis: living together with another organism in ___________ association Types of Symbiosis Commensalism: one organism is ____________ and the other is _____________ What is an example of commensalism? Barnacles on _______________ Define Mutualism: _______ organisms benefit from the association (+,+) What is an example of mutualism? Nile crocodile & Egyptian plover Parasitism: the organism benefits at the __________ of the host (+,-) What is an example of parasitism? ___________________________________________ Summary of Symbiotic Relationships Fill in the proper term with its corresponding picture Energy Flow in an Ecosystem Food Chain: a _________ pathway of feeding relationships among organisms that involves the transfer of energy. Food Web: _______________ food chains in a community Below fill in organisms from the food web: ______________________ Make their own food ______________________ Herbivores ______________________ Carnivores ______________________ Break down organic waste and dead organisms (Ex. Bacteria) Trophic levels An organism’s position in a sequence of energy transfers There is a ________ in the overall energy as you move up in __________ levels. There is much more ______ in the __________ level in a food web than at the __________ levels Approximately ____% of ingested nutrients is passed on to the next trophic level to build new tissue Why is the % of energy passed on to the next trophic level so low? 1. Energy is lost in the form of __________ 2. Some animals _________ from being eaten & just die. Their energy in their bodies do not pass to a higher energy level. 3. Some animal parts can not be eaten. Cougar eats deer, can not extract energy from _______, __________ or ________ Biomass Biomass: _________________________________________________________ Less or More biomass can be supported at each trophic level. ***The total mass of carnivores in an ecosystem is less than the total mass of the producers.*** Label the following Biomass Pyramid with the following terms: producers, tertiary consumers, secondary consumers and primary Level A: _____________________ consumers Level B: ______________________ Level C: ______________________ Level D: _____________________ Terrestrial Energy Pyramid Complete the Energy Pyramid using the following organisms: Eagles, Green Plants, Heat, Mice, and Snakes Succession Succession: a gradual process of change and ___________ of populations in a community. What causes an environment to be changed? When the environment is ______________________ These changes cause rapid or gradual changes in an ecosystem. Ecosystems change until ______________ _________________ is formed. Primary Succession: The development of plant communities in an area that has not never supported life. Examples: __________ _________, _________ ________ or ___________. The Start of Primary Succession • Pioneer Organism: the first organisms to inhabit a given location (example: _________ on bare rock) Breaks down rock into __________ The following is an example of Primary Succession: 1. water plants at pond edge 2. sedges and sediments begin to fill pond 3. sphagnum moss and bog shrubs fill pond (cranberries) 4. black spruce and larch 5. birches, maple, or fir . Secondary Succession: is the change of species that follows disruption of an existing community created by natural __________ or ___________ activity. Occurs in areas that previously contained life and ___________!!! Example: forest fire at Yellowstone National Park The following is an example of Secondary Succession: 1. ______________________________________________ 2. ______________________________________________ 3. ______________________________________________ 4. ______________________________________________ 5. ______________________________________________ What is the difference between primary and secondary succession? Primary succession takes place on _______, whereas Secondary succession takes place on ___________. Is this primary or secondary succession? ____________________________________ Define Climax Community: _______________________________________________ Populations remain ___________________and exist in __________________ with each other and their environmen ecosystems may reach a point of stability that can last for ___________________ _________________________________________________________________ _ A climax community persists until a catastrophic change alters or destroys a major biotic or abiotic resource (examples: forest fires, abandoned farmlands, floods, areas where the topsoil has been removed) After the original climax community has been destroyed, the damaged ecosystem is likely to recover in stages that eventually result in a stable system similar to the original one. Biomes Define Biome: a large region characterized by a specific type of climate & certain ______ and __ communities. A certain biome may exist in more than one location on earth. Biomes are ___________________________ or ______________________________. Biomes are dependent on the following three things: 1. _________________________________ 2. _________________________________ 3. _________________________________ Terrestrial Biomes In general. _________ __________ biomes. Characterized by climax _________________________. Have characteristic _________(plants) and _________ (animals). Tundra Climax Flora: Climax Fauna: Characteristics: long & extremely cold winters permanently frozen subsoil Location: Taiga Climax Flora: Climax Fauna: Characteristics: Location: south of the tundra & north of temperate forest Temperate-Deciduous Forest Climax Flora: Climax Fauna: Characteristics: moderate precipitation, cold winters, warm summers Location: South of taiga Tropical Forest Climax Flora: Climax Fauna: Characteristics: heavy rainfall(300 inches/year), constant warmth Biodiversity: The size of 2 football fields may have 300 species of trees Location: near the equator Grasslands Climax Flora: Climax Fauna: Characteristics: rainfall and temperature vary greatly, strong winds Grasslands: also known as prairies, steppes, savannas & pampas. Location: interior of continents Desert Climax Flora: Climax Fauna: Characteristics: Extreme temperature. Hot days cool nights. Temperatures may have a 50 degree drop. Aquatic Biomes What is the largest ecosystem on Earth? _______________________________________ How much of the Earth's surface is covered with water? __________________________ What are two reasons why aquatic biomes are more stable then terrestrial biomes? 1. ______________________________________________________________________ 2. ______________________________________________________________________ What are the two types of aquatic biomes? 1. ________________________________ ______________________________ 2. Give 4 examples of freshwater biomes: ____________, _____________, ______________, & ___________ 2 Types of Lakes: 1. Eutrophic - rich in ___________ matter & vegetation ___________ water Bacteria feed on decomposing matter & uses up all the oxygen, killing all life. 2. Oligotrophic - __________ organic matter & vegetation Clear water. • Wetlands: aka ___________ & marshes an area of land that is covered by water for a certain amount of time during the year. Why are wetlands so important? filters out ____________ controls ___________ stopover for migratory birds recreational Where does plant production occur in this aquatic environment? ______________________________________________ ____________ Where does plant production not occur? _______________________________________ Why?__________________________________________ _____________________________________ Competition Competition: occurs when two different species or organisms living in the same environment (habitat) utilize the same limited resources What are some things organisms compete over? ________________________, ______________________, ______________________, ________________________, ________________________, and ________________________. When does competition become more intense? __________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________ __ Habitat: A place where an organism lives out its life. It is an organism’s home, their address. Niche: The organism's role in the community. How an organism meets its need for food, shelter, how it survives & reproduces. Interactions with biotic & abiotic factors. Material Cycles What happens to materials in a self-sustaining ecosystem? ________________________ ______________________________________________________________________ __ Can the same materials be reused? _____________________ Water Cycle In the provided space, fill in the proper terms that make up the Water Cycle. Carbon-Oxygen Cycle In the provided space, fill in the proper terms that make up the Carbon-Oxygen Cycle. Nitrogen Cycle Why do organisms need nitrogen? ____________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________ __ ***Living things cannot use nitrogen gas in the air*** How do living things obtain nitrogen? ______________________________________ What is Nitrogen-Fixation? ________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________ __ What type of organism can “fix” nitrogen so it can be used by other Alfalfa living things? _____________________________ In what type of plant can these organisms be found? __________________________________ In the provided space, fill in the proper terms that make up the Nitrogen Cycle. Nitrogen Gas (N2) Nitrogen fixation Animals eating plants Decomposition Nitrogen-fixing bacteria in plant roots Soil bacteria Biodiversity Evolutionary processes have resulted in a diversity of organisms and a diversity of roles in ecosystems. Define Biodiversity: ______________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________ __ Increased biodiversity does four things. What are they? 1. ______________________________________________________________________ 2. ______________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________ __ 3. ______________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________ __ 4. ______________________________________________________________________ Define Monoculture: _____________________________________________________ Monoculture leaves an area more vulnerable to predation or disease. Why? ______________________________________________________________________ __