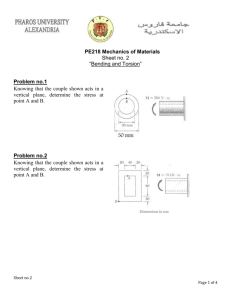
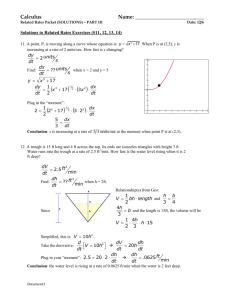
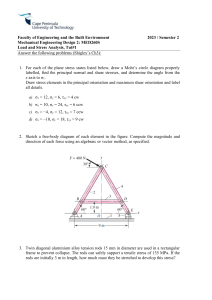
Strength of Materials Q1 Using Mohr’s Circle, determine the principal stresses, the maximum in-plane shear stress, and average normal stress. Specify the orientation of the element in each case. Q1 - Solution Q2Determine the equivalent state of stress on an element at the point which represents (a) the principal stresses and (b) the maximum in-plane shear stress and the associated average normal stress. Also, for each case, determine the corresponding orientation of the element with respect to the element shown and sketch the results on the element. Q2 - Solution Q2 - Solution Q2 - Solution Q3 Gear B supplies 15 kW of power, while gears A, C and D withdraw 6 kW, 4 kW and 5 kW, respectively. If the shaft is made of steel with the allowable shear stress of τallow = 75 MPa, and the relative angle of twist between any two gears cannot exceed 0.05 rad, determine the required minimum diameter d of the shaft to the nearest millimeter. The shaft is rotating at 600 rpm. Gst = 75(109) Q3 - Solution Q3 - Solution Q4 The plug has a diameter of 30 mm and fits within a rigid sleeve having an inner diameter of 32 mm. Both the plug and the sleeve are 50 mm long. Determine the axial pressure p that must be applied to the top of the plug to cause it to contact the sides of the sleeve. Also, how far must the plug be compressed downward in order to do this? The plug is made from a material for which E = 5 MPa, ν = 0.45. Q4 - Solution