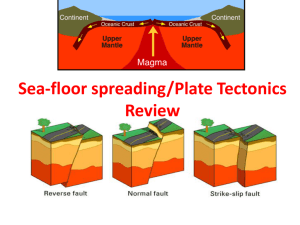
Earth’s Changing Surface Test Name: Date: Directions: Read each question and circle the best answer. 1. An area where one plate slides under another is called a a. Divergent boundary b. Transform boundary c. Subduction zone d. Continental zone 2. Which process is an example of physical weathering? a. a nail rusting b. acidic water dissolving calcite c. rock weathering to make clay d. plant roots breaking rock 3. What forms along divergent boundaries? a. Mid-ocean ridges and rifts b. Subduction zones and trenches c. Folded Mountains and volcanoes d. Canyons 4. The main force acting along a convergent boundary is a. shear b. tension c. convection d. compression 5. Shear is the main force acting at which type of boundary? a. divergent b. transform c. oceanic-continental convergent d. continental-continental convergent 6. Which statement correctly describes a force acting at a plate boundary? a. Shear is the main force acting along a transform boundary. b. Tension is the main force acting along an oceanic-continental convergent boundary. c. Compression is the main force acting along divergent boundary. d. Convection is the main force acting along a continental-continental convergent boundary. 7. Most volcanoes and earthquakes occur a. Over hot spots b. Next to calderas c. In the middle of tectonic plates d. Along plate boundaries Earth’s Changing Surface Test 8. A is NOT a possible effect of an earthquake. a. b. c. d. tsunami hot spot landslide liquefaction 9. Which landform is NOT associated with volcanic eruptions? a. caldera b. fault c. lava flow d. mid-ocean ridge 10. Rifts form at which type of plate boundary? a. Convergent b. Divergent c. Hot spot d. Transform 11. Sediment is made by a. erosion b. deposition c. weathering d. transportation 12. The force produced when two plates move away from each other is a. compression b. subduction c. tension d. shear 13. The sediment deposited by glaciers creates a. flood plains b. moraines c. sand dunes d. sedimentary boundaries 14. Tectonic plates slide horizontally past each other at a. convergent boundaries b. divergent boundaries c. mid-ocean ridges d. transform boundaries 15. Which type of weathering is most common in cold, mountainous areas? a. crystallization b. dissolving c. frost wedging d. melting Earth’s Changing Surface Test 16. Tectonic plates generally move toward or away from each other at what speed? a. Few centimeters per second b. Few centimeters per day c. Few centimeters per year d. Few centimeters per million years 17. Volcanic ash is produced during a. explosive eruptions b. lava flows c. liquefaction d. subduction 18. What feature is marked by the X on the image below? a. b. c. d. subduction zone continental rift mid-ocean ridge transform fault 19. What term best describes what is happening when a tree’s roots apply enough force to uplift and break sidewalk into small pieces? a. chemical weathering b. erosion c. liquefaction d. physical weathering 20. Which landforms are NOT examples of deposition? a. moraines and deltas b. valleys and mountains c. floodplains and sand dunes d. none of the above Directions: Answer the following questions in a complete sentence. 21. List two types of evidence and explain how it supports the theory of plate tectonics. (2pt) 22. How is magma different from lava? (2pts) Earth’s Changing Surface Test 23. Compare and contrast chemical and physical weathering. (2pts) Directions: On the line before each definition, write the letter of the term that matches it correctly. Each term is used only once. ____ 24. Boundary where plates slide past each other A. composite volcano ____ 25. A process that changes the composition of a rock B. chemical weathering ____ 26. Type of Volcano that is large, explosive, steep sided, C. divergent and cone shape. ____ 27. Small pieces of rocks and minerals are called D. sediment ____ 28. Force that pushes rock together E. physical weathering ____ 29. Boundary where plates move away from each other F. transform ____ 30. Force that pulls rock apart G. compression ____ 31. Type of Volcano that tends to be large, has a circular H. shield Volcano base, and is non-explosive. ____ 32. Breaking rock into small pieces without changing the I. tension composition. ____ 33. Dangerous waves that can be caused by earthquakes. A. Plate tectonics ____ 34. This theory states that Earth’s crust is broken into rigid plates. B. Geological Evidence ____ 35. Alfred Wegner developed the hypothesis that continents move called C. Subduction zones ____ 36. Evidence that shows that similar rocks and mountains are found on different continents called D. Tsunamis ____ 37. The area where one plate slides under another E. Lava flows ____ 38. Long streams of molten rock that build up as flat layers when the lava cools F. Continental drift ____ 39. A rupture and sudden movement of rocks along a break or a crack in Earth’s crust. G. Caldera ____ 40. Large indentation in the center of a volcano that forms when the surface above the magma chamber collapses. H. Earthquake