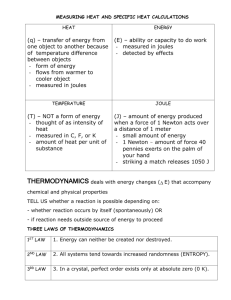
Energy, Work and Power Study Guide Energy – (unit: joule) Measure of the capacity to do work. Forms of energy: kinetic, potential, mechanical, chemical, electric, magnetic, radiant, nuclear, gravitational, thermal, heat, etc.. Kinetic Energy Formula: Ek = ½ m v2 Potential Energy Formula: Ep = m g h Law of conservation of energy – The total energy of an isolated system is constant. Energy can be transferred/converted from one form to another but energy cannot be created or destroyed. (also known as the first law of thermodynamics) Work – (unit: joule) Occurs when an object is displaced (moved) due to a force. Work Formula: W = F d or work (J) = force (N) x distance (m) Joule (J) - Unit of energy and work. One joule is defined as being equal to the force of one Newton on an object moved a distance of one meter. One joule of electrical energy is equal to one amp flowing through a one Ohm conductor for one second. Power – (unit: Watt) The rate at which work is done. 1 Watt = 1 Joule of work/second 1 Watt is also equal to the electrical power of 1 amp at 1 volt. Power Formula: P = J/s or power (W) = joules (J) seconds (s) Efficiency – A measure of how well a device’s input energy is converted to useful output energy. For example, if we input 100 joules of energy into a machine that lifts an object and has an output energy of 100 joules, the machine is 100% efficient. There is no machine that is 100% efficient because energy will be lost/transferred to something other than the intended purpose of the machine. Efficiency Formula: Efficiency = useful energy(work output) total energy(work input) x 100 Force – (unit: Newton) Causes a change in an object’s motion. In other words, a force will cause an object to accelerate (change velocity). One Newton (N) is equal to the amount of force required to accelerate a 1 kg mass at 1 m/s2. Math Problem Examples (formulas and solved equations) 1) How much power is used by a light bulb that uses 2000 joules in 40 seconds? 2000 𝐽 Formula: J/s = Watts 40 𝑠 = 50 Watts of power 2) How much power does a pulley system provide if 5000 joules of energy are applied for 10 seconds? (assume 100% efficiency) 5000 𝐽 Formula: J/s = Watts 10 𝑠 = 500 Watts of power 3) How many seconds did a light bulb stay lit if it uses 3000 J of energy and has a power output of 100 watts? (assume 100% efficiency) 3000 J Formula: J/s = Watts 30 s = 100 Watts of power 4) What is the efficiency of a light bulb in which you input 150 joules of electrical energy and get out 30 joules of light? Formula: useful energ output total energy output x 100 = efficiency 30 𝐽 150 𝐽 x 100 = 20% efficiency 5) How much work has been done if a dude pushes with all his might on a wall with 150 N of force and is not able to move the wall? Formula: Fd = work (150 N ) x (0 m) = 0 joules of work 6) How much force is required to lift a box that requires 400 J of work to lift the box 2 m? Formula: Fd = work (200 N) x (2 m) = 400 Joules of work 7) What is the kinetic energy of a ball that has a velocity of 30 m/s and a mass of 2 kg? Formula: Ek = ½ m v2 ½ x (2 kg) x (30 m/s)2 = 900 joules of kinetic energy 8) What is the mass of a ball that has a kinetic energy of 250 J and a velocity of 50 m/s? Formula: Ek = ½ m v2 ½ x (0.72 Kg) x (50 m/s)2 = 250 Joules of kinetic energy 9) What is the velocity of a ball that has a kinetic energy of 500 J and a mass of 5 kg? Formula: Ek = ½ m v2 ½ x (5 kg) x (14 m/s)2 = 500 Joules of kinetic energy 10) What is the potential energy of a 5 kg ball that sits on a roof of a 20 m tall building? Formula: Ep = m g h (5 kg) x (10 m/s2) x (20 m) = 1000 joules of potential energy 11) What is the height of a ball that has a potential energy of 5000 J and a mass of 2 kg? Formula: Ep = m g h (2 kg) x (10 m/s2) x (250 m) = 5000 joules of potential energy