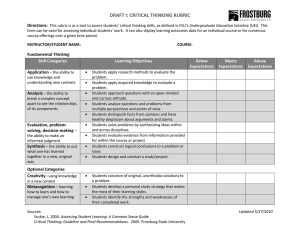
Rubric Formats Rubrics can be classified into four formats (Assessing Student Learning: A common sense guide by Suskie 2004) Checklists – simple list indicating the presence of 'things you are looking for' A checklist rubric for evaluating a web site (Assessing Student Learning: A common sense guide by Suskie 2004) X Titles are meaningful Each page loads quickly X The text is easy to read Rating scales – a checklist with a rating scale added to show the degree to which the ‘things you are looking for' are present A rating scale rubric for an information literacy assignment (Assessing Student Learning: A common sense guide by Suskie 2004) Please indicate the student's skill in each of the following respects, as evidenced by this assignment, by checking the appropriate box. If this assignment is not intended to elicit a particular skill, please check the N/A box. Outstanding Ver y Acceptable Marginally Inadequate N/A (A) Good (C) acceptable (F) (B) (D) Identify, locate, and access sources of information Critically evaluate information, including its legitimacy, validity, and appropriateness Organize information to present a sound central idea supported by relevant material in a logical order Use information to answer questions and/or solve problems Clearly articulate information and ideas Use information technologies to communicate, manage, and process information Use information technologies to solve problems Use the work of others accurately and ethically What grade are you awarding this assignment? If you had to assign a final course grade for this student today, what would it be? A rating scale for an oral presentation (Assessing Student Learning: A common sense guide by Suskie 2004) The presenter … Strongly agree Clearly stated the purpose of the presentation Was well organized Agree Disagree X X Answered questions authoritatively Appeared confident Strongly disagree X X It should be noted that rating scales can be vague in nature leading to problems (Suskie 2004): When several faculty are doing the rating, they may be inconsistent in how they rate performance Students don't receive thorough feedback; i.e., a scored rubric may not explain why something was less than superior Holistic rating scales Do not have a list of the ‘things you're looking for' Have short narrative descriptions of the characteristics of outstanding work, acceptable work, unacceptable work, and so on HOLISTIC rubric for assessing student essays (Assessing Academic Programs in Higher Education by Allen 2004) Inadequate The essay has at least one serious weakness. It may be unfocused, underdeveloped, or rambling. Problems with the use of language seriously interfere with the reader's ability to understand what is being communicated. Developing competence The essay may be somewhat unfocused, underdeveloped, or rambling, but it does have some coherence. Problems with the use of language occasionally interfere with the reader's ability to understand what is being communicated. Acceptable The essay is generally focused and contains some development of ideas, but the discussion may be simplistic or repetitive. The language lacks syntactic complexity and may contain occasional grammatical errors, but the reader is able to understand what is being communicated. Sophisticated The essay is focused and clearly organized, and it shows depth of development. The language is precise and shows syntactic variety, and ideas are clearly communicated to the reader. Descriptive rubrics Replace the checkboxes of rating scale rubrics with brief descriptions of the performance that merits each possible rating Descriptions of each performance level make faculty expectations explicit and student performance convincingly documented. But, coming up with succinct but explicit descriptions of every performance level for every ‘thing you are looking for' can be time-consuming. Are a good choice when several faculty are collectively assessing student work, it is important to give students detailed feedback, or outside audiences will be examining the rubric scores. A descriptive rubric for a slide presentation on findings from research sources (Assessing Student Learning: A common sense guide by Suskie 2004) Well done (5) Satisfactory (4-3) Needs improvement (2-1) Incomplete (0) Organization Clearly, concisely written. Logical, intuitive progression of ideas and supporting information. Clear and direct cues to all information. Logical progression of ideas and supporting information. Most cues to information are clear and direct. Vague in conveying viewpoint and purpose. Some logical progression of ideas and supporting information but cues are confusing or flawed. Lacks a clear point of view and logical sequence of information. Cues to information are not evident. Introduction Presents overall topic. Draws in audience with compelling questions or by relating audience's interests or goals. Clear, coherent, and related to topic. Some structure but Does not orient does not create a sense audience to what of what follows. May will follow. be overly detailed or incomplete. Somewhat appealing. Etc. ANALYTIC rubric for peer assessment of team project members (Assessing Academic Programs in Higher Education by Allen 2004) Below expectation Good Exceptional Project contributions Made few substantive Contributed a “fair contributions to the share” of substance to team's final product the team's final product Leadership Rarely or never exercised leadership Accepted a “fair share” of leadership responsibilities Routinely provided excellent leadership Collaboration Undermined group discussions or often failed to participate Respected others' opinions and contributed to the group's discussion Respected others' opinions and made major contributions to the group's discussion Contributed considerable substance to the team's final product ANALYTIC rubric for grading oral presentations (Assessing Academic Programs in Higher Education by Allen 2004) Below expectation Satisfactory Exemplary The presentation has a focus and provides some evidence that supports conclusions. The presentation is carefully organized and provides convincing evidence to support conclusions (0 – 2) (3 – 5) (6 – 8) The content is inaccurate or overly general. Listeners are unlikely to learn anything or may be misled. The content is generally accurate, but incomplete. Listeners may learn some isolated facts, but they are unlikely to gain new insights about the topic. The content is accurate and complete. Listeners are likely to gain new insights about the topic. (0 – 2) (5 – 7) (10 – 13) Organization No apparent organization. Evidence is not used to support assertions. Content Style The speaker appears anxious and uncomfortable, and reads notes, rather than speaks. Listeners are largely ignored. The speaker is generally relaxed and comfortable, but too often relies on notes. Listeners are sometimes ignored or misunderstood. (0 – 2) (3 – 6) Score The speaker is relaxed and comfortable, speaks without undue reliance on notes, and interacts effectively with listeners. (7 – 9) Total Score Generic rubric for assessing portfolios (Assessing Academic Programs in Higher Education by Allen 2004) Unacceptable: Evidence that the student has mastered this objective is not provided, unconvincing, Marginal: Evidence that the student has mastered this objective is provided, Acceptable: Evidence shows that the student has generally attained this objective Exceptional: Evidence demonstrates that the student has mastered this or very incomplete Learning objective 1 Learning objective 2 Etc. but it is weak or incomplete objective at a high level