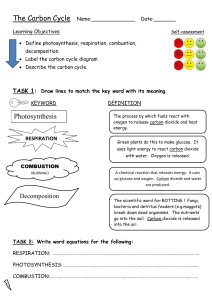
There are a number of cycles found in nature, continuously circulating nutrients and substances around biological systems. • Water cycle • Carbon cycle • Nitrogen cycle Why do biologists care about Carbon? • Carbon is the main constituent of all living cells. • Living things need carbon to make most of the molecules in our body (fats, carbohydrates, nucleic acids (DNA) and proteins) Carbon is abundant in the air… …as carbon dioxide. Which is great news for plants. They can’t eat food, so they make their own sugar by photosynthesis. Photosynthesis: Plants take in water (H2O) from the soil through their roots. And carbon dioxide (CO2) from the air in through their leaves. Then they use sunlight energy to rearrange these into molecules of glucose. Some Whichglucose is greatisnews stored forby consumers, the as plant they can as starch eat plants (e.g. and potatoes) use theorenergy in as thecellulose food to in move theand plant build celltheir walls.bodies. photosynthesis Respiration: To move and grow, both plants and animals need to Plants animals taketoinrelease oxygen (O the air. 2) from break and down glucose that chemical energy. They to break down glucose, producing carbon Theyuse do the thisoxygen by respiration. dioxide (CO2) and water (H2O) as waste. feeding photosynthesis respiration feeding photosynthesis Some day, this goat will die… The carbon which is locked up in is great newslost for the body …which of organisms is not decomposers like bacteria and fungi. forever. They break down dead organisms and in doing so, release the carbon into the air as carbon dioxide (CO2). respiration feeding photosynthesis respiration feeding photosynthesis decomposition Millions of years ago, some decaying organisms were covered by layers of sand and rock. The pressure caused them to fossilise and form fossil fuels. respiration feeding photosynthesis decomposition We can extract these fossil fuels from underground and burn them to release energy. This process is called combustion. It releases carbon dioxide (CO2) into the atmosphere. respiration feeding photosynthesis decomposition The Carbon Cycle combustion respiration feeding photosynthesis decomposition carbon cycle animation