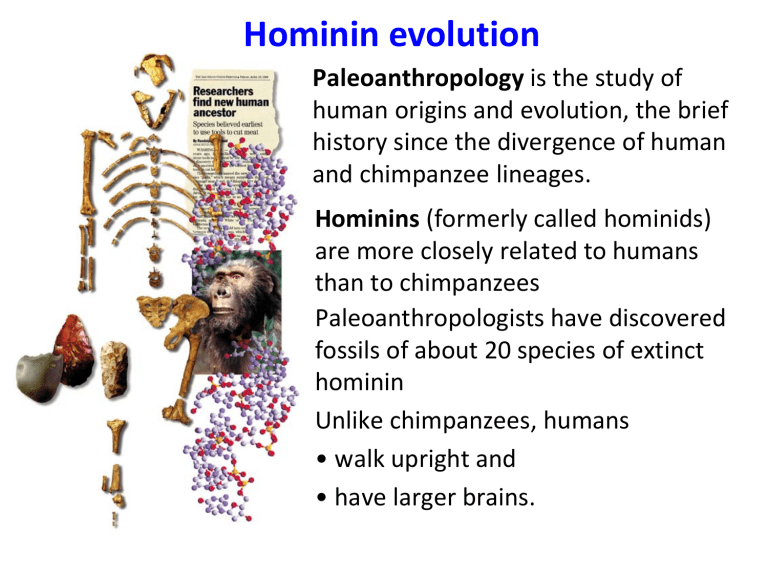
Hominin evolution Paleoanthropology is the study of human origins and evolution, the brief history since the divergence of human and chimpanzee lineages. Hominins (formerly called hominids) are more closely related to humans than to chimpanzees Paleoanthropologists have discovered fossils of about 20 species of extinct hominin Unlike chimpanzees, humans • walk upright and • have larger brains. Human evolution Human evolution is the evolutionary process that led to the emergence of anatomically modern humans, beginning with the evolutionary history of primates – in particular genus Homo – and leading to the emergence of Homo sapiens as a distinct species of the hominid family, the great apes. https://en.wikipedia.org https://en.wikipedia.org Hominins originated in Africa about 6–7 million years ago • Early hominins had a small brain but probably walked upright Two common misconceptions about early hominins: – Thinking of them as chimpanzees – Imagining human evolution as a ladder leading directly to Homo sapiens Humans are mammals that have a large brain and bipedal locomotion The species Homo sapiens is about 200,000 years old, which is very young, considering that life has existed on Earth for at least 3.5 billion years. Derived Characters of Humans A number of characters distinguish humans from other apes: Upright posture and bipedal locomotion Larger brains Language capabilities and symbolic thought The manufacture and use of complex tools Shortened jaw Shorter digestive tract Bipedalism arose millions of years before larger brain size Evidence of bipedalism includes 3.6-million-year-old upright-walking hominin footprints fossil skeletons. Evidence of bipedalism Unlike chimpanzees, humans – walk upright and – have larger brains. Skeletal implications of bipedalism Location of foramen magnum Tool Use • The oldest evidence of tool use, cut marks on animal bones, is 2.5 million years old • Tool use is considered a human trait Rapid expansion of our species may have been preceded by changes to the brain that made cognitive innovations possible Art, a human hallmark – For example, the FOXP2 gene is essential for human language, and underwent intense natural selection during the last 200,000 years – Homo sapiens were the first group to show evidence of symbolic and sophisticated thought Throughout evolution brains changed in: Size Complexity the ratio of brain weight to overall body weight Human and Ape Brains Humankind Emerging, 7th ed., p. 389 Hominid cranium comparison provides evidence of evolution Comparison of hominin skull structures Larger brains mark the evolution of Homo Cranial Capacity. Understanding Physical Anthropology and Archaeology, 8th ed., p. 234 Australopiths had such small brains (400–450 cc) that they were too small to be members of Homo. Homo habilis (2.4–1.6 million years ago) had a brain size of 510–690 cc. Their fossils are found with stone tools. Homo ergaster (1.9–1.6 million years ago) had a brain size ranging from 750 to 850 cc. Their fossils are found with more sophisticated stone tools and - long, slender legs were adapted for long-distance walking. Homo sapiens has a brain size of around 1,300 cc. Comparison of hominin skull structures Prognathism “Muzzle” angles (prognathism) of ape and modern human Sagittal crests and temporal muscle orientations. Hominid compared to pongid. (Line of greatest muscle force is shown in red.) Sagittal crest Sagittal crest Understanding Physical Anthropology and Archaeology, 8th ed., p. 245 Comparison of hominin skull structures Teeth / Dental Arcade Teeth of a male patas monkey. Apes (and monkeys) still possess conical, daggerlike canines which project well beyond the surface of the opposite teeth. The gap is a diastema. Monkey & Ape Canines Understanding Physical Anthropology and Archaeology, 8th ed., p. 231 Homo sapiens • Homo sapiens appeared in Africa by 195,000 A 160,000-yearyears ago old fossil of Homo sapiens • All living humans are descended from these African ancestors • The oldest fossils of Homo sapiens outside Africa date back about 115,000 years and are from the Middle East • Humans first arrived in the New World sometime before 15,000 years ago • In 2004, 18,000 year old fossils were found in Indonesia, and a new small hominin was named: Homo floresiensis Hominid cranium omparison provides evidence of evolution Modern human Common ancestor