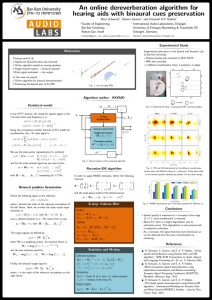
The Impact of Beta Binaural Beats on Working Memory Capacity HUSNA MD ISA 58647 PROF MADYA DR. NORSIAH FAUZAN Introduction Binaural beats stimulation is two pure tone with similar frequency that are being presented separately into each ear that result the brain will perceive the difference frequency of these two tones. Working memory capacity refers to the ability to control, sustained and manipulates information despite having a distraction or interference. Following Frequency Response (FFR) – the brain has a tendency to change the current brainwaves pattern into the frequency of binaural stimulation. Research Objective General objective: To study the effect of listening to beta binaural betas on ability to hold and manipulate information in working memory capacity. Specific objective: To study what and how the brain response when listening to beta binaural beats. To study the brain parts that are stimulated by the beta binaural beats. To investigate the after effect of listening to beta binaural beats in storing and maintain information in memory span task. Problem Statement Binaural beats with beta frequency is associated with improvement of working memory capacity that leads to higher performance in other cognitive processes such problem solving skill, decision making and judgment. However, past studies on effect of beta binaural beats on working memory capacity are not enough to support the theory above. According to Garcia-Arglbay, Santed and Reales (2018), most researches that were done in between 2007 until 2017: Only eight researches investigated the effect on long- and short-term memory. Four studies on effects of binaural beats on attention. Research Hypothesis Ho: The frequency of beta binaural beats stimulus significantly affect the brainwaves pattern. Ho: There is a significant difference in score of memory span task before and after listening to beta binaural beats frequency. Ho: There is a significant difference in score of memory span task between group of participants that listen to beta binaural beats stimulation and participants who are not listening to auditory stimulation. Literature Review Article Description Methodology Year of Published Summary The effect of binaural beats stimulation in attention and EEG To explore the potential of binaural beats in tasks that required focus and concentration. Quantitative study 2012 - There is no significant difference in cognitive test. - There is no significant difference in brain activity. - The result show no evidence for improvements in cognitive function also no changes in brain activity after listening to binaural beats. Alpha and Beta Brainwave Characteristics to Binaural Beat Treatment Explain the effect of 10 Hz binaural Mixed method beat towards alpha and beta waves that can reduce stress 2013 - After listening to binaural beats (10Hz), alpha waves while beta waves decrease that indicates the brain is in relaxation. Impact of binaural beats on creativity Investigating the effect of alpha and gamma binaural beats on overall creative thinking Quantitative study 2013 - There is no evidence for any influenced on binaural beats on convergent thinking. - There is no difference between alpha and gamma on divergent thinking. - Binaural beats cannot be considered as all-around tools for cognitive enhancement. The effect of binaural beats on working memory capacity Demonstrate how binaural beats can improve working memory capacity based on the AOSPAN test. Quantitative study 2015 - Alpha binaural beats had a temporary positive effect on the capacity of working memory where participants achieved a significance increases in the capacity of their working memory compare to the participants in control group. Article Objective Methodology Year of Published Summary More attentional focusing through binaural betas: evidence from the global-local task Investigate whether binaural beats impact attentional focusing and top down control over irrelevant information Quantitative study 2017 - Binaural auditory beats affect long term memory To determine the effect of binaural auditory beats on long term memory Quantitative study 2017 - Beta binaural auditory beats result in greater word recall and recognition compare to the participants who listen to alpha binaural auditory beats. Analysis of EEG activity in response to binaural beats with different frequencies To track any changes in brain waves using EEG during binaural beats stimulation were presented Quantitative study 2014 - The brainwaves pattern did not change according to the binaural beat's stimulation presented. therefore, relative power(RP) were used to indicate changes in strength of brainwaves. Tracking EEG changes in response to alpha and beta binaural beats To investigate any changes in EEG throughout alpha and beta binaural stimulation. Quantitative study 2012 - There were no effect of beta and alpha binaural beats frequency on the brainwaves pattern recorded using EEG in both left and right hemisphere. - Gamma frequency binaural betas do not lead to engagement in suppression of irrelevant information in working memory. High frequency of binaural beats have a significant impact on the global precedence effect Research Methodology Type of Research Quantitative study Research Sample 24 students from UNIMAS are selected randomly Age of participant is 21 years old and above (adult age group) Instrumental Quantitative Electroencephalogram (qEEG) to detect brain region that respond to beta binaural beats stimulation and changes in brainwaves pattern during listening period of auditory stimulation Memory span task: to measure working memory capacity Beta binaural beats stimulation audio Research Methodology Procedure of data collection I. Group A Pre-test : participants are required to take memory span task. Rest-period: participants are presented with beta binaural beats for 15 minutes using headphones. Post-test: participants are required to retake memory span task. II. Group B Pre-test: participants are required to take memory span task. Rest-period: participants will be asked to remain sited and relax for 15 minutes. Post-test: participants are required to retake memory span task. Data collection analysis • Independent Sample T-test • Paired Sample T-Test • Microsoft Excel