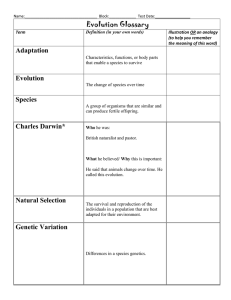
How does evolution explain biological diversity? Science Module Submitted to: sir Arnel Martinez Submitted by: Jhan Martin Digo Hi there!!!! My name is panda and we will have lesson do you have an idea about evolution and biological diversity? This lesson will show you answers on how evolution can explain biological diversity so let’s go and enjoy the fun. Objectives: Read the direction carefully Explain the lesson This lesson helps you to your questions Pre-test Define whether it’s true or false. 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. evolution is defined as true change in a species through time. adaption, survival, and extinction are closely related concepts. evolution was the theory of Isaac newton. the earth is estimated to be about 4.5 billion years old. polyploidy refers to the established natural relationship among organisms based on evolutionary history or line age. Lesson: In the previous grade level, we defined biological diversity or biodiversityas the variation and variability of living organisms and ecological complexes occur. Biodiversity covers “the genetic species, and ecological diversity in a given place at a given time. What do we know about species diversity? Species diversity refers to the number and variety of living organisms. How many species are there? Although only an estimated two million species of plants, animals and microorganisms have yet been discovered, named, and documented worldwide, taxonomists believe that are between 5 to 100 million species of living things on earth. Why do living things share common characters? Apparently, different species appeared at different geological periods. As cells come from pre-existing cells, so do living things come from pre-existing life forms. Old species that emerged first changed and diverged into more advanced forms of life primitive species may have given rise to new ones. Why are there so many different species? The earth is estimated to be about 4.5 billion years old. For more than a billion years, there was not a single living thing on earth. So how did these species of living things emerge? And why are there so many different species now? The answer is speciation, a process that explains how a new species evolved from a previously existing one. Speciation involves isolation, divergence and the consequent loss of the ability to interbreed with the old species. One of the mechanism by which populations give rise to new species is by polyploidy. Polyploidy involves the development of multiple homogenous sets of chromosomes. The brassica species are what we commonly eat as vegetables. How does evolution contribute to biological diversity? Evolution is defined as change in species over time. It may be expressed through variation, speciation or phylogeny. Evolution accounts for the variation that occurs in members of the same species. It explains why no two individuals in the same population are exactly alike. We may be fair complexioned or dark skinned, with straight or curly hair, tall or short. These different traits and the many different combinations in which they appear may have resulted from genetic recombination or mutation. Genetic recombination is achieved during sexual reproduction when genes of two parents combine in the offspring. Mutation is a drastic change in the genes are translated to changes in the expression of certain physical characteristics. Post-test Identify the sentences and find there meaning. 1. all of the different types of organisms/ecosystems on earth, and the ecological process they are a part of? 2. where living interacts with non-living? 3. variety of different populations? 4. variety of genetic material found in living things? 5. organisms adapt to changes in the environment for survival? 6. different populations of species living in the same area? 7. refers to the changes in characters of organisms in a population due to genetic recombination or mutation. Ecosystem Diversity Community Natural Selection Genetic Diversity Biological Diversity variation Community Diversity Key to correction: Pre-test 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. true true false true false Post-test 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. biological diversity ecosystem diversity community diversity genetic diversity natural selection community variation