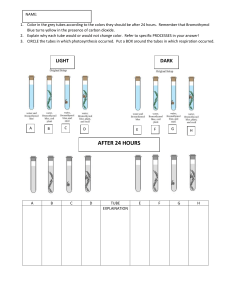
PHOTOSYNTHESIS Group 4 Bello, Dela Cruz, Laguyo, Torres Photosynthesis ● ● ● ● People: Eating Plants: Photosynthesis Production of glucose in plants which later converts as ATP which gives chemical energy to the plants. Uses light energy, water and carbon dioxide (provided by us). Byproduct is oxygen which we use, in return. OBJECTIVES Objectives 1. To determine the why plants need the process of photosynthesis. 2. To measure the rate of photosynthesis as affected by some factors such as light, carbon dioxide, and 3. To obtain and identify the pigments involved in photosynthesis through the experiments performed. METHODOLOGY and RESULTS AND DISCUSSION Light as a Requirement for Photosynthesis ● ● ● ● ● 2 Mayana leaves were each placed in a dark place and the other under direct sunlight for 48 hours. This test will determine the leaves’ starch component. Boiling the leaves using distilled water should remove most of its pigment. After removing most of the pigment, the leaves were immersed in 95% ethyl alcohol and boiled in a water bath. After boiling in 95% ethyl alcohol solution, iodine solution was added. Light as a Requirement for Photosynthesis ● ● ● The first boiling of the leaves with distilled water removed most of its piment showing the leaves naked form. On the second boil, the leaves were immersed in 95% ethyl alcohol which made the solution more green than its starting color and left the leaves less green. We may assume that some of the pigment that weren’t removed by the distilled water is now removed by the alcohol solution. Adding iodine determines the presence of starch which is indicated by a bluish black color. After adding iodine and leaving it for 10 mins, the results show that the mayana leaf that was exposed under direct sunlight has starch. Light Intensity and the Rate of Photosynthesis ● ● ● ● 5 test tubes labeled A to E were prepared and each filled with 1% NaHCO3 (sodium bicarbonate) solution almost completely. Each test tube was immersed with a 8 cm long healthy Hydrilla sprig from under water and covered with a stopper. Test tube A was placed in the dark while test tubes B to E were placed in front of a light source 20cm, 40cm, 60cm, and 80cm away respectively. All test tubes were placed in their following positions for a total of 1 ½ hours. Afterwards, all test tubes were observed for the formation of bubbles. Light Intensity and the Rate of Photosynthesis All test tubes did not contain any bubbles due to the poor condition of the Hydrilla plant. According to the laboratory technician, the condition of the Hydrilla plant was not good because of the bad weather that it grew in. Carbon Dioxide as a Requirement for Photosynthesis ● ● ● 3 test tubes were labeled with A, B and C and filled halfway with phenol red solution In test tubes A and B, a straw is used to blow gently in the test tubes until the solution became pale orange Afterwards, test tubes B and C were each placed with a Hydrilla plant and all 3 test tubes were set in a bright light and observed changed for 2 hours. Carbon Dioxide as a requirement ● ● ● The carbon dioxide provided by the experimenters turned the solution orange; absence of carbon dioxide was shown by the red solution. Ideally: Test tube B was supposed to turn back to red (like in test tube C) since the hydrilla was supposed to use up the oxygen Actual: The hydrilla was not in the best condition due to the weather, which in retuern was not able to utilize the carbon dioxide present in the test tube. Separation of Chloroplast PIGMENT EXTRACTION: Green vs Variegated leaf 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 10g cut into small pieces Crush with 5mL acetone using blender Add 3mL acetone Squeeze using cheese Collect extract with a dropper PAPER CHROMATOGRAPHY 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Cut a filter paper in a shape of a pen Place the drop of the extract 1 inch from the tip of the paper that would touch the solution Place 1:9 acetone:petroleum ether on a beaker (not too many. Approximately 10 cm from the base of the beaker Place the filter paper in the beaker, allowing only the tip to touch the solution DONT LET THE EXTRACT TOUCH THE SOLUTION Wait for 15-30 minutes before taking off the filter paper and observing color bands produced Separation of Chloroplast After the 30 minute waiting period, both leafs had clear yellow band produced clearly, while a very light green band can be seen at the bottom. Carotene: involved in the primary light absorption Chlorophyll a: is the pigment that makes plants and algae green. CONCLUSIONS Light and Carbon Dioxide are two key factors in the process of photosynthesis, although given the condition, we weren’t able to manifest the importance of it in the experiment.