Integumentary System Worksheet: Skin, Hair, Nails
advertisement

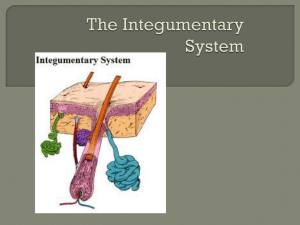
Name_________________________________________Date_________________Advisory______________________ Integumentary System (skin, hair and nails) Today’s Vocabulary: Dermis- Epidermis- Pore- FollicleReading about: The ___________________________ of the skin 5 Major Functions of the Skin Are… (1) Protecting the body: The skin protects the body because it is a barrier that keeps disease-causing organisms and other harmful materials from entering the body. Like plastic wrap that keeps food from drying out, the skin keeps water in the body. How does the skin protect? (2) Temperature: Another function of the skin is to help the body keep a steady temperature. Many blood vessels run through the skin. When you become too warm, these blood vessels get larger and the amount of blood that flows through them increases. These changes allow heat to move from your body into the outside environment. Also, sweat glands (tiny sacks) in the skin respond to heat by making perspiration (sweat). As perspiration evaporates from your skin, the skin cools off. How does the skin maintain temperature? (3) Getting rid of waste: Perspiration contains waste materials that come from your cells. Your skin is also helping get rid of waste when you sweat. How does the skin get rid of waste? What is another word for perspiration? Name_________________________________________Date_________________Advisory______________________ (4) Gathering information: The skin gets information about the environment around you. To understand how the skin does this, place your fingers on the skin of your arm and press down. Then lightly pinch yourself. You have just tested some of the nerves in your skin. The nerves in skin give information to your brain about pressure, pain, and temperature. Pain messages are important because they warn you that something in your surroundings may have injured you. How does the skin gather information? (5) Producing Vitamin D: Lastly, some of the skin cells make Vitamin D when you are in the sun. Vitamin D is important for healthy bones because it helps cells in your digestive system get calcium from food (for your bones!). Your skin cells need only a few minutes of sunlight to make all the Vitamin D you need in a day. How does the skin produce Vitamin D? 5 Functions of the Skin Name_________________________________________Date_________________Advisory______________________ BRAINPOP – The SKIN! After Questions – You and your partner! 1. Which of the 5 functions do you think is the most important? WHY? 2. What are the two reasons for sweat glands? (Why do we sweat)? 3. What is in the skin that helps it to gather information? Why is this important? Name_________________________________________Date_________________Advisory______________________ Homework: Additional FUNCTIONS of the Skin! 1) Top layer: Epidermis The epidermis is the top layer of the skin. In most places, the epidermis is thinner than the dermis. It does not have nerves or blood vessels. This is why you usually don’t feel pain from light scratches and they don’t bleed. Like all cells, the cells in the epidermis have a life cycle. Each epidermal cell begins life deep in the epidermis, where cells divide to form new cells. The new cells get older and move up to the top. After about two weeks, the cells die and sit at the top of the layer. These are more valuable dead than alive because the layer of dead cells provides protection from the outside environment. The thick layer of dead cells in your fingertips cushions your fingertips. Also, the shedding of dead cells carries away bacteria that settle on the skin. Every time you rub your hands together, you lose thousands of dead skin cells and bacteria on them. 1. What is the name of the top layer of skin called? 2. What type of cells does it mostly contain? 3. When you rub your hands together what comes off? The epidermis on the fingers and palms of your hands and on the toes and soles of your feet contain ridges and lines that are formed before birth. These ridges increase friction, which improves the skin’s grip. Each person has a unique pattern of ridges and grooves. Because these patterns are unique, footprints and fingerprints can be used to identify people. Some of the cells in the inside layer of the epidermis contain melanin. Melanin is a colored material that gives the skin its color. The more melanin in your skin, the darker it is. Sunlight makes more melanin in the skin. Melanin helps protect the underlying body cells from sun damage, by absorbing ultraviolet (UV) light. 1. What does melanin do? 2. What is the function (job) of the lines and ridges on your hands? Name_________________________________________Date_________________Advisory______________________ 2) Inner layer: Dermis The second layer of the skin is called the dermis. The dermis is the inner, thicker part of the skin. The thickness of the dermis changes from body part to body part. The thickness depends on how the body part is used. The dermis contains structures such as blood vessels, nerves, nerve endings, hair follicles, sweat glands and oil glands. Sweat glands make perspiration, which gets to the top through holes called pores. You probably saw these when you observed your skin with a hand lens. Strands of hair also grow from the dermis in structures called follicles. The hair that you see above the surface is made up of dead cells. Oil produced (made) in glands around the hair follicles help waterproof the hair. The primary function of the hair is to protect the skin from injury and damage from the sun. In addition, oil that reaches the surface of the skin helps to keep the skin moist. Layer 1) 2) Where is it located? What does it contain? What are its functions? Name_________________________________________Date_________________Advisory______________________ After-Reading Questions 1. What are the two reasons for sweat glands? (Why do we sweat)? 1 2 2. What is the reason for having nerves in the dermis? 3. Where is hair located in the skin? Be Specific! 4. Why do we have hair in the skin? (What is the purpose/function of hair?) 5. Why is it good to have dead cells in your epidermis? 6. Why do we have ridges on our fingers and toes? 7. What is the function of our pores? 8. What could happen if your pores became blocked? 9. Do you think it is possible to wash your skin too much and damage it? Why / why not? Explain!