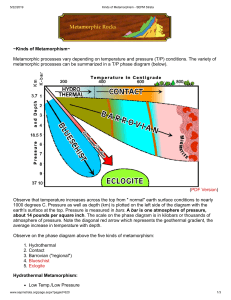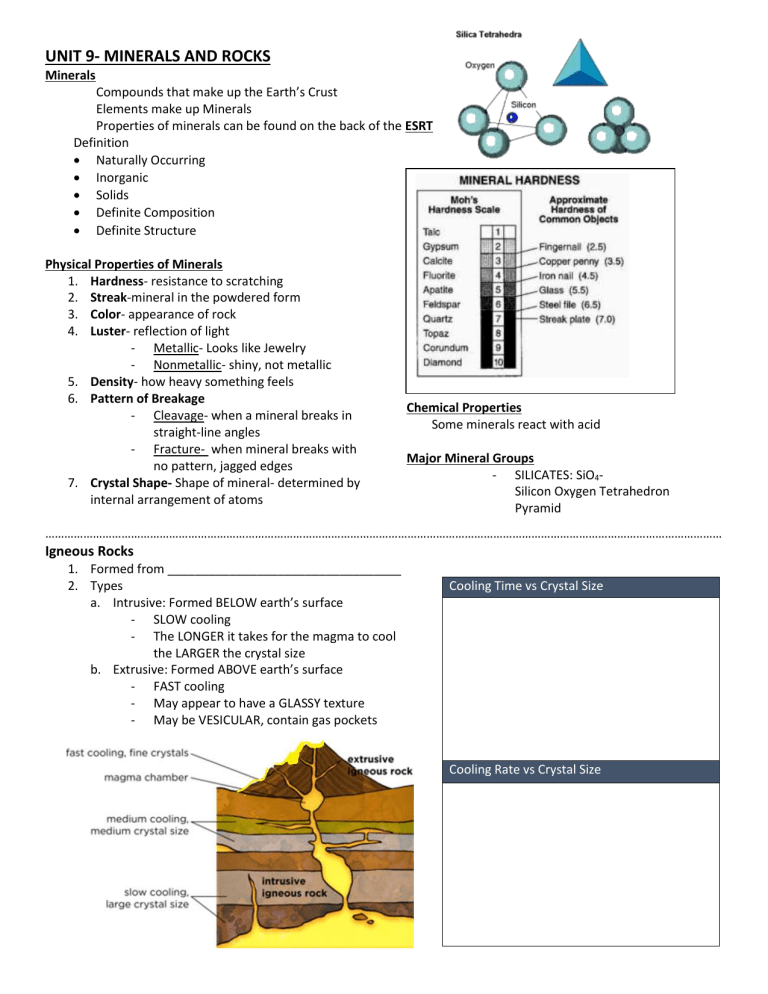
UNIT 9- MINERALS AND ROCKS Minerals Compounds that make up the Earth’s Crust Elements make up Minerals Properties of minerals can be found on the back of the ESRT Definition Naturally Occurring Inorganic Solids Definite Composition Definite Structure Physical Properties of Minerals 1. Hardness- resistance to scratching 2. Streak-mineral in the powdered form 3. Color- appearance of rock 4. Luster- reflection of light - Metallic- Looks like Jewelry - Nonmetallic- shiny, not metallic 5. Density- how heavy something feels 6. Pattern of Breakage - Cleavage- when a mineral breaks in straight-line angles - Fracture- when mineral breaks with no pattern, jagged edges 7. Crystal Shape- Shape of mineral- determined by internal arrangement of atoms Chemical Properties Some minerals react with acid Major Mineral Groups - SILICATES: SiO4Silicon Oxygen Tetrahedron Pyramid …………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… Igneous Rocks 1. Formed from __________________________________ 2. Types a. Intrusive: Formed BELOW earth’s surface - SLOW cooling - The LONGER it takes for the magma to cool the LARGER the crystal size b. Extrusive: Formed ABOVE earth’s surface - FAST cooling - May appear to have a GLASSY texture - May be VESICULAR, contain gas pockets Cooling Time vs Crystal Size Cooling Rate vs Crystal Size Sedimentary Rocks 1. Formed from___________________________________ 2. Types a. Clastic: fragments of INORGANIC (nonliving matter) materials formed on land b. Bioclastic: fragments of rock containing ORGANIC (living matter) materials c. Crystalline/ Chemical: occurs when water evaporates and minerals become solid and settle out or precipitate to the bottom of the lake or ocean floor. 3. Characteristics a. Form layers/ stratification b. Lithification- the process of turning sediments into solid rock c. Layers are horizontal and the oldest is on the bottom d. Only rock to contain FOSSILS Metamorphic Rock 1. Formed from ___________________________________ 2. Conditions needed for metamorphism to occur: _____________________________ and ___________________ 3. Effects of metamorphism a. Recrystallization d. Distorted structure b. Foliation e. Increased Density c. Banding f. Harder 4. Parent Rock : __________________________________________ 5. Types of Metamorphism a. Regional Metamorphism Metamorphism that occurs - deep in the crust - large area - high pressure/ high temperaure b. Contact Metamorphism Metaphorism that occurs along a boundary where magma and other rock meet. - Near surface - small area - low pressure/ high temp