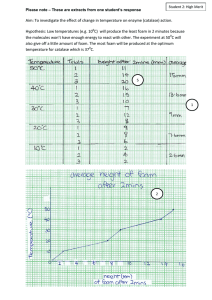
CREATING THE A-SOLID Data to start up Foam A-surface • • • • • H-point oscar, frame, mating components(plastics, pillars, console, etc...), trim drawings (trim cover thickness,tie down locations, tie down types, etc…) Critical foam areas that should be checked • Foam thickness at the top surface, bottom surface and side surfaces from frame to STO. • Foam thickness at centerline, paying particular attention to foam thickness below seams. • Foam thickness at radial corners of STO from frame to STO. • Foam thickness above frame components. • Potential thin foam to thick foam areas. • Foam thickness behind frame (back frame). • Value or absence of blend radii on STO. • Foam thickness between A and B surface. • Foam interface to plastics and mating components Creating Cutting Planes for Sections CUTTING PLANE • Back Pad – perpendicular to the torso angle(HORIZONTAL) – (Y) plane through H-point(LONGITUDINAL) • Cushion pad – (Y) plane through H-point(LONGITUDINAL) – (X) plane, which is perpendicular to the a-surface line at H-point of the STO Cut sections through the STO Pad Symmetry Sections AGGRESSIVE BOLSTERS PACKAGING TO A CONSOLE Try to match the STO as close as possible using 1) Circles 2) Conics 3) Arcs 4) Splines Insert surface creation Avoid bridge across the insert area Sidewall Sidewall Sidewall cushion Bolsters surface • 1.Create a horizontal line tangent to the high line of the bolster at each section • 2. Create a circle which is tangent to the high line of the bolster and the offset sidewall curve with a radius that is 60% of the STO radius (15mm MINIMUM) • 3. Next, create a curve (circle, conic, arc, or spline) that is tangent to the 60% STO radius (15mm MIN) through the endpoint of the trimmed insert offset curve with a radius that is equal to the STO bolster radius Step-1 and 2 Step-3 4.Need to check the integrity of the bolster offset curve when a tie down trench is added 5. To revise the bolster offset curve, change the endpoint of the insert offset curve by moving it toward the center of the pad without going Bolsters (multiple curves): 1. the foam will be line to line with the high line 2. determine the theoretical intersection of the flat top and bolster curve on the STO • Create a curve that is equal to the bolster curve radius that intersects the endpoint of the trimmed offset insert curve and the theoretical intersection of the flat top and bolster curve Top (back pads): Front & Rear (cushion pads): Bottom (back pads) – BITE LINE CREATING THE SLAB SURFACES FOR THE FOUNDATION SOLID CREATING TRENCHES FOR TIE DOWNS AND SELVEDGE LOCAL TRENCH OVERBUILD SET UP Hog ring location B-SIDE Completed foam PAD WHAT IS POLYURETHANE FOAM? It is chemical reaction between polyisocyanate + polyol Character of foam 1.Elasticity 2.Thermal Insurability PROCESS 1.Hot Cured molding method –low density, higher investment cost, longer cycle time 2.Cold cured molding method –high density ,lower investment cost, lower cycle time Hot cured Molding Method Cold cured Molding Method How foam are produced ? Typical Cushion DIE https://youtu.be/66JsLIfwclI Typical Back DIE Performance of Seat foam 1.Density 2.Hardness (ILD-INDENTATION LOAD DEFLECTION) 3.Impact Resilience Rate 4.Deflection amount Density: Usually higher density is preferred Hardness: 3.Impact Resilience Rate :Is more related to Ride comfort Usually measured a steel ball of 16 diameter (weight of 16.29 gram) from a height of 460 mm 4.Deflection amount This refer to the amount when a constant load is applied to foam