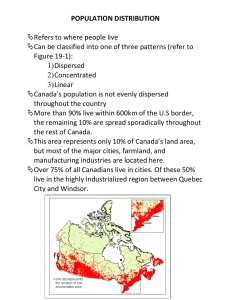
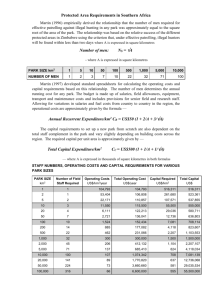
Micro hydro projects (MHPs) Overall electricity supply shortfall: 7,000 MW Hydropotential: 60,000 MW; only 15% utilized Ideal location in Khyber Pakhtunkhwa (KPK) Rampant rurality – off-grid & unsustainable sources Ideal geography – “run-of-river”/no dam needed General MHP Overview 5-150 kW hydropower unit Water head & flow from river/stream penstock tube turbine powerhouse transmission lines: & no seasonal impact Cheap electricity provision & consumption Easy operation & maintenance (O&M) – community runs MHP No direct GHG emissions (generators, lamps, and no indirect emissions either vs if national grid was used) 1 MHP implementation mandates collaboration and optioneering Details of Implementation MHP vs Photovoltaic Solar Panels Reliability *Initial investment: PKR 150,000-200,000 per kW 100 kW unit: provides for 150+ households MHP: high (can run all day, throughout the year) Completion time: 6-12 months; 25-year lifespan Solar: medium (expensive batteries & seasonal impacts) Collaboration with NGOs (for contractors, surveyors, engineers): Aga Khan Rural Support Program (experience >260 MHPs) Production Emissions MHP: medium Solar: high Tariffs Sarhad Rural Support Program MHP: low (experience >200 MHPs) Solar: high (similar to grid) Pakhtunkhwa Energy Development Organization (PEDO) Community Involvement & Development facilitates with government (generally no legal barriers) MHP: high (sharing, income-generating activities) O&M is community responsibility Solar: low (underutilized capacity factor) Provides support for small businesses Potential for MHP IPP 2 Successful implementation satisfies myriad social and business goals Outcomes *Carbon Offset (Scopes 1 & 2) per kW 100 kW unit **Grid 3 tCO2e/yr 310 tCO2e/yr Diesel Generator 2 tCO2e/yr 205 tCO2e/yr Kerosene 1.9 tCO2e/yr 190 tCO2e/yr Role in Management AKRSP overlooks community’s tariff revenue reinvestment in: Seeking O&M technical support Small business funding Infrastructure Improvements Mitigating Challenges Unskilled operators Training provision Flood protection Barrier funding Legal approvals Effective collaboration [Community Development] [Common challenges for community] • • SOCIAL • Extensive improvement to quality of life in rural KPK (Counter-poverty effort) Affordable provision of clean electricity Increase in income-generating activities Direct employment opportunities Better educational conditions Lowered kerosene use & hazard BUSINESS • Offset GHG emissions = smaller carbon footprint New social investment example for companies More attractive brand image Adding to global initiative vs. climate change Corporate Social Responsibility (CSR) initiative High potential for an Independent Power Producer (IPP) hydro project (eg. Laraib Energy) in the future Clean Development Mechanism (CDM) registration 3 Framework for MHP Problem Goal Resource Allocation Type Input Social Output/ Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) Business Output Lack of proper electricity access in rural Gilgit Baltistan Provide electricity via MHP(s) Social Investment PKR 200k/kW CAPEX; collaboration w/ NGOs (~6 months); O&M + development guidance Number of households connected Number of employment positions created # Street lamps installed % Decrease in kerosene consumption + Long term development # Number of tCO2e offset + Increased reputation 4 Potential Inependent Power Producer Hydropower project Example of a private company initiating an IPP hydroproject: (Laraib Energy Ltd., subsidiary of HUBCO) – 84 MW New Bong Escape Hydroelectric Power Project in AJK, on River Jhelum • • • • • • • • • • • • Planning & Construction 2019 – 2024, commenced 2019 Power purchase agreement with National Transmission and Despatch Company (NTDC) Local & Intl Banks for financing loans & documentation Gov. of Pak, Gov. of AJK, and other AJK entities for water use and land use agreements Sambo Construction company for water-to-wire process, E&M equipment subcontractor and design subcontractor NTDC REMACO Pak for O&M of project Construction monitoring by Montgomery Harza (MWH, NESPAK) & tech advising by Mott MacDonald (UK) Offshore project insurances, Investment Advisor – Marsh Registered as a CDM with the UNFCCC (first hydroproject in Pak to do so) BOOT (build own operate transfer) basis; concession period – 25 years. Low Tariff –Rs 6.84/kWh/adjustable –based on cost plus tariff mechanism Great source of revenue, attractive returns on investment based on IPP success here 5 Viable Regions in KPK for MHP Development District Chitral Relatively optimal Malakand Relatively mediocre Swat Relatively sub-par Hydropotentia l (Streams & Mountainous Terrain) Space-wise Untapped Potential Site Familiarity Population Density 600/km2 <200 km to Taru Jabba & Chaklala 235/km2 ~150 km to Taru Jabba 195/km2 >200 km from Taru Jabba and Chaklala 450/km2 ~150 km to Taru Jabba 270/km2 <200 km to Taru Jabba & Chaklala 275/km2 ~200 km to Taru Jabba 25/km2 >200 km to Taru Jabba and Chaklala 272/km2 ~150 km to Chaklala 450/km2 ~200 km Taru Jabba & ~150 km to Chaklala 465/km2 ~150 km to Taru Jabba & ~70 km to Chaklala 895/km2 ~60 km to Taru Jabba & ~150 km to Chaklala Upper Dir Lower Dir Upper Dir Buner Swat Shangla Lower Dir Chitral Shangla Malakand Buner Mansehra Ease of Legal Approval Mansehra Mardan Abbotabad Abbottabad Haripur (PEDO, NEPRA) Proximity to Shell Facilities (Depots) Haripur Mardan 6 15