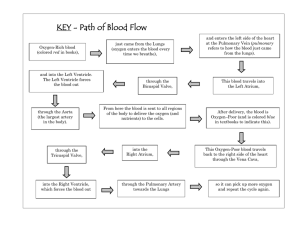
Three essential components of the circulatory system are: 1. Heart – a pump to push blood through the system 2. Blood vessels – a connecting series of tubes through which blood travels 3. Blood – a transport medium used to move materials throughout the system. The human heart is an organ that pumps blood throughout the body via the circulatory system, supplying oxygen and nutrients to the tissues and removing carbon dioxide and other wastes. The function of the heart is to maintain a constant circulation of blood around the body by its pumping action. The walls of the heart consist of cardiac muscle, which never tires. Heart muscles are myogenic Four (4) chambers Right Atrium Left Atrium Right Ventricle Left Ventricle Superior and Inferior vena cava > right atrium > tricuspid valve > right ventricle > pulmonary valve > pulmonary arteries > lungs > pulmonary veins > left atrium > bicuspid valve > left ventricle > aortic valve > aorta > body (except lungs). A group of special muscle cells that sends electrical signals to the heart from the brain to speed up or slow down. There are two (2) types of systole: 1. Atrial systole – Atria contracts, tricuspid and bicuspid valves open for blood to be expelled into the ventricles and pulmonary and aortic valve are closed to prevent backflow of blood. 2. Ventricular systole – Ventricles contract, pulmonary and aortic valves open for blood to be expelled into the arteries (aorta and pulmonary artery) and the bicuspid and tricuspid valves close to prevent backflow of blood. Diastole is a pause during which all parts of the heart relax and atria fill with blood. With each beat the heart moves blood through the body. Complete contraction and relaxation of the heart produces two-tune sound, lub-dub. The first tone, lub, heard is due to the closing of the bicuspid and tricuspid valve as the ventricles contract during systole. The second, dub, comes from the closing of the semi-lunar valves when the heart is relaxing during diastole. ___ ___ ___ ___ ___ ___ ___ ___ ___ ___ ___ ___ ___ ___ ___ ___ ___ The heart has its own blood supply, called coronary circulation, providing it with oxygen and removing dissolved metabolic waste substances. A heart attack can be caused by a accumulation of fatty substances, cholesterol, calcium and other substances that make up plaque. Plaque begins to build up in the inner linings of larger arteries of the body. However it takes a very long time for this condition to become dangerous. This process of plaque build up is called atherosclerosis. High blood pressure, cholesterol, diabetes or especially smoking can accelerate this process. A heart attack can also be caused by a severe spasm or tightening of the coronary artery, which can cut off blood flow to the heart. Obesity High blood levels of cholesterol Permanently raised blood pressure Excessive psychological and emotional distress. UNAVOIDABLE RISK FACTORS Increasing age Men are more at risk than women It tends to run in the family Severe pain in the chest, neck and arm Sweating Faintness and sickness Tiredness Shortness of breath Anxiety A fast heart beat Low blood pressure A sense of indigestion Coronary by-pass surgery: coronary artery damaged by atherosclerosis can be by-passed using parts of an artery or a vein taken from another part of the body. Heart transplant surgery: becomes necessary with severe heart damage or complete heart failure. Not very common because of: Shortage of donors High costs Risk of rejection of the heart by the patients immune system. Stroke condition where carotid arteries, arteries supplying the brain with blood, are blocked or rupture. They can be blocked by plaque or a blood clot Hypertension Smoking Obesity High Cholesterol Diabetes Cardiovascular disease It tends to run in families Men are at a higher risk Increasing age Not smoking Exercising regularly Proper diet Taking aspirin Usually surgery to open up the carotid arteries to remove plaque or blood clot. A stent maybe inserted to support the artery.