Active & Bulk Transport Worksheet: SBI 4U Biochemistry
advertisement
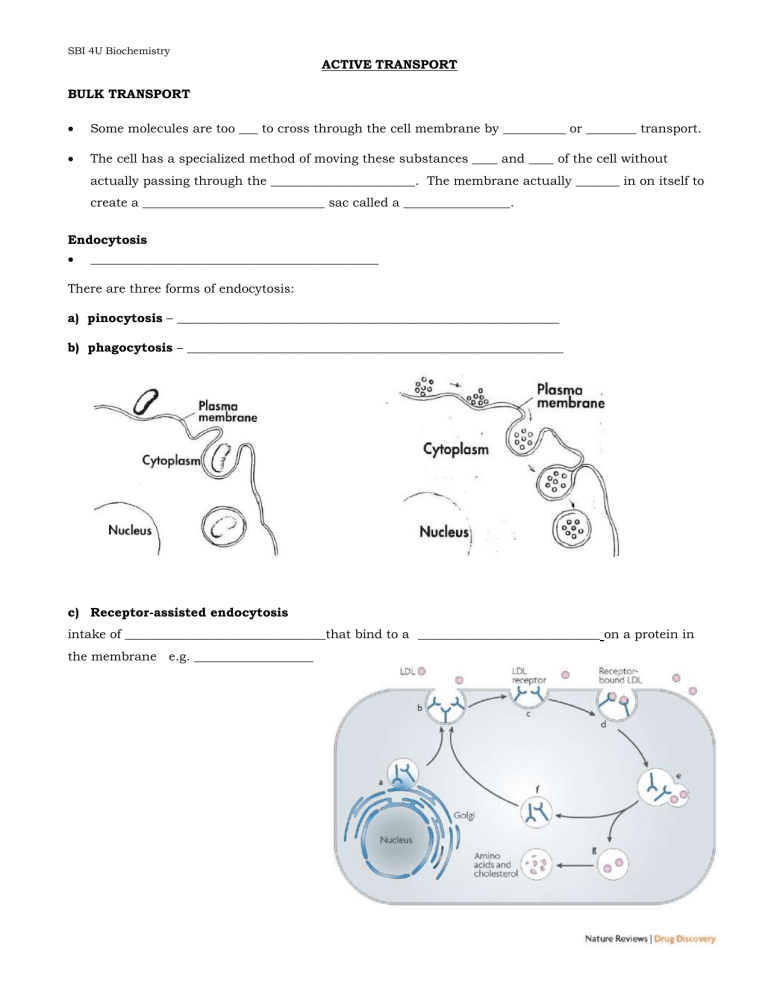
SBI 4U Biochemistry ACTIVE TRANSPORT BULK TRANSPORT Some molecules are too ___ to cross through the cell membrane by __________ or ________ transport. The cell has a specialized method of moving these substances ____ and ____ of the cell without actually passing through the _______________________. The membrane actually _______ in on itself to create a _____________________________ sac called a _________________. Endocytosis ______________________________________________ There are three forms of endocytosis: a) pinocytosis – _____________________________________________________________ b) phagocytosis – ____________________________________________________________ c) Receptor-assisted endocytosis intake of ________________________________that bind to a _____________________________ on a protein in the membrane e.g. ___________________ SBI 4U Biochemistry Exocytosis Bulk transport of material _______________________ the cell A ___________ formed inside the cell moves to the ___________________ and _________ (joins) with the _____________________, releasing its contents _________________ of the cell e.g. _______________________________________ Active Transport requires a membrane _______________ protein (pump) and _____________ in the form of ____ (adenosine triphosphate). How much energy is needed to move a substance into and out of the cell depends on how ________ the _______________________________________ is. eg. [Ca+] in one compartment can be as much as ______X greater than another compartment this is required for normal muscle function 1. Primary Active Transport ____________ of a cell’s energy requirements are for active transport All primary active transport pumps move positively charged ions such as ___, ___, ____ and ____ Ex. H+ (proton pump) moves H+ from cytosol to cell exterior pump temporarily binds to a phosphate group removed from ATP Ex. Ca2+ pump moves Ca2+ from cytosol to cell exterior and into vesicles of ER THE SODIUM - POTASSIUM PUMP Animal cells have a _____ [Na+] inside the cell and a __________[K+] inside the cell. These concentrations are maintained by pumping ____ Na+ out of the cell and ___K+ inside the cell. The pump is a highly specific membrane protein channel. Pumping action involves changes to the protein __________ and is very rapid (300 Na+ per second). Energy from ATP (adenosine triphosphate) drives the pump. SBI 4U Biochemistry 2. Secondary Active Transport _______________ and ____________ are accumulated by the cell ______________ a concentration gradient. Accomplished by coupling with _________ which pass simultaneously through a channel by facilitated diffusion. Special channel only allows ___________ back into the cell when a ______________ or an _________________ is also bound the channel's exterior surface. Occurs as a direct result of the activity of the ____________________ pump. Symport a _______________ moves through the membrane channel in the ___________ direction as the ___________________ Antiport the transported _____________moves in the direction that is _______________ to the gradient of the ____________________ion



