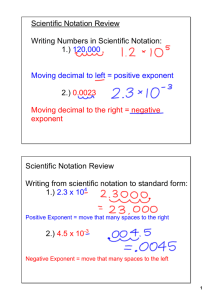
Analyzing Data: Units & Measurements Units • Le System Internationale d'Unites (SI measurement) is an internationally agreed upon system of measurements • Prior systems would vary, even if they used the same/similar naming • A base unit is a defined unit of measurement that is based upon some object or event in the physical world and is independent of all other units of measurement • A prefix is added to specify for larger or smaller measurements Units • Time – Second (s) • Based on the frequency of radiation given by a cesium-133 atom • Length – Meter (m) • The distance light travels in a vacuum in 1/299792458th of a second • Mass – kilogram (kg) or gram (g) • 1 kilogram is approximately 2.2 pounds (based on Earth's gravity) • Temperature – Kelvin (K) • • Absolute Zero (0K) is the point at which kinetic energy does not exist Other systems include Celsius (used by scientists in labs) and Fahrenheit Derived Units • Not all quantities or measurements can be measured with the SI base units – some require a combination or 2 or more bases units • Volume – cubic meter (m3) or liter (L) • 1L = 1 dm3 (1000 cm3 = 10cm x 10cm x 10cm) • Density – the amount of mass per unit of volume (g/cm3) • Density = mass/volume Analyzing Data: Scientific Notation & Dimensional Analysis Scientific Notation • A system in which extremely large or small numbers are expressed as a number between 1 and 10 (coefficient) multiplied by 10 raised to some power (the exponent) • • The exponent is determined by the direction and number of places a decimal is moved A move to the left gives a positive exponent; a move to the right gives a negative exponent Magic Ruler Kilok* Hectoh* Decada* Base Unit * Decid* Centic* Millim* 1000 100 10 1 0.1 0.01 0.001 x 103 x 102 x 101 x 100 x 10-1 x 10-2 x 10-3 Calculations with Scientific Notation • Addition and Subtraction • • • The exponents must be the same – rewrite values if needed Add or subtract the coefficients (normal calculation) Rewrite the answer & exponents if not in scientific notation Calculations with Scientific Notation • Multiplication and Division • Multiplication • • Multiply the coefficients; add the exponents Division • Divide the coefficients; subtract the exponents (divisor from dividend) Dimensional Analysis • A systematic approach to problem solving – allows us to convert units of measurement while still measuring the same object • • Equivalence Statement – showing equal measurements with different units of measurement Conversion Factor – a ratio made from an equivalence statement – for each problem, MUST be written so that one unit is cancelled and a new unit is introduced