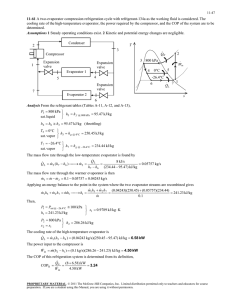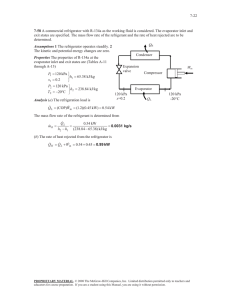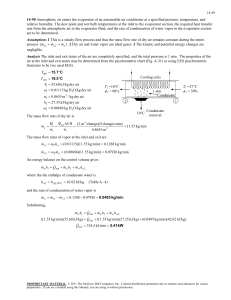
PRESENTED BY: DARSHAL VITHALANI SUTARIYA ZEEL RAMANI JAY ROKAD DARSHIT COLLEGE OF FOOD PROCESSING TECHNOLOGY AND BIO ENERGY, ANAND AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY, ANAND-388110. SUBJECT: REFRIGERATION AND AIR CONDITION FPT B.TECH. (4TH SEM.) EVAPORATORS •AT LOW PRESSURE SIDE OF REFRIGERATION SYSTEM •REFRIGERENT CHANGES FROM LIQUID PHASE TO VAPOUR •HEAT ABSOPTION CAPACITY OF AN EVAPORATOR THE AMOUNT OF HEAT ABSORBED BY IT OVER A GIVEN PERIOD OF TIME. HEAT TRANSFER CAPACITY OF AN EVAPORATOR: Q = UA(T2 - T1) ….. W or J/s WHERE; U = OVERALL HEAT TRANSFER COIFICIENT A = AREA OF EVAPORATOR SURFACE T2 = TEMPERATURE OF MEDIUM TO BR COOLED T1 = SATURATION TEMPERATURE OF REFRIGERENT AT EVAPORATOR PRESSURE FACTORS AFFECTING THE HEAT TRANSFER CAPACITY OF AN EVAPORATOR 1. MATERIAL 2. TEMPERATURE DIFFERENCE 3. VELOCITY OF REFRIGERENT 4. THICKNESS OF THE EVAPORATOR COIL WALL 5. CONTACT OF SURFACE AREA TYPES OF EVAPORATORS According to type of construction 1. Bare tube coil evaporator 2. Finned tube evaporator 3. Plate evaporator 4. Shell and tube evaporator 5. Shell and coil evaporator 6. Tube in tube evaporator According to the manner in which liquid refrigerant is fed 1. Flooded evaporator 2. Dry expansion evaporator According to the mode of heat transfer 1. Natural convection evaporator 2. Forced convection evaporator According to operating condition 1. Frosting evaporator 2. Non-frosting evaporator 3. Defrosting evaporator Bare tube coil evaporator •Prime surface evaporator •Easy to clean and defrost Finned tube evaporator •Over the bare tube metal fins are fastened •s/f contact area is less •Shape, size, spacing can be adapted for better rate of heat transfer •Limited applications •Extended surface evaporators Plate evaporator •The bare coils are either welded on the plate or between the two plates which are welded together •Used in household refrigerators, beverage cooler, ice cream cabinets Shell and tube evaporator •Contraction is same as shell and tube type of condenser •Available in flooded as well as dry expansion type •Baffle plates are provided for good turbulence of liquid •Capacity 2TR to 250TR Shell and coil evaporator Tube in tube evaporator •Generally dry expansion evaporators for chilling water •Used for small capacity 2TR to 10TR •Restricted to operate above 5 degree calicoes to prevent freezing problems •Double tube evaporator •Refrigerant can flow in outer pipe and liquid to be cooled can flow in inner pipe •The flow of refrigerant can be parallel or counter Natural convection evaporators •Low velocity and min. hydration is require •Velocity of air depends upon temp. difference •Circulation of air around coil depends upon its size shape and location •The coil should occupy 2/3rd of width of the path & 3/4th the length of the box Forced convection evaporators •Air is forced over refrigerant coils •Fins are provided to increase heat transfer rate •More efficient than natural convection evaporators •Require less cooling surface and high evaporator pressure can be used which save power input to the compressor Frosting evaporators •Operates below 0°C •The frost forms on the evaporator comes from the moisture of the air •Cooling efficiency is decreases until the ice and frost is removed Non-frosting evaporators •Operates above 0°C therefore frost does not forms on evaporators •Temp. close to cooling 0.6°C to 1°C •RH from 75-80 % in the cabinet •This keeps the food fresh & stops shrinking in weight DEFROSTING EVAPORATORS •Frost creates on the coils when the compressor is running & melts after the compressor shuts off •Temp. of about -7°C to -6°C •It also keeps high RH of about 90% to 95% APPLICATIONS: EVAPORATORS ARE USED IN WIDE RANGE OF PROCESS INDUSTRIES, PAPER AND PULP INDUSTRIES, WINERY, BEVERGARES, FOOD PRESERVATION, ICE PLANTS, CHEMICAL, POLYMERS AND RESINS, INORGANIC SALTS, ACIDES AND VERITY OF OTHER MATERIALS.