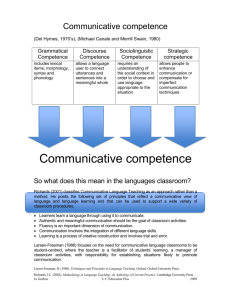
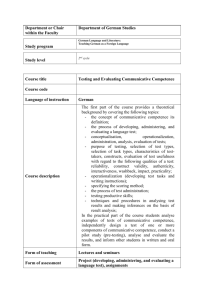
Chapter 1 THE PROBLEM AND ITS SCOPE INTRODUCTION Rationale of the Study Mastery and Proficiency of the English Language has become a necessity in all aspects of Filipino life. Being able to effectively use the language especially in oral correspondence gives an edge to everyone, in education, employment and even marks as a social status. Fluency in English will continue to be a most useful skill set of every educated Filipino. It is already part of our culture and global identity as a bilingual nation. The Philippine educational system has been upgraded because of the implementation of the K to 12. For the English program, oral communication in context aim for the optimum development of students oral speaking skills. However, recent results of 2015 International English Language Testing System (IELTS) shows the Philippines have dropped its rank from first to just second in terms of Academic and General Training Efficiency in the English Language. Clearly, this is a solid evidence of the decadence and attrition of the use of the language. English standards in the Philippines are slipping, according to the results of a major international testing system, IDP. On an SWS survey that was commissioned by Promoting English Proficiency (PEP) in March 2006. The British Cambridge International is an Institution with globally accepted standards in English Poficiency. According to the recent results of the Midterm exams taken by the Grade 11 students of the Nissi Acedemy International who is an accredited partner of BCI to offer the program, only 20% of the students were able to pass in the Customer Service Midterm Examinations which focuses on the ability of the students to use customer service specific language and use it according to the suggested meaning and functions in the module. This is an alarming result and a clear evidence that intervention should be done in order to prevent further decadence of the oral competence of the students. With the demand of being able to speak fluently in the English Language as a basic requirement for global market, many graduates are not able to get a decent job because they fail to pass preliminary interviews because of poor speaking skills. If this problem further resonates, not only will the Filipinos have a hard time adapting into environments where English speaking is frequently involved, they will also lose the recognition of the world as the best speakers of English in Southeast Asia This study will be conducted to identify the difficulties in oral communication skills faced by every learner in a language classroom and address it with the use of Situational Based Teaching. Situational Based Teaching aims to promote deep learning and awareness by involving participants in realistic critical incidents where they are forced to consider a wide range of factors, make decisions and reflect on the outcomes and what they have learned from this”, (CLPD, University of Adelaide). This method promotes intellectual and practical ways to improve oral communication in context. Theoretical Background of the Study This study assumes that Situational Based Teaching facilitates the students’ Oral Communication in Context of the Grade 11 students of the Nissi Accademy International. This study is anchored on Canale and Swain’s Communicative Competence Theory and Jerome Bruner’s Constructivist Theory. Communicative competence has always been the goal of every language classroom wherein instructions are geared toward the components on organizational, pragmatic, systematic and psychomotor. SBT stresses that authentic language and real-world tasks enable students to see the relevance of classroom activity to their long term communicative goals by simply introducing natural texts rather than artificial ones where students will more readily dive in to the activity and that these communicative goals are best attained if enough attention is given to language use and not just usage, to fluency and not just accuracy, to realistic language and contexts and to how these students’ apply the learning in real life situations. The Theory of Communicative Competence. Assumptions in the Theory of Communicative Competence are that language is social behavior, which concerns conveyance of meaning like the grammar of a language is a means of organizing meaning. In this theory Hymes assumes that second language learners need to know not only the linguistic knowledge but also the culturally acceptable ways of interacting with others in different situations and This study assumes that Situational Based Teaching may enhance the Oral Communication in Context of the Grade 11 students of Nissi Academy International. Theory of Communicative Communicative Competence Competence by Dell Hymes Model of Canale and Swain GRADE 11 PRE-TEST POST- TEST STUDENTS ASSESS FOR ORAL COMPETENCE IN ASSESS FOR ORAL INTERVENTION OF ACCURACY, CONTENT FLUENCY COMPETENCE IN ACCURACY, AND SITUATIONAL BASED TEACHING SIGNIFICANT DIFFERENCE ORAL ENHANCEMENT MODULE Figure 1. Theoretical Background of the Study CONTENT FLUENCY AND relationships. His theory of communicative competence consists of the interaction of grammatical, psycholinguistic, sociolinguistic, and probabilistic language components. Hymes’ notion of communicative competence was further defined and developed by other practitioners such as Canale and Swain (as cited in Radzi et al 5) in their dissertation Adopting Communicative Language Teaching (CLT) Approach to Enhance Oral Competencies Among Students: Teachers’ Attitudes and Belief who offered the four dimensions of communicative competence. According the them, the learner must possess grammatical competence, discourse competence, sociolinguistic competence and strategic competence to gain mastery in the second language they are acquiring. Which means, grammar is only one face of learning the American English Language, the rest of the three faces requires more than just lecture to facilitate learning but application through interaction. SBT believes that authentic experiences would cater most if not all of the four dimensions perceived by Canale and Swain. In a communicative approach, language teaching makes use of real-life situations, i.e. situations that students are likely to encounter in real life, that necessitate communication. Thus, students are provided with ample opportunities to events in using the language. be involved in communicative Hence, the activities are geared towards promoting selflearning, interaction in authentic situations, peer teaching, negotiation of meaning, completing tasks through language, etc. where the lessons focus on some operation which the student would want to perform in the target language. As asserted by Lapp (11), communicative competence embraces the skill of formulating statements correctly and be able to deliver it in a correct manner. If the students are able to perform this function, the communicative communication in context is achieved. To be fluent in English orally, learners should have complete command of the language. As expressed by Smiley (21) command of the language in relation to communicative competence is when the student is able to participate and interact using the language to create fluidity in the interaction. SBT requires the teacher to stimulate oral communication in the context of authentic scenarios to aid students make use of the language. Participation and interaction is a lot easier if the students are driven by interest which is natural when a situation is easily relatable and comfortable. On the other hand Tuan and Mai (8) stressed out there are instances that when students are tasked to work in groups, not all of them are eager to contribute their opinions in English. Some of them participate actively but others prefer to speak minimally or not at all. This is one of the factors that affect the English speaking performance of the students. Generally speaking, language is perceived by Hymes as the the ability to communicate in a personally effective and socially appropriate manner.To be able to give the right and appropriate responses to usual conversations which would also help the child socially active and effective. The current practice in local education shows evidences of dictation and modeling by the teacher. Teachers dictate grammar rules and the students mimic. However, on actual real life situations students fail to use the language effectively without the teacher modeling. However, SBT proposes that the ultimate test for oral proficiency is through application and therefore in spoken interactions. Learning a foreign language is supported by various sociocultural contexts, government policies, and historical language practices. Therefore, there is no single best method to implement foreign language teaching to young learners. However, teachers should try to find effective language teaching for young learners by having clear understanding of the following factors and the relation amongst them. This is why SBT could encourages the learner to be comfortable with the language by making them interact through teacher guided activities. Mastery in Oral Communication in Context and being able to effectively use the language appropriately as the situation arises is the goal of this study. Based on the explanation from Clark and Clark (223) speaking is fundamentally an instrumental act. Speakers talk in order to have some effects on their listeners. They assert things to change their state knowledge. They ask them questions to get them to provide information. They request things to get them to do things for them. It refers to oral proficiency and is very similar to the notion of communicative competence. Proficiency itself refers to a high degree of competence trough training (2). How then can a teacher assess mastery in oral communication in context? Nem Singh (19) emphasizes that good English is very clear and concise. It is conveyed in the most forceful way possible in terms of accuracy, fluency and content. SBT believes that through interaction and immersion of the language by exposing the learners to real life scenarios and questions, this could be achieved. A study entitled The Proficiency in English of the Secondary Students of Bradford School by Tabaque (7) asserts that Communicative Approach purposely engages the learners in authentic situations with focus on the social dimension of language. In the study, exercises in simulation of real life communication are utilized. Her study proposes a similar concern to this study, that is to find out the extend of oral communication in context of the students through authentic real life communication. However, they differ because this study focuses on contemporary methods of situational based exposure while her study is conducted without any coexistent methods. According to Kim Nuri in his dissertation which assesses the Effectivity of Using CLT in the Oral Proficiency in Korean Secondary School Students in 2015 Korean English teachers had negative attitudes towards adopting of CLT as a new teaching method. Korean teachers of English deal with the dilemma between reality and the ideal goal. Teachers’ positive beliefs about the communicative approach often do not coincide with their practices in the classroom. While most teachers accept the theory of the communicative approach, many of them would not practise it in their classes because they think it is not applicable to their contexts. Korean students still are reluctant to participate in English lessons which are based on CLT due to their own lack of proficiency. According to Kim (67)based on her findings in teachers’ interviews, teachers were not exposed to trainings to prepare them with things that they need to do in their classrooms.Therefore, the ‘communicative-based’ method I was taught in Korea, has, at times inflicted self-doubt and lack of confidence. However, this negativity has instilled in this researcher a determination to adopt communicative-based teaching methods for South Korean EFL speakers. This research is similar in ways that it exposes the current real status of Communicative Language Teaching, an approach where SBT belongs. SBT is something new to teachers and are usually time consuming since the students are exposed to situation based activities to elicit communication. However, this study highlights on the means to integrate SBT into the curriculum and suggest a learning module to help the teachers promote communication to enhance the oral proficiency of students and speak confidently as if the language is their own. Although there are a lot of challenges, this study proposes to address these issues by providing the necessary activities for enhancement and assure proficiency in terms of content, pronunciation and fluency through collaborative and integrated pronunciation strategies. Constructivism, and its close relative, discovery theory, is an offshoot of cognitive theory that that proposes learning will happen as a man effectively forms data to build answers for issues based on what they have experienced and learnings (Salandanan 19). According to its primary proponent, Jerome Bruner, to promote a student centered classroom is to promote skills that is greatly encouraged through active participation and self involvement. Students are encouraged to be exposed to various situations and make past experiences and learnings be related and incorporated in learning the language. In this way, the Theory of Constructivism is used in a communicative approach. For decades, the proponent of the Cognitive Theory have initiated many explanations for how children learn from a very young age. The understanding of this learning process could then possibly be applied to learning at any age. The “natural” process by which a child learns, without any training at all, ought to be applicable to a trained mind as well. The basics of cognitive theory are considered to have begun with John Dewey (206). In the mid- and latter-twentieth century, Jean Piaget and Jerome Bruner affirmed that discovery leads one to become a constructionist. Processing stimuli from a problem that has been presented and working to a solution fundamentally lead to learning in the problem solver. Learning occurs as the solution is discovered. This learning requires that certain facts must already be known, but the discovery leads to new insights concerning the relationship between various facts that are known. Though the ideas of constructivist theories, teachers of the English Language has innovated learning modeled by providing relevant scenarios where students could make out their own meanings as explained by Duke (325). The teacher acts as a stimulant by creating a scenario or situation to excite the interest of the students and allow them to seek and demonstrate knowledge These scenarios may be in the form of circumstances for the students to complete or provide solutions of, information gaps for students to fill in, simulation activities where their roles are clear for them to come up with relevant utterances. This premise is supported by the Self Regulated Language Learning where in according to Oxford (12) language learners take active roles in their learning and assist them to becoming autonomous learners through pusposive and outcomes oriented attempts to manage and control the efforts for the learner to use the English Language. On the other hand, Lightbown and Spada (215), also mention the function and purposes that a language serves. SBT is based on the premise that successful language learning involves not only a knowledge of the structure and forms of a language, but also the functions and purposes that a language serves in different communicative settings. In SBT, the role of theteacher is different to other teaching methods. According to McGrath (189),the role of teachers in SBT, is to facilitate,to communicate and to encourage learners to interact on purpose by speaking with their peers. In short, it is more likely that the audio-lingual and the grammar translation approach rely mainly on a teacher-lead instructional approach, while SBT is focused on task-based learning of English. In addition,the CLT approach is essentially teaching English with the intention of communication, which is to provide students with the ability to use the language instead of simply knowing the grammatical rules, vocabulary and structure. In turn, communicative language learning, with the use of relatable situations and activities should be delivered by teacher facilitation rather than teacher led instruction and by definition, on how the language works in discourse rather than the focus on language practice. Hence, the above features indicate that SBT can support the learners to engage in their learning so as to communicate competently. Also it indicates that SBT is the teaching method which takes the learners’ position into account. Apparently, it is considered that the learners can be encouraged to use English in real life by applying CLT. Meanings are generated though the instances where students interact with each other. These interactions are triggered by the teacher who creates a scenarion which may have happened in the students life or are most likely to happen. Block (88) as quoted by Tecson (5) suggests that teachers formulate specific situiations in which students naturally speak because the activties are relatable and interactive. Van der Heijden ( 117) claims that learners have been observed to be interested and get involved with scenario-based learning activities instinctively because it is in the nature of a person to plan out scenarios in order to find sense in what is happening in the world and how people decides to act and deal with these scenarios. Thus, this is a good indication that SBT will naturally bring out the natural interest and skill of every learner. It is with the constant exposure to authentic situations that mimics rel life that kindles students empathy and be more motivated to learning. This will not only develop the students decision making skills but will facilitate problem solving strategies. Teachers would need to be very active support coaches to help students succeed at making the students orally share these thoughts and have them successfully exchange it with one another. But the whole lerning process revolves around the students, the teachers acts as stimulators, simulators and supporters. This is a methods that supports the assertions of Dell (200) which clearly stipulates that teachers are not the only maven in the learning scenario. The teacher guides the students by prepare the lesson in a manner that she equips herself with skillful questioning and appropriate cognition processing. Because through this, students will be empowered and the communicative scenario will centered on what they can do and are willing to do. To sum up,the Theory of Communicative Competence and the Constuctivist Theory in this research would infer that the advancement of the students’ English Oral Proficiency may begin having the students’ as rationally dynamic members in the classroom collaboration, of giving them a chance to associate in certifiable circumstances through basic inquiries, and by method for using their earlier information with a specific end goal to learn and talk the English dialect all the more capably and adequately. Improv, Simulation Role Play, Impromptu and etc will be used to develop and enrich speaking skills as tasks will be assigned to students. THE PROBLEM Statement of the Problem This research evaluated the status of Situational Based Teaching in the teaching of Oral Communication in Context for Grade 11 Students at Nissi Academy International, Lapu Lapu City during School Year 2017-2018 as basis for proposed Spoken English Exercises. Specifically, this study answers the following sub-problems: 1. What is the entry performance of the students in the following oral communication competencies? 1.1 Accuracy 1.2 Fluency, and 1.3 Content 2. After the use of SBT, what is the post-test performance of the students in terms of the above-mentioned competencies? 3. Is there a significant mean difference in the pre-post-test performances? 4. Based on the findings, what Spoken English Exercises can be proposed? Null Hypothesis The following hypothesis will be tested using the 0.05 level of significance in order to answer the problem of this study. H0: There is no significant difference between the result of the pre test and the post test scores of the students based on the aforementioned competencies. Significance of the Study The findings of this study are beneficial in one way or another to the following entities: Students. The results of this research may be a great help toward the students to be engages in meaningful interactive activities which will further enhance their Oral Communication in Context skills. This may make them view learning as close to natural acquisition of speaking skill and not as an academic requirement. Language Teachers. The result of this study may help them appraise existing programs in terms of approach, methods and strategies. This may also assist as a guide for teachers in the exertion of incorporating fitting methodologies in the classroom keeping in mind the end goal to successfully lead the studetns to build up their English proficiency. School Administrators.The top management may use the results as baseline to improve programs relative to teaching English and furnished with a module particularly centered around students which is required for their basic leadership, program definition, and arrangement creation; similarly, they might be given the thought to embrace SBT and later coordinate it the establishment's educational programs. Administrators. The outcome of this research paper may provide school administratos the basis to promote productive communication platforms for their students. This may set the standards for them to implement on their teaches by encouraging them to attend enhancement seminars and the like on Situational Based Teaching to be more effective in their teaching. Future Researchers. The results can be basis for further inquiry on the factors that affects and improves students’ Oral Communication in Context. The qualified data and findings generated from this study may be of great use to those who has similar research endeavors. This study shall also give basis and opportunities for research development like using the method in other English Language Macro skills like reading and writing or whatever it is required to enhance oral communication in competence.. RESEARCH METHODOLOGY This part of the research includes design, flow of the study, research locale, subjets, instruments, data gathering procedure, statistical treatment of data and scoring procedure. These are discussed as part of the process in conducting this research. Design This research will use quantitative research (quasi experimental) as the research design. Quantitative research is a kind of research in which the data used to tend to use statistic measurement in deciding the conclusion (Hatch and Farhady, 1982:22). It will be conducted using one group pretest posttest design. The result will be taken from the comparison of the two tests (pre-test and post-test). According to (Setiyadi, 2006), the design is described as follows: T1 T1 : Pre-test X X : treatment T2 T2 : Post-test A pretest is an activity before treatment given to diagnose the entry level of the students on the desired competencies under study. After that, the researcher will give three treatments to the students using Improv, Simulation Role Play, Impromptu and other SBT Activties . Finally, a posttest aims to see the result of the research after the treatment conducted. Flow of the study Figure 2 presents how the study will be conducted. The input of this study will include the results of the subjects’ pre-test and post test to determine their initial Oral Coomunication in Context Level. Likewise, this will involve the classroom intervention and integration of the teacher toward the use of Situational Based Teaching. The input establishes the significant difference, data analysis and interpretation on the Oral Communication in Context skills of the Grade 11 students. The output of this study will be a Spoken English Packet. Research Locale This study will be conducted at Nissi Academy International. This institution is located at Panas, Suba, Bas-bas,, Lapu-Lapu City, 6015 Cebu, Philippines (see figure 3). It is an intstitution that values promotion of awareness and excellence through education, business and technology. With the school President's visionary leadership to help and serve the need of community in the character formation and academic excellence of our children that will contribute to the development of the society, Nissi Academy International aims to a world-class institution that will produce future leaders of integrity and excellence. With a population of 800 students, the school offers the INPUT Students’ PROCESS Oral Teacher Communication intervention Proficiency level using SBT in terms of: OUTPUT Spoken English EXPERIMENTAL Exercises Accuracy Fluency Content DATA GATHERING STATISTICAL TREATMENT (pre-post- DATA test scores) AND ANALYSIS INTERPRETATION (pre- post-test Scores) Figure 2. Flow of the Study Figure 3. Research Locale following programs: Pre-school, Primary, High School and Senior High school, British Cambridge International Accredited Site. Subjects The subjects of the study will be the twenty four (24) Grade 11 students (11 females and 13 males), an intact class of the Nissi Academy International. They will be chosen using the random sampling method. They were taught using SBT to meet its purpose of evaluating the status of the method. Furthermore, the students have regular class attendance in blocked schedule which ensures equal chance for every student to be a part of the research. The class will be conducted on their classroom three (3) times a week starting February as approved by the School heads (see appendix a) Instrument To facilitate the oral communication in context competence of the subjects, this study adapts the Preliminary English Test (PET) from Cambrige English for Speakers of Other Language (ESOL) test. The instruments are described as follows: a. Pre-Test (Speaking Test) Pretest was conducted to find out whether the students have relatively the same ability in speaking before treatment. The pretest that were given were speaking tests using a three part oral exam. Part 1. Interview (2-3 mins) is an interaction type of test wherein students were given a set of usual job interview questions and they are required to answer them in the most appropriate way possible. The students were asked to pick up from a number which corresponds to a set of job interview questions. They are given 2 minutes to prepare and 3 minutes to present in front of the class ( see appendix for the set of questions) The task is done by pairs. Round 1 makes student 1 as the interviewer and student 2 as the interviewee and vice versa on Round 2. The task focuses on giving factual and personal answers responding to job interview questions which would require the students to speak about themselves and relate past experiences and future plans. Part 2. Story Completion (4mins) is a free speaking activity where the whole class sits in a circle. For this activity, a teacher starts to tell a story, but after a few sentences he or she stops narrating. Then, each student starts to narrate from the point where the previous one stopped. Each student is supposed to add from four to ten sentences. Students can add new characters, events, descriptions and so on. Part 3. Game of Cards (Impromptu) (3mins) is a speaking activity that is content based and time bounded. The students aims to arrive at a conclusion, share ideas about an event, or find solutions about a topic, situation or a set of choices. The students will pick from the set of cards, each card will correspond a specific topic, situation or a set of choices. They were then asked to organize and share ideas to the class immediately. b. Post-Test (Speaking Test) Post-test is given to the students who had been included in the pretest. It was conducted in the end of the research. It was done after giving treatments and exercises to the experimental group. The result of the post-test will be used to compare the data of the pre-test and making conclusion weather SBT can increase students’ speaking ability. The procedure of post-test is in the form of an Impromptu speaking using relevant questions about the activties that the students have undergone. Data-gathering Procedure The gathering of data is done according to the following scheme; preliminary preparation, administration and collection of research instruments, scoring and statistical treatment of data. Collection and evaluation of data are done on February and March 2018 using the following procedures: Before the research is conducted to the subjects, verbal and written approval is sought from the administrators to allow the collection of data needed. A letter of request is sent to the School Directress. Once consent is given, administration and collection of data follows. The pre-test (Interview, Story Completion and Game of Cards) is administered to the class. For a two week schedule, the class is exposed to various SBT activities and a post test is conducted. The post test performance is recorded via video and transcribed for proper evaluation based on the rubric provided per component (see Appendix C). After the collection of data, tallying, tabulation of results, analysis of data, interpretation of results is conducted out of the interpretation, conclusions is drawn and serves as basis in formulating a Spoken English Exercises for the senior high school students. Treatment of Data This presents the study with the conceptualization of the design on data gathering. The qualitative data are gathered from the interview questions in the questionnaires. The responses were used in the analysis of the data. The study also uses quantitative tools to assist the analysis and interpretation of the gathered data: The t-test is used to determine the significant mean difference between the pre-post-test results. Weighted Mean is used in calculating the data gathered in the writing proficiency level of the respondents. Scoring Procedure In order to score the level of Oral Communication in Context performance of the subjects, a modified rubric adapted from the Hellenic American University Speaking Section Scoring Rubric: Descriptors of Salient Features. The speaking performance, as comprised of the different mechanics in speaking, both objective and performance will be measured according to each of its criteria. Each mechanic will be evaluated separately. In order to arrive at a definite interpretation of each scale, the researcher assigned the following hypothetical mean range to the scale: Range of Scores 9-10 Verbal Rating Outstanding Verbal Description The subject has mastery in Oral Communication 7-8 Very Good The subject has above average performance in Oral Communication 5-6 Satisfactory The subject has average performance in Oral Communication 3-4 Fair The subject has below average performance in Oral Communication 1-2 Poor The subject has poor performance in Oral Communication DEFINITION OF TERMS Terms used are defined conceptually and operationally in order to facilitate better understanding on the ideas embedded in this study. Competency is the ability to do something successfully or efficiently. In this study the term competency refers to the list of knowledge, skills and attitudes expected from the students to show learning. Oral Communication in Context means the ability of the respondents to speak the English language effectively according to the competencies required by the Department of Education. Accuracy pertains to the students ability to speak with mastery in gammar, syntax and vocabulary. Fluency pertains to the students ability to speak focusing on length of utterances, hesitations and flow of speech. Content pertains to the students ability to speak focusing on coherence, relevance and organization with consistent focus on the prompt. Situational Based Teaching aims to facilitate the development of this communicative competence. A language is learned best when the learners are engaged in real communication. The SBT proposes that students should talk to one another and share one another’s thought and feelings and also advocates a non- threatening collaborative and group atmosphere. Spoken English Exercises refers to an instructional material as an intervention to enhance students’ low performance in oral communication in context. These activities are concentrated on oral communication in context which includes instructions and suggestions using situation based teaching methods to facilitate learning. With the intervention of these activities. The students are given a whole new opportunity to acquire oral competence suggested from the K to 12 curriculum. These activities are heared towards providing authentic situations for students to easily relate to lessons, interact and have fun.