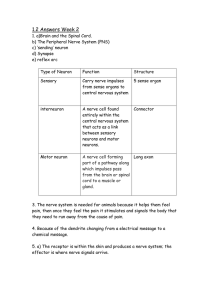
NERVOUS SYSTEM Table 9 P R E P A R E D B Y : P A D I L L O - O R E A - C A M P O S A N O B O R R O M E O NERVOUS SYSTEM Nervous system is a complex collection of nerves and specialized cells known as neurons that transmit signals between different parts of the body. TYPES OF NEURON NEURONS Neurons also called neurones or nerve cells are the fundamental units of the brain and nervous system, the cells responsible for receiving sensory input from the external world, for sending motor commands to our muscles, and for transforming and relaying the electrical signals at every step in between. Sensory Neurons Activated by sensory input and carry messages from the outside environment. Carry impulses from the sensory receptors, to the spinal cord and brain. Motor Neurons These neurons take impulses from the spinal chord to an effector. There are in fact two types of motor neurons: those that travel from spinal cord to muscle are called lower motor neurons, whereas those that travel between the brain and spinal cord are called upper motor neurons. Relay Neurons Relay neurons are found in the brain and spinal cord and allow sensory and motor neurons to communicate. It carry impulses through the spinal chord and up to the brain and from the brain back along the spinal chord. REFLEX ARC The neural pathway that controls the reflexes occurs through the reflex arc. It acts on an impulse even before it reaches the brain. There are some stimuli that require an automatic, instantaneous response without the need of conscious thought. It is an immediate response to a stimulus by the nervous system. R E F L E X A R C HOW IT WORKS: The receptor here is the sense organ that senses danger. The sensory neurons pick up signals from the sensory organ and send them through other neurons which are interconnected. It is then received by the relay neuron which is present in the spinal cord. Immediately, the spinal cord sends back signals to the muscle through the motor neuron. The muscles attached to the sense organ move the organ away from danger. In reflex actions, the signals do not travel up to the brain. R E F L E X A R C BLOCK DIAGRAM OF REFLEX ARC SYNAPSES Synapses is the connection between two neurons and it is where neurons communicate with one another. A small gap at the end of a neuron that allows a signal to pass from one neuron to the next. SYNAPSES Synapses are found where nerve cells connect with other nerve cells. Synapses are key to the brain's function, especially when it comes to memory. SYNAPSES WHAT SYNAPSES DO? 1. When a nerve signal reaches the end of the neuron, it cannot simply continue to the next cell. Instead, it must trigger the release of neurotransmitters which can then carry the impulse across the synapse to the next neuron. 2. Once a nerve impulse has triggered the release of neurotransmitters, these chemical messengers cross the tiny synaptic gap and are taken up by receptors on the surface of the next cell. 3. These receptors act much like a lock, while the neurotransmitters function much like keys. 4. Neurotransmitters may excite the neuron they bind to or inhibit it. Think of the nerve signal like the electrical current, and the neurons like wires. Synapses would be the outlets or junction boxes that connect the current to a lamp (or other electrical appliance of your choosing), allowing the lamp to light. THANK YOU FOR LISTENING!