Diffusion Lab Report: Chemistry Experiment
advertisement

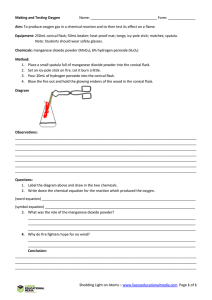
CHEMISTRY LAB REPORT (Name) ____________________________ (Date) _______________ Title: Diffusion Purpose/Problem: To demonstrate the process of diffusion Materials/Apparatus: Water, Conical Flask, Potassium permanganate crystals, Glass tube Procedure: 1. Prepare a conical flask. 2. Fill half of it with water. 3. Add a few crystals of KMnO4 (Potassium permanganate) to the bottom of the flask using the glass tube. 4. Observe what happens to the crystals. Also observe the change in the colour of water in the flask. 5. Leave the flask undisturbed for 10 minutes. Observation: 1. The particles of KMnO4 crystals start dissolving in water. 2. Particles move away from their high concentration region in the flask. 3. Particles of KMnO4 crystals spread throughout the water. 4. Water in the flask turns from colourless to pink, and then to violet. Conclusion: 1. Change in colour of the water shows the process of diffusion. 2. Uniform pink colour shows the uniform distribution of particles of KMnO4 crystals throughout the water. Precaution: Handle the conical flask properly. Do not disturb the flask after addition of KMnO4 crystals in the water. CHEMISTRY LAB REPORT Experiment A (Name) ____________________________ (Date) _______________ Title: Diffusion Purpose/Problem: To demonstrate the process of diffusion Materials/Apparatus: Water, Conical Flask, Potassium permanganate crystals Procedure: 1. Prepare a _____________________________ 2. Fill __________________________ with water. 3. _____________________ of KMnO4 (Potassium permanganate) to ___________________ using the glass tube. 4. Observe what happens to the crystals. Also observe _________________________of water in the flask. 5. ____________________ the flask undisturbed for 10 minutes. Observation: 1. The particles of KMnO4 crystals ________________________________ 2. Particles move away from their __________________________________in the flask. 3. Particles of KMnO4 crystals __________________________________________ 4. Water in the flask turns from ________________________________________ Conclusion: 1. Change in colour of the water shows __________________________ 2. Uniform pink colour shows the _____________________________of particles of KMnO4 crystals throughout the water. Precaution: Handle the conical flask properly. Do not disturb the flask after addition of KMnO4 crystals in the water. Experiment B Problem: How is diffusion affected by hot and cold temperature? Materials: Conical Flask, Potassium permanganate crystals, __________________________________ Procedure: 1. Fill one conical flask with hot water. Fill the second conical flask with cold water. 2. Add a few crystals of KMnO4 (Potassium permanganate) to the bottom of each flask using the glass tube. 3. Leave the flask undisturbed for 10 minutes. 4. Watch and wait for color to disperse entirely. Observations & Results: The crystals of potassium permanganate in the hot water dispersed much more quickly than in cooled water. Interpretation: This is because particles vibrate faster and harder when they’re warmer—the hot water molecules struck the crystal particles harder and more frequently, scattering them until the conical flask ended up containing a homogeneous solution. Conclusions: Temperature affected the rate of diffusion. Experiment C Title: Diffusion Purpose/Problem: To demonstrate the process of diffusion Materials/Apparatus: petri dish, forceps, white piece of paper, lead nitrate crystal, potassium iodide crystal, distilled water Procedure: 1. Prepare a conical flask. a. Place a Petri dish on a white tile or piece of white paper. Fill it nearly to the top with distilled water. b. Using forceps, place a crystal of lead nitrate at one side of the petri dish and a crystal of potassium iodide at the other. c. Observe as the crystals begin to dissolve and a new compound is formed between them. The lead nitrate and potassium iodide each dissolve and begin to diffuse through the water. When the lead ions and iodide ions meet they react to form solid yellow lead iodide which precipitates out of solution. lead nitrate + potassium iodide lead iodide + potassium nitrate Pb (aq) + 2I- (aq) PbI2 (s) The precipitate does not form exactly between the two crystals. This is because the lead ion is heavier and diffuses more slowly through the liquid than the iodide ion. Conclusion: 1. Diffusion happens when the crystals of lead nitrate and potassium iodide dissolve and diffuse towards each other they form clouds of yellow lead iodide. Precaution: Handle the conical flask properly. Do not disturb the flask after addition of KMnO4 crystals in the water.