A Physics & Chemistry exam
advertisement

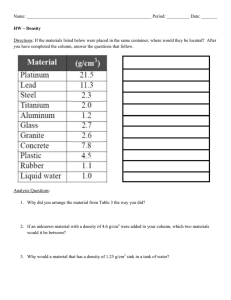
Subject: Physics and Chemistry Grade: 2nd ESO Date: / /2016 Term: 1st term (midterm) Students name: Group: Grade: Important! You must show your calculations on every activity. Always write down the units in all your results. 1. Look at the scales of the picture. (2 p) a) What is the mass of the liquid? b) What is the mass of the iron ball? c) Explain how what process you would use to measure the volume of the iron ball. 2. Put in order the following masses from heaviest to least heavy using a conversion factor. (2 p) In order a) 6700 g a) b) 4,5 kg b) c) 0.004 mg c) d) 4500000 mg d) Calculations: 3. Using a conversión factor, express (1 p): a) 0.025 kL in dm3 b) 7300 cm3 in L c) 0.004 mg in kg d) 8500 g in kg 4. The tag of a soda can indicates that it has a capacity of 33 cL. How many dm3 of liquid can it contain? 5. A fisht tank with several objects inside is filled up with water. The fish tank has the following measures (2 p): a. 30 cm wide b. 0.6 m long c. 40 cm high We take out the objects that were inside the fish tank and the water level drops 3 cm. Calculate: a) The volume of the fish tank. b) The volume of the objects. c) The volume of the water. 6. Answer: a) What is the difference between a volumetric instrument and a calibrated instrument? b) Write down the name of the following instruments and classify them into volumetric or calibrated (2 p): Name: Name: Name: 6. Answer the following questions (1 p): a) Define matter: b) Classify: air, student, heat, light, iron, fire, sea, clouds, foot, sound waves Matter Not matter c) Classify the following units according to the magnitude: Kg, cm3, cL, dg, m3 g, g/cl, kg/m3, kL, Hg MASS VOLUME DENSITY 7. Write down the volumes contained in each graduated cylinder. A: B: C: BONUS QUESTION (1 p) We weight a liquid in the container A and the same liquid in the container B. Then, we weight the two empty containers together. In the picture you can see the obtained results. Calculate the mass of the liquid and the mass of each one of the containers. Define density using as example the following image: Make a list of the different laboratory instruments used to measure liquid volumes. Draw them and write down their names. 24 cm3 of a liquids have a mass of 120g and 12 cm3 of another liquid have a mass of 60 g. Indicate if the two liquids are made of the same substance or not. Explain why. A rock has a mass of 565 g. We measure the volume of the rock in the laboratory as you can see in the image below. Calculate the density of the rock. What is the mass of a 70 cl of olive oil knowing that its density is 0.92 g/cm3? A metallic object has been discovered at an archeological site and the archeologists want to know if it is made of copper or not. When they measure the mass, the scale says it has 137 g of mass and when it is fully immersed in a 100 ml of water, the volume increases upt 115 cm3. Knowing that density of copper is 9200 kg/m3, is the object made of copper? One of the densest substances on earth is platinum, whose density is 21.4 g/cm3. Calculate the mass of 1 L of platinum.