World Trade
World Trade Organisation
The world trade organisation was set up to reduce tariffs on exports. The WTO has the power to settle
trade disputes and aims to create global free trade.
It is supposed to treat MEDCs & LEDCs equally to allow everyone to trade freely. However, LEDCs
feel that they are shut out of negotiations by the rich countries. They feel that the interests of the USA
& the EU influence the WTO too much & in some cases feel that the WTO is just a way of the rich
countries exploiting poorer ones as some LEDCs are pressurised into opening their borders to trade
with MEDCs.
Disagreement among WTO members:
Every member should have an equal vote but the rich ones shut out the poorer nations.
Agreements have been more & more difficult to reach leading to disputes.
Banana war – Disagreements of the use of hormones in bananas damages relations between the EU
& USA.
American steel import tariffs have been put up to protect its own industry. The EU argues this
breaks the rules of the EU & so they have recently been removed.
Regional Trade Agreements
These are where regions agree to work together with easier trade between them. Participating countries
have preferential trade over others & so this can raise trade barriers against others. Examples include
the EU & NAFTA.
Bilateral Free Trade Agreement
These are agreements between 2 countries to lower trade barriers & give preferential trade to each
other. However, this discriminates against 3rd world countries. The EU is based on a number of
bilateral agreements. These agreements prevent a seamless global economy.
Problems:
Regional agreements divert trade inducing a country to import from a member of its trading bloc.
Regional groups may raise barriers against each other creating protectionist blocs.
Regional trade rules complicate the global regulations.
Levels of integration
Differences between degrees of integration between countries:
Free trade areas – Tariffs & quotas are abolished on trade amongst themselves but is independent
of tariffs on other countries e.g. NAFTA
Customs unions – Closer economic integration with free trade between countries & common
external tariffs on imported goods from other countries e.g. Mercosur (Latin America).
Common Markets – Same as customs unions but also have free movement of labour & trade.
Economic Unions – Same as common markets but there are also common economic policies on
agriculture, transport & industry e.g. EU.
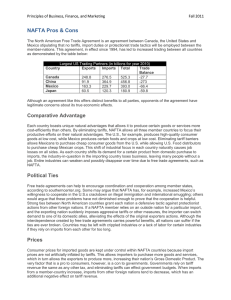
NAFTA
NAFTA was agreed in 1994 between the USA Canada & Mexico. It was introduced to remove tariffs
between the countries, as there were concerns that countries outside a trading bloc would be
commercially disadvantaged, especially with the EU.
Differences between EU & NAFTA:
NAFTA does not include:
Free movement of labour.
Redistribution of wealth to poorer countries.
A common currency
Political union
A customs union with common external tariffs
Change of border controls.
Impacts of NAFTA on USA
There is mixed opinion on the impact of NAFTA. Some say it is better as it allows countries to
specialise in what they are best at. This is the law of comparative advantage, which says that countries
should specialise in producing goods that they produce at a lower relative cost than other countries.
However, many US companies have moved to Mexico to take advantage of the cheap labour & slack
environmental controls. To remain competitive there has been a reduction in wages in the US & so
many high paid workers have been forced to take lower paid jobs. The roads are also more dangerous
as Mexican drivers & trucks are not as safe as US ones.
Impact of NAFTA on Canada
NAFTA has had a positive impact on Canada with merchandise trade with the US up 80%. There is
also greater American investment in Canada creating 1-mlln jobs. Canada is further from Mexico than
the US and so doesn’t have the same problems.
Impact of NAFTA on Mexico
NAFTA has forced Mexican companies to adopt higher standards & business practices to remain
competitive. Mexico’s economy has benefited as it has gone from economic crisis to stable economy.
Mexico receives investment from the USA and is also used by Europe & Asia as a springboard into US
markets.
However, there are worries that Mexico is too dependent on the US with greater exports to the US.
Mexican farmers have also been badly hit, as they can’t compete with the US agri-business. Most of
the Maquiladora are close to the US border so do not help the S of the country. There are also concerns
over the environment because of Mexico’s slack environmental laws.