Fixedincomeglossary-1455747043278(1)
advertisement

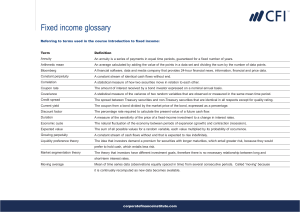
Fixed income glossary Referring to terms used in the course Introduction to fixed income: Term Definition Annuity An annuity is a series of payments in equal time periods, guaranteed for a fixed number of years. Arithmetic mean An average calculated by adding the value of the points in a data set and dividing the sum by the number of data points. Bloomberg A financial software, data and media company that provides 24-hour financial news, information, financial and price data. Constant perpetuity A constant stream of identical cash flows without end. Correlation A statistical measure of how two securities move in relation to each other. Coupon rate The amount of interest received by a bond investor expressed on a nominal annual basis. Covariance A statistical measure of the variance of two random variables that are observed or measured in the same mean time period. Credit spread The spread between Treasury securities and non-Treasury securities that are identical in all respects except for quality rating. Current yield The coupon from a bond divided by the market price of the bond, expressed as a percentage. Discount factor The percentage rate required to calculate the present value of a future cash flow. Duration A measure of the sensitivity of the price of a fixed-income investment to a change in interest rates. Economic cycle The natural fluctuation of the economy between periods of expansion (growth) and contraction (recession). Expected value The sum of all possible values for a random variable, each value multiplied by its probability of occurrence. Growing perpetuity A constant stream of cash flows without end that is expected to rise indefinitely. Liquidity preference theory The idea that investors demand a premium for securities with longer maturities, which entail greater risk, because they would prefer to hold cash, which entails less risk. Market segmentation theory The theory that investors have different investment goals, therefore there is no necessary relationship between long and short-term interest rates. Moving average Mean of time series data (observations equally spaced in time) from several consecutive periods. Called 'moving' because it is continually recomputed as new data becomes available. corporatefinanceinstitute.com Fixed income glossary Term Definition Nominal value The value of a security, such as a stock or bond, remains fixed for the duration of its life. Par value The amount returned to the bond investor by the issuer upon maturity. Pension funds A fund established by an employer to facilitate and organize the investment of employees' retirement funds contributed by the employer and employees. Pure expectations theory The idea that long term interest rates predict what short term rates will do in the future. So when the market expects short term rates to fall, we expect to see lower long term rates. Standard deviation A measure of the dispersion of a set of data from its mean. The more spread apart the data, the higher the deviation. Standard deviation is calculated as the square root of variance. Sum of squares The Sum of Squares Regression (SSR) measures how much variation there is in the modelled values and this is compared to the Total Sum of Squares (SST), which measures how much variation there is in the observed data, and to the Sum of Squares Residual (SSE), which measures the variation in the modelling errors. Supranational An international organization, or union, whereby member states transcend national boundaries or interests to share in the decision-making and vote on issues pertaining to the wider grouping. Time value of money The concept that holds that a specific sum of money is more valuable the sooner it is received. Time value of money is dependent not only on the time interval being considered but also the rate of discount used in calculating current or future values. Variance A measure of the dispersion of a set of data points around their mean value. Variance is a mathematical expectation of the average squared deviations from the mean. Weighted average An average in which some values count for more than others. Yield curve A line that plots the interest rates, at a set point in time, of bonds having equal credit quality, but differing maturity dates. Yield to maturity The annual return earned by a bond investor if purchasing a bond today and holding it until maturity. Zero-Coupon Bond A debt security that doesn't pay interest (a coupon) but is traded at a deep discount, rendering profit at maturity when the bond is redeemed for its full face value. corporatefinanceinstitute.com