Physics Questions
advertisement

Questions
Q1.
A student wanted to observe dividing cells under a microscope.
The student squashed the root tip of an onion plant on a microscope slide.
(i) Describe how the student should use a light microscope to view the squashed root tip.
(3)
.............................................................................................................................................
.............................................................................................................................................
.............................................................................................................................................
.............................................................................................................................................
.............................................................................................................................................
.............................................................................................................................................
(ii) Even though the slide was at the correct magnification, the student could not see the
chromosomes in the dividing cells.
State what could be done to the slide to make the chromosomes more visible.
(1)
.............................................................................................................................................
(Total for question = 4 marks)
Q2.
Figure 4 shows a photomicrograph of onion cells.
Figure 4
(i) The width of the labelled cell in Figure 4 is 6 mm. The cell has been magnified 750 times.
Calculate the actual width of this cell in mm.
Give your answer in standard form.
(3)
........................................................... mm
(ii) The most appropriate unit of measurement to record the length of a cell under a light
microscope is a
(1)
A
centimetre
B
micrometre
C
nanometre
D
picometre
(Total for question = 4 marks)
Q3.
DNA can code for the amino acids in the active site of an enzyme.
Explain the role of the active site of an enzyme.
(2)
.............................................................................................................................................
.............................................................................................................................................
.............................................................................................................................................
.............................................................................................................................................
.............................................................................................................................................
Q4.
Different enzymes catalyse specific reactions.
Explain why enzymes can only catalyse specific reactions.
(2)
.............................................................................................................................................
.............................................................................................................................................
.............................................................................................................................................
.............................................................................................................................................
(Total for question = 2 marks)
Q5.
Red blood cells can be stored for use in blood transfusions. They are stored in a solution that has
the same concentration of solutes as the blood cells.
What name is given to the movement of solutes, such as glucose, into and out of cells?
(1)
A
osmosis
B
diffusion
C
absorption
D
transmission
(Total for question = 1 mark)
Q6.
Osmosis is one method that single-celled organisms, such as bacteria, use to obtain molecules
from their environment.
Which of the following is a correct description of a process involving the transport of molecules?
(1)
A
Diffusion is used to transport molecules against the concentration gradient
B
Active transport is used to obtain molecules in a low concentration environment
C
Active transport moves substances along the concentration gradient
D
Diffusion uses energy to transport molecules into cells
(Total for question = 1 mark)
Q7.
(a) Complete the sentence by putting a cross (
) in the box next to your answer.
The particles in atoms are electrons, neutrons and protons.
The mass of an electron is
(1)
A greater than the mass of a neutron
B the same as the mass of a proton
C smaller than the mass of a proton
D the same as the mass of a neutron
(b) The atomic number of oxygen is 8.
The mass number of an atom of oxygen is 17.
Describe the number and type of particles in the nucleus of this atom.
(2)
.............................................................................................................................................
.............................................................................................................................................
.............................................................................................................................................
.............................................................................................................................................
(c) Sulfur and oxygen are both in group 6 of the periodic table.
Explain, in terms of their electronic configurations, why they are both in group 6.
(2)
.............................................................................................................................................
.............................................................................................................................................
.............................................................................................................................................
.............................................................................................................................................
(d) An atom of phosphorus contains 15 electrons.
Describe how these 15 electrons are arranged in a phosphorus atom.
(2)
.............................................................................................................................................
.............................................................................................................................................
.............................................................................................................................................
.............................................................................................................................................
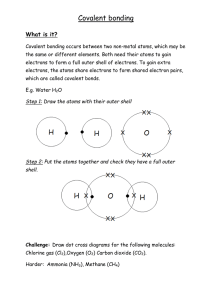
(e) Phosphorus oxide is a compound that contains covalent bonds.
(i) Describe what is meant by a covalent bond.
(2)
.............................................................................................................................................
.............................................................................................................................................
.............................................................................................................................................
.............................................................................................................................................
(ii) The formula of a molecule of phosphorus oxide is P4O10
Give the empirical formula of this oxide.
(1)
............................................
(Total for Question = 10 marks)
Q8.
Which row of the table correctly shows the boiling point and ability to conduct electricity of a
simple molecular, covalent liquid?
Put a cross (
) in the box next to your answer.
(1)
Q9.
The freezing point of water is 0°C.
What is the structure of water?
(1)
A
ionic
B
simple molecular (covalent)
C
giant covalent
D
metallic
(Total for question = 1 mark)
Q10.
Hydrogen sulphide, H2S, is a simple molecular, covalent compound.
(i) A hydrogen atom has one electron in its outer shell.
A sulfur atom has six electrons in its outer shell.
Which of the following is the dot and cross diagram of a molecule of hydrogen sulfide?
(1)
(ii) Which row in Figure 5 shows the properties of a simple molecular, covalent compound such
as hydrogen sulfide?
(1)
(Total for question = 2 marks)
Q11.
The freezing point of water is 0°C.
Describe how the movement and arrangement of water particles changes when water is cooled
from 10°C to –10°C.
(2)
.............................................................................................................................................
.............................................................................................................................................
.............................................................................................................................................
.............................................................................................................................................
(Total for question = 2 marks)
Q12.
Figure 13 shows a model of how particles are arranged in a solid.
Figure 13
State two ways in which this model fails to accurately represent a crystal of sodium chloride.
(2)
1 ..........................................................................................................................................
.............................................................................................................................................
2 ..........................................................................................................................................
.............................................................................................................................................
(Total for question = 2 marks)
Q13.
Figure 4 shows two students investigating their reaction times.
Student B supports his left hand on a desk.
Student A holds a ruler so that the bottom end of the ruler is between the finger and thumb of
student B.
When student A releases the ruler, student B catches the ruler as quickly as he can.
The investigation is repeated with the right hand of student B.
Figure 4
(a) The students took five results for the left hand and five results for the right hand.
Figure 5 shows their results.
Figure 5
(i) Calculate the average distance dropped for the right hand.
Give your answer correct to 2 significant figures.
(2)
distance = ........................................................... cm
(ii) Calculate the average time for the left hand.
Use the equation
(2)
average time = ........................................................... s
(b) Explain whether any of the readings are anomalous.
(2)
.............................................................................................................................................
.............................................................................................................................................
.............................................................................................................................................
.............................................................................................................................................
(c) Give two ways that the students can improve the quality of their data other than ignoring
anomalous results.
(2)
1 ..........................................................................................................................................
.............................................................................................................................................
2 ..........................................................................................................................................
.............................................................................................................................................
(d) Describe how the students could develop their investigation to investigate how reaction time
changes with another variable.
(2)
.............................................................................................................................................
.............................................................................................................................................
.............................................................................................................................................
.............................................................................................................................................
.............................................................................................................................................
.............................................................................................................................................
(Total for question = 10 marks)
Q14.
A car driver sees a rabbit on the road.
The driver makes an emergency stop after he sees the rabbit.
Figure 6 shows the speed of the car from the time the driver sees the rabbit until the car stops.
Figure 6
Calculate the distance that the car travels in the first 0.5 seconds.
(3)
distance = ........................................................... m
(Total for question = 3 marks)
Q15.
A student investigates the motion of a trolley along a horizontal runway using the apparatus in
Figure 2.
Figure 2
A trolley is attached to a string passing over a pulley.
A block of metal hangs on the end of the string.
Each light gate measures the time it takes for the card to pass through the gate.
When the trolley is released, it moves along the track.
A computer measures the time it takes for the card to pass between each light gate.
(i) The card took 0.080 s to pass through the first light gate.
The width of the card is 5 cm.
Calculate the average speed, in m/s, of the trolley through the first light gate.
(2)
average speed = ........................................................... m/s
Another trolley passes through the first light gate at a velocity of 0.72 m/s.
This trolley passes through the second light gate at a velocity of 1.1 m/s.
The time it takes for the card on the trolley to travel between the two light gates is 0.53 s.
(ii) State the equation relating acceleration, change in velocity and time.
(1)
(iii) Calculate the acceleration of the trolley between the two light gates.
(2)
acceleration = ........................................................... m/s2
(Total for question = 5 marks)
Mark Scheme
Q1.
Q2.
Q3.
Answer
An explanation including twoof the
following points:
ref to specific shape (1)
to bind to substrate / form
enzyme substrate complex (1)
for reaction to take place /
catalysed(1)
joining together {substrates /
molecules} / break down
{substrates / molecules} (1)
ref to lock and key mechanism
/ hypothesis (1)
Q4.
Acceptable answers
Mark
(2)
Q5.
Q6.
Q7.
(a)
(b)
Answer
C smaller than the mass of a proton
An description linking
8 protons (1)
(and) {17-8/9} neutrons (1)
(c)
Explanation linking
Acceptable answers Mark
(1)
(2)
ignore references to electrons in shells
/ charges on particles
if electrons in nucleus max 1 protons
and neutrons with incorrect numbers
(1)
correct electronic configurations or
(2)
diagrams alone max 1
(both have) same number (of
electrons) in outer shell(1)
'they both have 6 in the outer shell'
6 (electrons in outer shell)
scores both marks allow 'both need 2
(consequent on first point) (1) (more) (electrons) to fill outer shell' for
both marks
(d)
A description to include
suitable diagram in place of
(2)
2.8(1).5(1)
2.8 (in 1st and 2nd shell)(1)
5 (in outer shell)(1)
electrons in {shells / orbits / rings}(1)
(e)(i) A description to include
can be shown in a diagram of a
(2)
covalent bond
electron(s) shared (1)
{pair(s) of / two} (electrons) any mention of ions scores zero
(1)
(e)(ii) P2O5
Reject P2O5 / P2O5
(1)
Q8.
Q9.
Q10.
Q11.
Q12.
Q13.
Q14.
Q15.
Powered by TCPDF (www.tcpdf.org)