Kingdom Protista: Protist Biology Presentation
advertisement
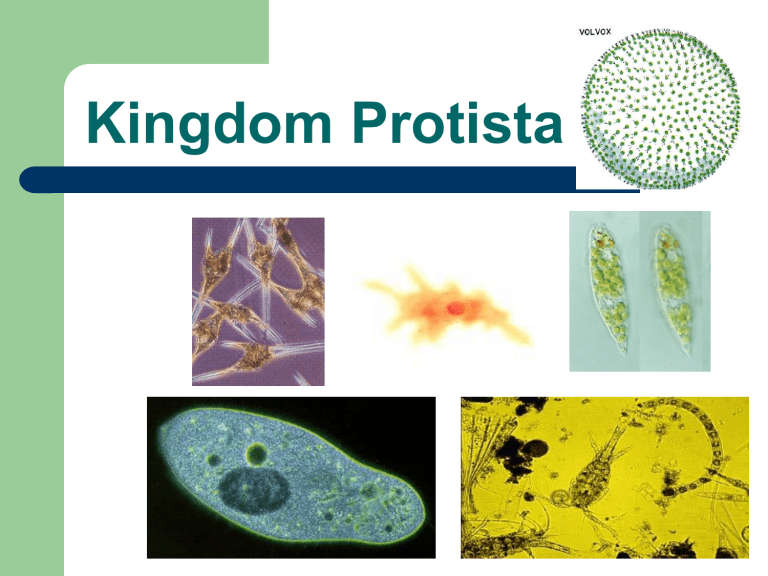
Kingdom Protista Kingdom Protista Eukaryotic Heterotrophic, (but some autotrophic) Living freely and/or Parasites Microscopic Mostly Unicellular Plankton Free living protozoa and algae that drift in the water Microscopic in size Used by larger organisms that filter feed the water for food Plankton Plankton AMOEBA Bottom dwelling scavengers that feed on decaying matter in the water. Amoebas Movement – by pseudopodia cytoplasmic extensions that blob “Amoeboid movement” Feeding – surrounds food with pseudopodia and engulf the food by phagocytosis. Reproduction- binary fission. Diagram an AMOEBA, label structures PARAMECIUM – by cilia, short hair-like projections-for movement & acquiring food. Feeding –cilia sweep food down the oral groove to the mouth pore of paramecium. Movement PARAMECIUM Paramecium Binary Fission Asexual Reproduction Paramecium Conjugation Sexual Reproduction Symbiotic Relationships – Relationship between different species living in close association with one another. Example: Trichonympha live in the digestive tract of termites. One of the few organisms that can digest cellulose (cell wall) and thus utilize glucose for energy Symbiosis Trichnympha Illnesses caused by Protists African Sleeping Sickness transmitted by the tsetsee fly which live only in Africa Illnesses caused by Protists Giardia “Hiker’s Diarrhea” – carried by muskrats and beavers, transmitted when we drink contaminated drinking water Illnesses caused by Protists Illnesses caused by Protists – carried by an infected mosquito and transmitted when a mosquito bites. The parasitic plasmodium uses the mosquito as its vector. Malaria Illnesses caused by Protists Plasmodium Life Cycle (Malaria) CHLAMYDOMONAS Unicellular green algae. They are common in the soil, fresh water and streams. CHLAMYDOMONAS Volvox Volvox – Are green algae that live in large round colonies. (colonial) Diatoms – golden brown algae. Walls of diatoms contain shells. These shells never decompose (animal dies), the diatom shell sinks and forms a layer of material called diatomaceous earth (used as an abrasive in silver polish, detergents, paint and insulators) Diatoms Diatoms DINOFLAGELLATES –bioluminescent algae. “fire algae” Can produce red tides - large populations of dinoflagellates (algal blooms). Water looks red and contains nerve toxins. Infects shellfish, fish - can become deadly if eaten. Dinoflagellates Dinoflagellates EUGLENAS – flagellum. Feeding - Contain chlorophyll, but are not completely autotrophic. Has an eyespot that functions as a light detector. Movement EUGLENA End of the Road for Protista