Lesson 3 Carbon cycle
advertisement

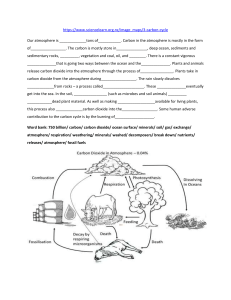
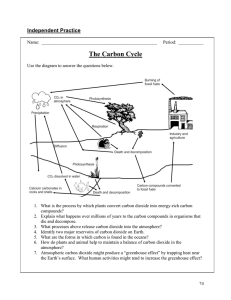
Lesson 3 The Carbon Cycle Nutrient Cycles Includes carbohydrates, fats, proteins, vitamins and minerals 95% of our bodies are made of four elements Obtained from food, water and air Plants obtain from soil, water and air Cycles can move quickly or can remain in one place for a long time When matter accumulates in one place its known as a reservoir o Ex. Ocean, Atmosphere, Rocks, Plants Carbon In the atmosphere, carbon is attached to some oxygen in a gas called Carbon Dioxide Even though carbon dioxide makes up only 0.04% of the gases in the atmosphere, plants receive the needed carbon dioxide to grow The Carbon Cycle Large quantities of carbon is stored in several different reservoirs/sinks in ecosystems o Ex. Ocean, Forests, Soil, Atmosphere The majority of the exchange between the various carbon reservoirs/sinks occurs because of two important processes o o Carbon Reservoirs These locations are also referred to as Oceans Largest active carbon sink in the world Organisms in the ocean use the carbon from the dissolved carbon dioxide to build their tissues A large portion of the matter in trees are made of carbon which is collected from the atmosphere Underground These deposits were formed from decomposing organisms compressed over million years o EX. Forest Human Activities Change the Carbon Cycle The burning of the fossil fuels release the stored carbon into the atmosphere increasing the concentration of carbon dioxide now higher than it has been over the past 800, 000 years o This concentration of carbon dioxide has been linked to causing global climatic change which has the potential to change the most important abiotic factors in ecosystems: water availability and temperature