APES Chapter 7 Review 17 ed.
advertisement

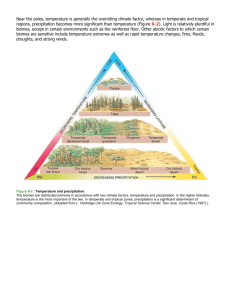
Bryant Hernandez Chapter 7 Review & Critical Thinking 1.) Review the Key Questions and Concepts for this chapter on p. 148. Describe how differences in climate lead to formation of tropical, temperate, and polar deserts, grasslands, and forests. A.) Climate is weather averaged over a long time, Climate also varies all over the different parts of the world. This is because of the different patterns of air circulation and ocean currents. This affects the temperature, which decides lead to the formation of the 6 described environments. 2.) Distinguish between weather and climate. Describe three major factors that determine how air circulates in the lower atmosphere. Describe how the properties of air, water, and land affect global air circulation. Define ocean currents and explain how they, along with global air circulation, support the formation of forests, grasslands, and deserts. A.) Weather is a set of physical conditions of the lower atmosphere. Climate is an area's general pattern of atmospheric conditions over periods ranging from at least three decades to thousands of years. B.) Three factors that determine how the air circulates in the lower atmosphere are the uneven heating, the rotation of the earth’s axis and the properties of air, water, and land. C.) Heat from the sun evaporates ocean water and transfers heat from the oceans to the atmosphere. This evaporation of water creates giant cyclical convection cells that circulate air, heat, and moisture both vertically and from place to place in the atmosphere. D.) The earth's air circulation patterns, prevailing winds, and configuration of continents and oceans result in giant convection cells in which warm, moist air rises and cools, and cool, dry air sinks. 3.) Define and give four examples of a greenhouse gas. What is the greenhouse effect and why is it important to the earth's life and climate? A.) Greenhouse gases include several gases in the atmosphere, including water vapor, carbon dioxide and methane which release heat into the atmosphere. B.) The earth's surface absorbs solar energy and transforms it to heat, which then rises into the lower atmosphere, this then escapes into space and is then transferred to the lower atmosphere. Greenhouse gases and the natural greenhouse effect are crucial when taking the earths average temperature. 4.) What is the rain shadow effect and how can it lead to the formation of deserts? Why do cities tend to have more haze and smog, higher temperatures, and lower wind speeds than the surrounding countryside? A.) The rain shadow effect is a reduction of rainfall and loss of moisture from the landscape on the side of mountains facing away from prevailing surface winds. B.) Cities have building materials that absorb and hold heat and block wind flow. Motor vehicles release large quantities of heat and pollutants, resulting in more haze and smog, higher temperatures. 5.) What is a biome? Explain why there are three major types of each of the major biomes (deserts, grasslands, and forests). Describe how climate and vegetation vary with latitude and elevation. A.) Biomes are large terrestrial regions with distinct climates and certain species adapted to them. B.) Differences in climate lead to the formation of tropical, temperature, and polar deserts, grasslands, and forests. C.) Both climate and vegetation vary with latitude and elevation. That’s why the base of a mountain has vegetation while the top section turns into ice and snow. 6.) Describe how the three major types of deserts differ in their climate and vegetation. Why are desert ecosystems fragile? How do desert plants and animals survive? A.) Tropical deserts are hot and dry most of the year with very few plants a hard surface. B.) Temperate deserts have high daytime temperatures in summer and low in winter, there is little vegetation, in which cacti are most common, C.) Cold deserts have cold winters and warm summers, it generally has low precipitation and most animals there have become accustom with the cold climate. 7.) Describe how the three major types of grasslands differ in their climate and vegetation. What is a savanna? Why have many of the world' s temperate grasslands disappeared? What is permafrost? Distinguish between arctic tundra and alpine tundra. A.) Cold grasslands are mostly cold, stark and treeless. Tropical grasslands are mostly warm with a little bit of precipitation, it normally has an array of trees throughout. Temperate grassland is a mix of both, cold in winters and hot in summers and fairly regular precipitation that falls unevenly throughout the year. B.) Most of temperate grasslands have disappeared because they have been over grazed due their fertile soil. C.) Permafrost is the underground soil in which captured water stays frozen for more than two consecutive years. D.) - The Alpine tundra o A large, flat or gently sloping, treeless tract of land above the timberline. - The Arctic tundra o A treeless area between the icecap and the tree-line of Arctic regions, having a permanently frozen subsoil and supporting low- growing vegetation such as lichens, mosses, and stunted shrubs. This is a fragile biome o Animals of this biome survive the intense winters by burrowing and going under to stay warm. 8.) What are the three major types of forests? Describe how these three types differ in their climate and vegetation. Why is biodiversity so high in tropical rain forests? Why do most soils in tropical rain forests hold few plant nutrients? Describe what happens in temperate deciduous forests in the winter and fall. What are coastal coniferous or temperate rain forests? What important ecological roles do mountains play? A.) Tropical, temperate and cold forests. Tropical rain forests are near the equator, warm air rises uniformly and creates large amounts of precipitation. Temperate forests are in average-medium temperatures that change depending on the season. Cold forests are intensively cold during the winter with low precipitation. B.) Since it’s constantly warm and has a wet climate, it is ideal for a wide variety of plants and animals. Tropical rain forests have a very high net primary productivity; they are teeming with life and boast incredible biological diversity. C.) Because instead of being stored in the actual soil, about 90% of plants nutrients are released by decomposition and are quickly sucked up and stored by trees, vines and other plants. D.) Their leaves change colors a lot in fall and in winter. They grow in areas with moderate average temperatures that change significantly with the season. They survive the winters by dropping her leaves and going dormant for the winter E.) Temperate rain forests are scattered around the coastal areas and have a sufficient amount of precipitation. F.) Some of the world’s most spectacular environment are high on mountains, steep or high lands which cover about a quarter of the earth’s land surface. They contain majority of the world’s forests, which are habitats for much of the planet’s terrestrial biodiversity, which provide many endemic species their habitats and these animals are often found nowhere else on earth. 9.) Describe how human activities have affected the world's deserts, grasslands, forests, and mountains. - Deserts: 1. Large desert cities. 2. Sol destruction by off-road vehicles. 3. Soil salinization from irrigation. 4. Land disturbance and pollution from mineral extraction. - Grasslands 1. Conversion to cropland 2. Release of CO2 to atmosphere from burning grasslands 3. Overgrazing by livestock 4. Oil production and off-road vehicles in arctic tundra - Forests 1. Clearing for agriculture, livestock grazing, timber, and urban development. 2. Conversion of diverse forests to tree plantations 3. Damage from off-road vehicles 4. Pollution of forest streams - Mountains 1. Agriculture 2. Timber Extraction 3. Mineral Extraction 4. Hydroelectric dams and reservoirs 5. Increasing tourism 6. Urban Air pollution 7. Increased ultraviolet radiation from ozone depletion 10.) What are the chapter’s three big ideas? Describe the connections between the climates, terrestrial systems, and the three principles of sustainability (see back cover). A.) What factors influence climate, how climate affects the nature and location of the biomes and how we’ve affected the world’s terrestrial ecosystems. B.) Climate is made up of solar energy and affects the biodiversity in a terrestrial system. Critical Thinking 1.) What would be likely to happen to the earth’s climate (a) if most of the world’s oceans disappeared and (b) if most of the world’s land disappeared? A.) The oceans absorb and redistribute solar energy. They essentially control the temperature of the earth. If most of the world's oceans disappeared the earth’s climate would turn into a dessert. Everything would eventually die out. If most of the world's land disappeared the water would be the only thing that would be absorbing the solar energy. I believe this will make the earth’s climate liken to that of a tropical setting. 2.) Describe the roles of temperature and precipitation in determining what parts of the earth’s land are covered with: (a) desert, (b) arctic tundra, (c) temperate grassland, (d) tropical rain forest, and (e) temperate deciduous forest. A.) In a desert, annual precipitation is low and often scattered unevenly throughout the year. During the day, the baking sun warms the ground and evaporates water from plant leaves and from the soil. But at night, most of the heat stored in the ground radiates quickly into the atmosphere. This explains why in a desert; you may roast during the day but shiver at night. B.) Cold grasslands, or arctic tundra, lie south of the arctic polar ice cap. During most of the year, these treeless plains are bitterly cold, swept by frigid winds, and covered with ice and snow. Winters are long with few hours of daylight, and the scant precipitation falls primarily as snow. C.) In a temperate grassland, winters can be bitterly cold, summers are hot and dry, and annual precipitation is sparse and falls unevenly throughout the year. Grasslands occur primarily in the interiors of continents in areas that are too moist for deserts to form and too dry for forests to grow. Grasslands persist because of a combination of seasonal drought, grazing by large herbivores, and occasional fires. D.) Tropical rain forests are found near the equator, where hot, moisture-laden air rises and dumps its moisture. These lush forests have year-round, uniformly warm temperatures, high humidity, and almost daily heavy rainfall. This constant warm, wet climate is ideal for a wide variety of plants and animals. E.) Temperate deciduous forest typically sees warm summers, cold winters, and abundant precipitation. 3.) Why do deserts and arctic tundra support a much smaller biomass of animals than do tropical forests? Why do most animals in a tropical rain forest live in its trees? A.) Deserts and arctic tundra support smaller biomass animals than tropical forests because both deserts and arctic tundra are placed on the extreme sides of temperature ranges that are tolerable for animals. In addition, deserts and arctic tundra have less precipitation and vegetation for animals to consume than tropical rainforests. B.) Animals live in up in trees for food and predators as well as shelter, since on the ground there is not much hiding places. 4.) How might the distribution of the world’s forests, grasslands, and deserts shown in Figure 7-7 differ if the prevailing winds shown in Figure 7-3 did not exist? A.) It would differ if the prevailing winds did not exist in figure 7-3 due to the fact that the heated air would stay at the equator and heat and moisture would not be distributed in the atmosphere to different areas of the world, causing a majority of the earth to be considered too cold and uninhabitable for both humanity and many types of animals. 5.) Which biomes are best suited for (a) raising crops and (b) grazing livestock? Use the three principles of sustainability to come up with three guidelines for growing food and grazing livestock in these biomes on a more sustainable basis. A.) Grasslands, specifically temperature, have deep and fertile soil which allows the biome to be widely used for growing crops and grazing cattle. Organic matter accumulates and produces a deep, fertile soil, because the aboveground parts of most of the grasses die and decompose each year. Due to the fact that temperate grasslands are great places for crops and animal grazing, many of the world’s natural temperate grasslands have disappeared. They are often flat, easy to plow, and have fertile, deep soils. 6.) What do you think would happen if all or most of the world’s mountain glaciers melted? Write a brief scenario describing the resulting problems and ways in which you think mountainous nations would deal with the problems. A.) If glaciers that were on land melted, then the oceans’ water level will rise due to the additional ice, the glaciers will displace the ocean. This could lead to many islands and countries that are at sea level to potentially sink. If the glacier are melting on the mountain, then it could lead to potential flooding, and perhaps the decline of animals living there. 7.) What type of biome do you live in? (If you live in a developed area, what type of biome was the area before it was developed?) List three ways in which your lifestyle could be contributing to the degradation of this biome? A.) Tropical rainforest B.) Littering, chopping down forests for more space for homes, wasting paper. 8.) You are a defense attorney arguing in court for sparing a tropical rain forest from being cut. Give your three best arguments for the defense of this ecosystem. A.) - The ecosystem helps stabilize the world’s climate - Provide homes for many plants and animals - Source for medicine and food. 9.) Congratulations! You are in charge of the world. What are the three most important features of your plan for helping to sustain the earth’s terrestrial biodiversity and the ecosystems services it provides? A.) In order to help sustain the earth’s terrestrial biodiversity, first I would create a variety of reservations that protect a mixture of biomes. Through such protection, biomes will be able to flourish without human disturbances. Second, I would form laws and regulations limiting deforestation and the hunting of animals. In biomes, such as the rainforest, deforestation and extinction of animalsare becoming a large problem. Lastly, to promote the protection of such ecosystems, people must be aware of the devastation of biomes and the impact humans have on them. 10.) List two questions that you would like to have answered as a result of reading this chapter. A.) With the significance of forests, why are we still clearing them for the construction of more homes and buildings? B.) Why do humans believe they are the top species in the world?