1-1-business-activity
advertisement

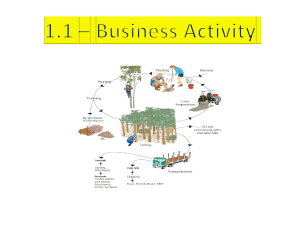
Compiled by: Shubhanshi Gaudani 1. Understanding Business Activity 1.1 Business Activity Business Studies 0450 1.1.1 The purpose and Nature of Business Activity • CONCEPTS OF NEEDS, WANTS, SCARCITY, AND OPPORTUNITY COST • The purpose of business activity is to provide consumers with their needs and wants. • Business Activity: the process of producing goods and services to satisfy the needs and wants of consumers. • Needs: A good or service which is essential for living. • Wants: A good or service which people would like, but is not essential for living. • There are just not enough goods with the sellers, and money with the consumers to satisfy their unlimited demand of wants. This is known as the economic problem. • Economic Problem: Unlimited wants cannot be met because there are limited factors of production. This creates scarcity. • Factors of Production: The resources needed to produce goods and services land, labour, capital and Enterprise. • Land: all the natural resources such as minerals, ores, fields, oil and forest. • Labour: Is the number of people available to work. • Capital: Is the machinery, equipment, and finance needed for the production of goods and services. • Enterprise: Is the people prepared to take the risk of setting up the business they are known as entrepreneurs. • However there are not enough of these factors of production to make all the goods and services needed or wanted by the world’s population. This is the problem of scarcity. • Scarcity: There are not enough goods and services to meet the wants of the population. 1 Compiled by: Shubhanshi Gaudani • Scarcity, forces us to make choices. When making a choice, you need to make sure the product or service you choose is worth more than the one you give up. The next best choice is the opportunity cost. • Opportunity Cost: The benefit that could have been gained from an alternative use of the same resource. • IMPORTANCE OF SPECIALISATION • Specialisation: People and businesses concentrate on what they are best at. • To make sure, that there is minimal wastage of the factors of production, specialisations is introduced. • Benefits of Specialisation (to business): Makes the business more efficient and reduces costs. • Benefits of Specialisation (to consumers): Goods and services have a higher quality, larger supply is available, and goods are available at a lower price. Pros of Specialisation Cons of Specialisation Specialised workers are good at one task, and increase efficiency and productivity of labour Boredom from doing the same task may result into lower efficiency Less time is wasted for switching jobs by individuals There is no flexibility as workers can do only one task, and not other well, if needed. Machinery also helps all jobs and can operate 24/7 If one worker is absent no one can replace him, so production process stops. Products have a better quality High number of employees are to be hired who are skilled, this increases costs. • Division of Labour: Production is divided into separate tasks and each worker does just one of those tasks. • PURPOSE OF BUSINESS ACTIVITY • Without the business activity, there would be no products and services. Businesses produce different types of goods and services these are: • Consumer Goods: Products which are sold to the final consumer. They can be seen (physical goods) and touched (tangible goods). They are divided into durable (goods which can be used over and over again. ex. Computers) and Non durable (Can be used only once. ex. Food and drink. ) 2 Compiled by: Shubhanshi Gaudani • Consumer Services: Non-tangible products such as insurance services, transport. • Capital Goods: Physical goods such as machinery ad delivery vehicles, used by another businesses to help produce other goods and services. • THE CONCEPT OF ADDED VALUE AND HOW IT CAN BE INCREASED • Added Value: It is the difference between the selling price and the cost of buying the raw materials and components • Businesses try to add value at every stage of the production process. This is done by taking raw materials and turning them into a good or service and selling them to a customer at a price greater than the cost of raw materials in the production process. • Other costs such as worker’s wages, and energy costs must be deducted from the added value to calculate profit. • It is one of the most important objectives of a business. • How business increase added value: • Branding: Branding increases added value because people want or fell they should buy an item, from a particular company. • Excellent Service Quality: Industries providing high quality, personalised service can charge higher prices. The cost of materials used will be very similar, but personalised services increases profits. • Product Features: Products that have more features and functions than similar products in the markets, will allow the producer to charge a higher price. • Convenience: Consumers are often ready to pay a higher price, for a product they can have immediately or which can save them time, ex. ready meals, home delivery. • Reducing the cost of materials but keeping the price of the product same. OR increasing selling price, but using the same raw materials with the old price. 3