GOOD BONDING PRACTICE
advertisement

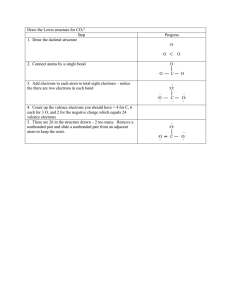
myp Practice Exercise 8 BONDING NAME: BOND TYPES Atoms and molecules form bonds with each other, usually resulting in compounds that are more stable than un-bonded atoms or molecules . Ionic Bonds are formed when the electromagnetic attraction between a metal and a non-metal bring them together. Covalent Bonds are formed when atoms share electrons. BOTH IONIC AND COVALENT BONDS RESULT IN FULL VALENCE SHELLS FOR THE ATOM (1s2 or 2s2 2p6 and so on) WHICH ARE MORE STABLE THAN ATOMS WITHOUT FULL VALENCE SHELLS. Metallic Bonds are the bonds that keep metals intact. These bonds are formed between the free valence electrons found in metals and the protons of adjacent nuclei. PROBLEMS: 1.) Predict what type of bond is most likely to be formed between the given substances: a. between magnesium and chlorine b. between two oxygen atoms c. between an iron and sulfur d. between carbon and nitrogen e. between atoms of silver BOND FORMATION IN CHEMICAL REACTIONS Most chemical reactions involve activity between the valence electrons, or those electrons present in the highest energy level. Ionic Bonds form when the valence electrons from the metal are transferred to the valence shell of the non-metal. As a result, the metal atom becomes a positive ion (it lost one or more electrons) and the non-metal atom becomes a negative ion (it gained one or more electrons). These atoms tend to acquire or lose electrons so that their valence shells are filled (it will have either 2 or eight electrons). Covalent Bonds form when the valence electrons of two or more non-metals share electrons. As a result, a special valence shell forms that will have two or eight electrons. LEWIS DOT DIAGRAMS Drawing dot diagrams is an easy way to visualize the valence electrons in an atom. To draw a dot diagram, first identify the number of valence electrons. Then, evenly distribute on four sides those electrons as dots around the symbol for an element. PROBLEMS 2.) Draw Lewis Dot diagrams around the following atoms: N 5.) Cl Mg Ti Li Na O When an atom loses or gains electrons, it becomes an ion. Unlike charges attract each other so ions that are positive will bond with ions that are negative. Using dots for the metal’s electrons and x’s for the non-metal’s electrons, draw the Lewis Dot diagrams for the following ionic bons between the atoms given. EXAMPLE x x H· + x Cl x x x x H x x · Cl x x x x x *********************************************************************************************************************************** K Mg + Br + O K Br Mg O + Cl Cl Mg 2Na + O Cl Mg Cl Na O Na LEWIS DOT DIAGRAMS AND COVALENT BONDS Drawing dot diagrams is an easy way to visualize the valence electrons in an atom and to predict covalent bonds. Use these steps to draw a correct covalent bond between two non-metals. 1.) 2.) 3.) Add up the total valence electrons. Draw a single bond between the central atom and each surrounding atom. Each bond accounts for 2 electrons. Arrange the remaining electrons symmetrically around the atoms so that each atom in the molecule has a full valence shell (usually the appearance of 8 electrons). Draw double and triple bonds to achieve this. EXERCISES: Construct the Lewis dot bond diagrams for the following compounds: 1. Fluorine gas (F2). 2. Oxygen gas (O2). 3. Nitrogen gas (N2). 4. Chlorine gas (Cl2). 5. Carbon tetrafluoride (CCl4). 6. Carbon monoxide (CO). 7. Silicone dioxide (SiO2). 8. Methane (CH4). 9. Water (H2O). 10. Iodine (I2). 11. Using your knowledge of electro negativity rank compounds 5 through 9 by polarity if the molecule. Rank them in left to right order, with the least polar molecule on the left and the most polar molecule on the right.