Land Biomes or Earth's Ecosystems
advertisement
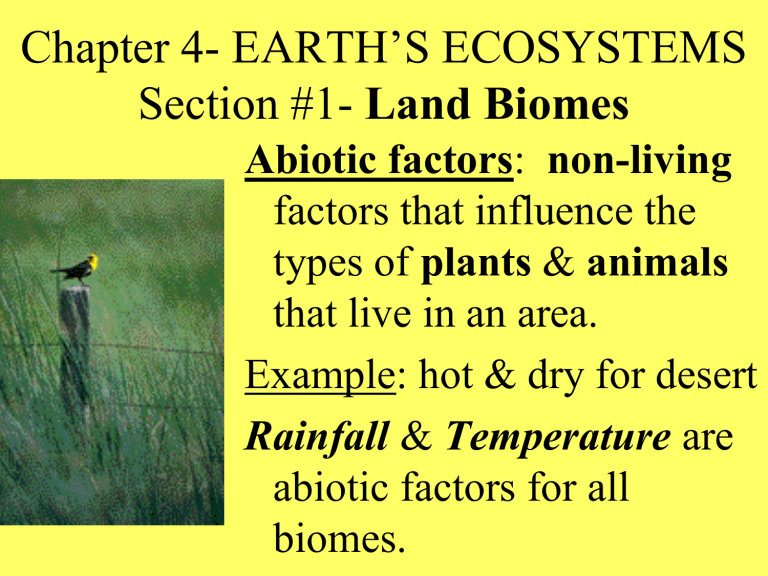
Chapter 4- EARTH’S ECOSYSTEMS Section #1- Land Biomes Abiotic factors: non-living factors that influence the types of plants & animals that live in an area. Example: hot & dry for desert Rainfall & Temperature are abiotic factors for all biomes. FORESTS- the type of forest that develops depends on temperature & rainfall. Temperate Deciduous Forest: • • • • different species of trees Different mammals, birds, & reptiles These animals eat leaves, seeds, nuts, and insects. Trees conserve water in winter by losing their leaves. Coniferous Forests • Don’t change much from summer to winter • Mainly have evergreen trees. • Most of the trees are conifers, meaning they produce seeds in cones. • Needles of conifers have a thick, waxy coating so they won’t dry out and get damaged during the winter. • Moose, deer, porcupines, chipmunks, foxes live here. Many of these animals hibernate or migrate during the winters. Tropical Rain Forests • The most diverse biome on the planet. • Contains more species than any other biome. (Plants & Animals) • Some animals live on the ground. Most live in the canopy (treetops). • Soil is very thin and poor in nutrients. • Most nutrients here come from the vegetation. • The rainiest biome. grasslands Temperate grasslandsCold winters, warm summers, exist on every continent. Found between forests & deserts. Vegetation are grasses mixed with flowering plants, with few trees. Fire prevents growth of slow-growing plants. Small, seed-eating animals like prairie dogs, mice & large herbivores like bison. Prairies, plains, steppes, and pampas are regions where grasses are the main plants. Savanna A Tropical Grassland • Tropical grassland with clumps of trees. • Dry season- grasses die back, but the deep roots survive through months of drought. • Wet season- can receive up to 59 inches of rain. • Savannas in Africa have abundant and diverse groups of large herbivores like elephants, giraffes, zebras, gazelles, & wildebeests. • These animals are eaten by lions & leopards or the “clean-up” crew of hyenas & vultures. DESERTS • Hot, dry regions • Most of the water that falls to the ground evaporates. • Organisms have special ways to survive extreme temps. with very little water. PLANT & ANIMAL ADAPTATIONS for survival • Plants grow far apart, to reduce competition for water. Other plants have deep root systems to reach ground water. • Jack rabbits’ huge ears help get rid of body heat. • Most animals are active at night, when it’s cooler. Tundras • Far north, at the tops of mountains. • It is so cold, no trees can grow. • Major feature is permafrost- this prevents rain from draining through the soil, so the ground stays wet & soggy. • Grasses, woody shrubs, sedges, rushes, mosses & lichens • Caribou, musk oxen, wolves, hares, lemmings, & migratory birds in the summer.