Acids and Bases Properties Worksheet
advertisement

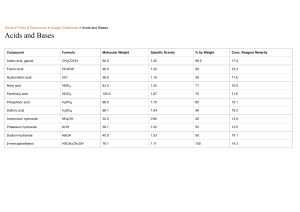
Properties of Acids Properties of Bases Common Acids Common Bases Acids Bases strong -------- weak pH: 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 high [H3O+] ------ low [H3O+] Properties of Acids weak -------- strong 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 low [OH-] ------ high [OH-] Properties of Bases contain hydrogen which produces hydronium produce hydroxide ions (OH-) in water ions (H3O+) in water tend to have a sour taste tend to have a bitter taste tend to sting/burn and are very corrosive tend to have a soapy/slippery feel and are very corrosive neutralize bases to form water plus a salt neutralize acids to form water plus a salt break up proteins, so are used in marinating break down oil and grease react with metals such as Mg, Zn and Al to form hydrogen gas Common Acids HCl hydrochloric acid (in stomach) HNO3 nitric acid (in fertilizers) H2SO4 sulfuric acid (in car batteries) CH3COOH acetic acid (vinegar) citric acid (lemons, oranges) acetylsalicylic acid (aspirin) ascorbic acid (Vitamin C) carbonic acid (carbonated drinks) Common Bases NaOH sodium hydroxide (lye, oven cleaner, drain cleaner) KOH potassium hydroxide NH4OH ammonium hydroxide (cleaning compounds) NH3 ammonia (fertilizers, cleaners) Mg(OH)2 magnesium hydroxide (antacids, cough syrup) sodium hypochlorite (bleach)