13. LPP-V

LPP- V
Prakash Awasthy
1
Where to invest?
Finance domain application
• You are CFO of one of the biggest e-tail company in India
• You foresee that your firm would require substantial capital for technological advancement on AI, Drone and self-driven logistics
Capital for
AI
Drone
Self-driven logistics
When
After 1 year
After 3 years
After 5 years
How much (minimum) [in Cr.]
2000
2000
3000
2
Where to invest?
• There are three types of assets where you can invest in order to fulfil the requirements of capital in future years
• Here are per unit returns for each of the terms for three investment options
AI (1 Year)
Drone (3 years)
Self-driven logistics (5 years)
Total
Huge
0.5
1.5
2.5
4.5
Growth Rapid
1.5
2.5
3
1.5
1
1
6 4.5
3
Where to invest?
• What should be the investment mix?
Huge
AI (1 Year)
Drone (3 years)
0.5
1.5
Self-driven logistics (5 years) 2.5
Growth
1.5
3
1.5
Rapid Minimum Capital
2.5
1
1
2000
2000
3000
4
Hiring and Training Problem
HR domain application
• The Feeder-Service Airlines Company must decide how many new flight attendants to hire and train over the next six months. The requirements expressed as the number of attendant-flight-hours needed are 8000 in January;
9000 in February; 8000 in March; 10,000 in April; 9000 in May; and 12,000 in
June
• It takes one month of training before a flight attendant can be put on a regular flight; so a person must be hired at least a month before (s)he is actually needed.
Also, a trainee requires 100 hours of supervision by experienced flight attendants during the month of training so that 100 less hours are available for flight service by regular flight attendants
• Each experienced flight attendant can work up to 150 hours in a month, and
Feeder-Service has 60 regular flight attendants available at the beginning of
January. Each month, approximately 10% of the experienced flight attendants quit their jobs
• An experienced flight attendant costs the company INR 2.4 lac and a trainee INR 1 lac a month in salary and other benefits
5
Duality
• Every LPP has an associated dual problem
Resource
Labor (hrs)
Clean Room (hrs)
Testing Room (hrs)
Profit (Rs)
LQP
1
1
3
1000
DMP
1
2
1
500
Availability
(‘000)
10
16
24
6
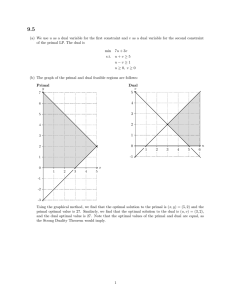
Product-mix: Primal and dual
• Primal: Maximize the profit such that resource(labor, cleaning, testing) usage is with in a limit
• Dual: Minimize the resource usage such that margin for each product is above a threshold
7
Product-mix: Primal and dual
Primal
𝑀𝑎𝑥 1000 𝐿 + 500 𝐷 𝑠𝑢𝑏𝑗𝑒𝑐𝑡 𝑡𝑜
1 𝐿 + 1 𝐷 ≤ 10
1 𝐿 + 2 𝐷 ≤ 16
3 𝐿 + 1 𝐷 ≤ 24
𝐿, 𝐷 ≥ 0
Dual
𝑀𝑖𝑛 10 𝑢1 + 16 𝑢2 + 24 𝑢3 𝑠𝑢𝑏𝑗𝑒𝑐𝑡 𝑡𝑜
1 𝑢1 + 1 𝑢2 + 3 𝑢3 ≥ 1000
1 𝑢1 + 2 𝑢2 + 1 𝑢3 ≥ 500 𝑢1, 𝑢2, 𝑢3 ≥ 0
8
Product-mix: Primal and dual
• What are u1, u2 and u3?
• Shadow prices of resources (Labor, cleaning and testing, respectively)
• Practice problem: Solve primal and dual problems (on solver) for the product-mix problem and compare their results
9
Why find dual of a problem?
• Shadow prices
• Computational reasons [Sometimes it is efficient to solve dual of a problem]
• Sometimes easier to do sensitivity analysis
• Effect of adding a new variable
10
Adding a new variable
• Suppose in addition to LQP and DMP, there is a third printer TQP
• You get a margin of INR 700 per TQP
• TQP takes 1.5 hrs each Labor, Cleaning and Testing
• What would be the optimal product mix now?
• Let’s write the primal and dual of this modified problem
• Effect of adding a constraint
11
Sensitivity analysis recap
• Changing OFC (objective function coefficient)
• Individually
• Simultaneously
• 100% rule
• Same multiplier for both OFCs
Range of optimality
• Changing RHSs
• Individually
• Simultaneously (100% Rule)
Range of feasibility, dual prices
• Adding a new constraint
• Adding a new variable
12