Notes 5.2 Basics of Bonding
advertisement

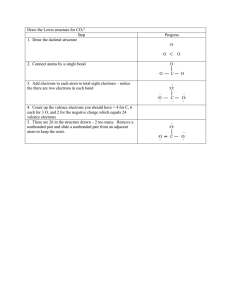
Kozinski 18/19 AP Chemistry Name _________________________________ Period ___ Date __/__/__ Unit 5 – Bonding and IMFs Notes 5.2 – Basics of Bonding Ionic Bonds: Transfer of electrons If the electronegativity difference is significant between two elements, the most electronegative element will pull the electron away from the least electronegative element creating two ions. These two ions will electrostatically attract each other forming an ionic bond. The strength of this bond depends on the lattice energy. Lattice Energy - Energy required to completely separate one mole of a solid ionic compound into its gaseous ions. NaCl(s ) Na (g ) Cl (g ) Hlattice 788kJ / mol Lattice energy depends on two things: Practice For each of the following pairs of ionic compounds, box the compound that has the highest lattice energy. a. LiF, LiCl b. MgF2 , MgO c. NaCl, Na2O d. MgO, BaS e. Fe(OH)2, Fe(OH)3 d. NaCl, KCl Covalent bonds: Sharing of electrons • If the electronegativity difference is not significant enough to transfer electrons, the two atoms will share electrons by overlapping their orbitals. They do this through hybridization (elaborated on later). There are several electrostatic interactions in these bonds: – • Attractions between electrons and nuclei, repulsions between electrons, repulsions between nuclei For a bond to form, the attractions must be greater than the repulsions. There are two types of covalent bonds we must familiarize ourselves with: polar covalent and non-polar covalent bonds. The difference between the two has everything to do with the two elements’ electronegativity. In a nonpolar covalent bond, the electrons are shared equally. Intro to hybridization 1. Consider this diagram: The equilibrium bond distance is ______ nm. The bond energy is ______ Joules which is the amount of energy you need to add to break the bond (i.e. separate the two atoms). 2. Consider this diagram again If two O atoms approach, their bond distance is 0.100 nm and bond energy is 498 J. Sketch the energy curve for O2. Elements use their valence electrons to make bonds. When they do this, they utilize ALL of their valence shell, meaning, the s and the p orbitals. When these orbitals overlap and share electrons amongst the orbitals, you create a bond. To get the orbitals to overlap, they must first hybridize. Hybridization: The mixing of two or more atomic orbitals of similar energies on the same atom to produce new orbitals of equal energies The number of “empty” spaces a hybrid orbital has will tell you how many bonds the atom can make in a covalent bond! Practice Drawing Lewis Structures HF Valence Electrons______ SiF4 Valence Electrons______ C2H6 Valence Electrons______ HCN Valence Electrons______ NH3 Valence Electrons______ F2 Valence Electrons______ C2H2 Valence Electrons______ CO Valence Electrons______ CH4 Valence Electrons______ O2 Valence Electrons______ C 2H 4 Valence Electrons______ CO2 Valence Electrons______ NF3 Valence Electrons______ N2 Valence Electrons______ C2F4 Valence Electrons______ CNValence Electrons______