Slide 1 / 25 Slide 2 / 25 Slide 3 / 25 Slide 4 / 25 Slide 5 / 25 Slide 6 / 25
advertisement
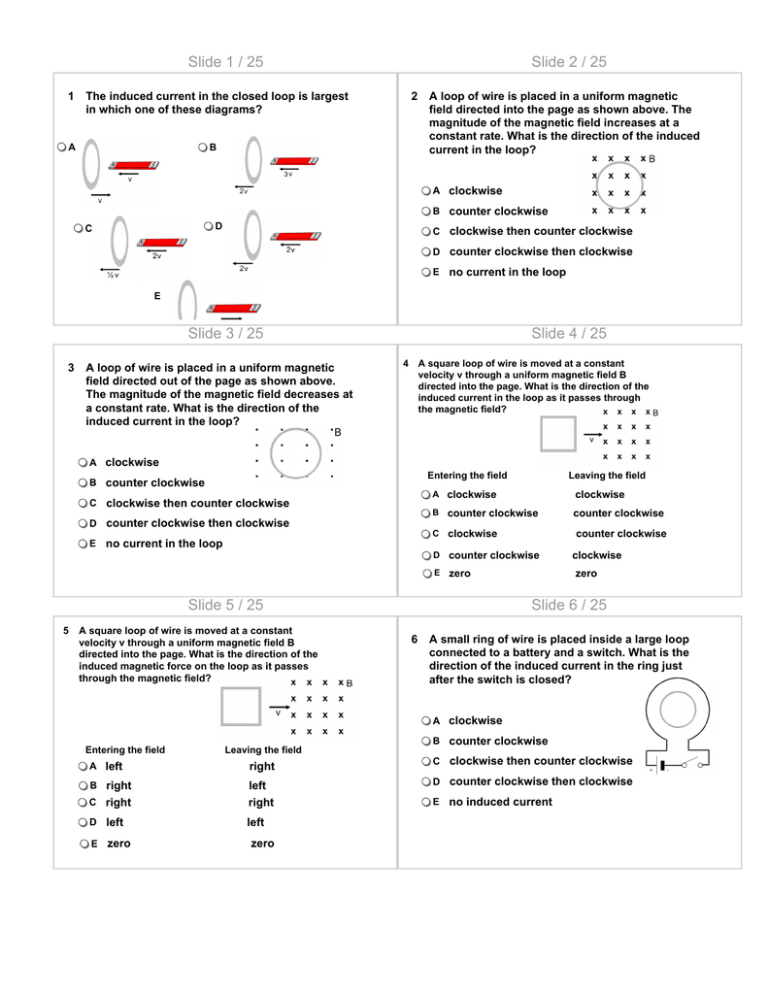
Slide 1 / 25 1 The induced current in the closed loop is largest in which one of these diagrams? A Slide 2 / 25 2 B A loop of wire is placed in a uniform magnetic field directed into the page as shown above. The magnitude of the magnetic field increases at a constant rate. What is the direction of the induced current in the loop? A clockwise B counter clockwise D C C clockwise then counter clockwise D counter clockwise then clockwise E no current in the loop E Slide 3 / 25 3 A loop of wire is placed in a uniform magnetic field directed out of the page as shown above. The magnitude of the magnetic field decreases at a constant rate. What is the direction of the induced current in the loop? Slide 4 / 25 4 A square loop of wire is moved at a constant velocity v through a uniform magnetic field B directed into the page. What is the direction of the induced current in the loop as it passes through the magnetic field? A clockwise Entering the field B counter clockwise C clockwise then counter clockwise D counter clockwise then clockwise A clockwise clockwise B counter clockwise counter clockwise C clockwise E no current in the loop counter clockwise D counter clockwise E zero Slide 5 / 25 5 Leaving the field A square loop of wire is moved at a constant velocity v through a uniform magnetic field B directed into the page. What is the direction of the induced magnetic force on the loop as it passes through the magnetic field? clockwise zero Slide 6 / 25 6 A small ring of wire is placed inside a large loop connected to a battery and a switch. What is the direction of the induced current in the ring just after the switch is closed? A clockwise Entering the field Leaving the field A left right B right C right left right D left left E zero zero B counter clockwise C clockwise then counter clockwise D counter clockwise then clockwise E no induced current Slide 7 / 25 7 A conducting rod is pulled to the right at a constant velocity v through a uniform magnetic field B directed into the page. The rod rides on two parallel conducting rails. What is the direction of the induced current in the circuit? Slide 8 / 25 8 A clockwise A conducting rod of length L is pulled to the right at a constant velocity v through a uniform magnetic field B. The rod rides two conducting rails connected to a resistor R. What is the induced current in the circuit? Ignore the resistance of the rod and the rails. A B counter clockwise B C clockwise then counter clockwise C D counter clockwise then clockwise E no induced current D E Slide 9 / 25 9 A conducting rod of length L is pulled to the right at a constant velocity v through a uniform magnetic field B. The rod rides two metallic rails connected to a resistor R. What is the rate of energy dissipation in the circuit? Ignore the resistance of the rod and the rails. Slide 10 / 25 10 A circular loop of wire is placed in the same plane as a long wire carrying a steady current I. Which of the following actions will not induce the current in the loop? A increasing current in the wire A B decreasing current in the wire B C moving the away from the wire D moving the loop in parallel to the wire C E rotating the loop with respect to its diameter D E Slide 11 / 25 11 A bar magnet with the north pole facing down is dropped above a conducting ring. As the magnet passes through the ring, what is the direction of the induced current in the ring? Slide 12 / 25 12 A bar magnet with the north pole facing down is dropped above a conducting ring. Which one of the following is true about the magnet’s acceleration as it passes through the ring? A always clockwise A less than g B always counter clockwise B greater that g C first clockwise then counter clockwise C equals g D first counter clockwise then clockwise D twice g E no induced current in the ring E zero Slide 13 / 25 13 Slide 14 / 25 14 A conducting rod moves to the right at a constant velocity. The rod crosses a uniform magnetic field directed out of the page. Which of the following choices correctly describes the electric polarity of the rod as it moves through the field? A square loop of wire with a side s and resistance R is placed in a uniform magnetic field of magnitude B directed into the page. The field begins to increase according to the formula B = β +γt, where β and γ are positive constants. What is the direction and magnitude of the induced current I in the loop? A Top End Bottom End A positive positive B negative negative C positive negative D negative positive E zero B C D zero E Slide 15 / 25 15 Slide 16 / 25 16 A circular loop of wire with radius a is placed in a uniform magnetic field perpendicular to the plane of the loop. The magnetic field varies with time generating an emf Ɛ = βπa2t1/2, where β is a constant. What is the rate of change of the magnetic field? A circular loop of wire with radius a is placed in a uniform magnetic field perpendicular to the plane of the loop. The magnetic field varies with time generating an emf Ɛ = βπa2t1/2, where β is a constant. Assuming B (t=0) = 0, which of the following formulas represents the magnetic field as a function of time? A A B B C C D D E E Slide 17 / 25 17 Slide 18 / 25 18 A rectangular loop of wire with dimensions a and b moves with a constant speed v across a uniform magnetic field B directed out of the page. Which of the following graphs represents the induced current in the loop as a function of the position x of the leading edge of the loop? A conducting rod moves to the right at a constant velocity. The rod crosses a uniform magnetic field directed out of the page. Which of the following graphs represents the induced voltage between the ends of the rod as a function of time? A C B A C D B E D E Slide 19 / 25 19 Which of the following equations states: “A changing magnetic field induces an electric field?” Slide 20 / 25 20 A The magnetic field B at all points within the shaded circle has an initial magnitude B. The magnetic field is directed into the page and begins decreasing at a constant rate. What is the shape and direction of the electric field lines induced in the circular space? B A parallel lines directed to the right C B parallel lines directed to the left C concentric circles in the clockwise direction D D concentric circles in the counter clockwise direction E parallel lines directed into the page E Slide 21 / 25 21 A circular loop of wire with an area of 6×10 -3 m2 is placed in a uniform magnetic field perpendicular to the plane of the loop. The magnetic field decreases at a constant rate from 0.04 T to zero in 12 µs. What is the induced emf in the loop? Slide 22 / 25 22 A circular loop of wire with an area of 4.0×10 -3 m2 is placed in a uniform magnetic field perpendicular to the plane of the loop. The magnetic field increases at a constant rate from zero to 0.050 T in 10.0 µs. If the electrical resistance of the loop is 400.0 Ω, what is the rate at which energy is dissipated in the loop as the field increases? A 10 V B 20 V A 0.4 W C 40 V B 1.6 W D 60 V C 3.2 W E 80 V D 1.2 W E 1.0 W Slide 23 / 25 23 A conducting ring with radius r = 0.10 m is placed in a region of a spatially uniform magnetic field perpendicular to the plane of the ring. The magnetic field is directed into the page and is decreasing at a rate of 0.050 T/s. What is the magnitude of the induced electric field in the ring? Slide 24 / 25 24 A conducting ring with a radius r = 0.10 m is placed in a region of a spatially uniform magnetic field perpendicular to the plane of the ring. The magnetic field is directed into the page and is decreasing at the rate 0.050 T/s. What is the magnitude of the induced current in the ring if its resistance is 5.0 Ω? A 5×10-3 V/m A 5π×10-3 A B 2.5×10 -3 V/m B 2.5π×10-3 A C 1.5×10 -4 V/m C π ×10-4 A D 1×10-5 V/m D π×10-5 A E 2×10-2 V/m E 2π×10-2 A Slide 25 / 25 25 An electric circuit consists of a charged capacitor C, a resistor R and a switch S. Initially, the switch is open and all devices are connected in series. A circular loop of wire is placed in the same plane as the circuit. Which one of the following is true about the induced current in the loop after the switch is closed? A it is clockwise and increases B it is counter clockwise and increases C it is clockwise and decreases D it is counter clockwise and decreases E it is clockwise and constant