Magnetic Induction & Lenz’s Law Chapter 22:
advertisement

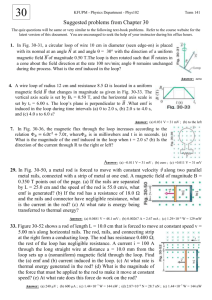
Chapter 22: Magnetic Induction & Lenz’s Law Example Problems motional vLB B A eff B ABcos induced N B t Example 22.1 A I5-cm-long metal rod is pulled along two frictionless conducting rails at a constant speed of 3.5 m/s. The rails have negligible resistance, but the rod has a resistance of 0.65Ω. a. What is the current induced in the rod? b. What force is required to keep the rod moving at a constant speed? Example 22.2 A loop of wire has the shape shown in the drawing. The top part of the wire is bent into a semicircle of radius r = 0.20 m. The normal to the plane of the loop is parallel to a constant magnetic field (φ = 08) of magnitude 0.75 T. What is the change ∆Φ in the magnetic flux that passes through the loop when, starting with the position shown in the drawing, the semicircle is rotated through half a revolution? Example 22.3 Parts a through f of figure show one or more metal wires sliding on fixed metal rails in a magnetic field. For each, determine if the induced current is clockwise, counterclockwise, or is zero. Example 22.4 The loop in figure has an induced current as shown. The loop has a resistance of 0.10Ω. Is the magnetic field strength increasing or decreasing? What is the rate of change of the field (∆B/∆t)?