Parallel Circuit Analysis Lab: PhET DC Kit Experiment
advertisement

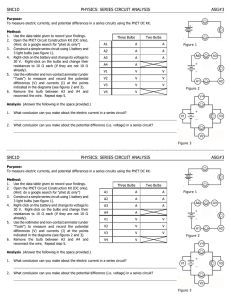
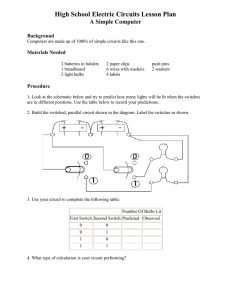
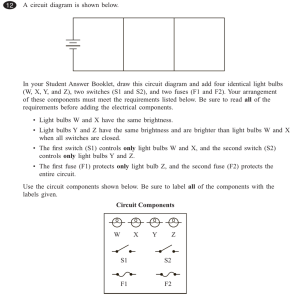
SNC1P PHYSICS: PARALLEL CIRCUIT ANALYSIS ASG#4 Purpose: To measure electric currents, and potential differences in a parallel circuits using the PhET DC Kit. Method: 1. Use the data table given to record your findings. 2. Open the PhET Circuit Construction Kit (DC only). (Hint: do a google search for “phet dc only”) 3. Construct a simple parallel circuit using 1 battery and 3 light bulbs (see figure 1). 4. Right-click on the battery and change its voltage to 30 V. Right-click on the bulbs and change their resistances to 10 S each (if they are not 10 S already). 5. Use the voltmeter and non-contact ammeter (under “Tools”) to measure and record the potential differences (V) and currents (A) at the points indicated in the diagrams (see figures 2 and 3). 6. Remove the bulb and connecting wires A4. Repeat step 5. Three Bulbs Two Bulbs A1 A A A2 A A A3 A A A4 A A5 A A V1 V V V2 V V V3 V V V4 V Figure 1 Figure 2 Analysis (Answer the following in the space provided.) 1. What conclusion can you make about the electric current in a parallel circuit? 2. What conclusion can you make about the potential difference (i.e. voltage) in a parallel circuit? SNC1P Figure 3 PHYSICS: PARALLEL CIRCUIT ANALYSIS ASG#4 Purpose: To measure electric currents, and potential differences in a parallel circuits using the PhET DC Kit. Method: 1. Use the data table given to record your findings. 2. Open the PhET Circuit Construction Kit (DC only). (Hint: do a google search for “phet dc only”) 3. Construct a simple parallel circuit using 1 battery and 3 light bulbs (see figure 1). 4. Right-click on the battery and change its voltage to 30 V. Right-click on the bulbs and change their resistances to 10 S each (if they are not 10 S already). 5. Use the voltmeter and non-contact ammeter (under “Tools”) to measure and record the potential differences (V) and currents (A) at the points indicated in the diagrams (see figures 2 and 3). 6. Remove the bulb and connecting wires A4. Repeat step 5. Three Bulbs Two Bulbs A1 A A A2 A A A3 A A A4 A A5 A A V1 V V V2 V V V3 V V V4 V Figure 1 Figure 2 Analysis (Answer the following in the space provided.) 1. What conclusion can you make about the electric current in a parallel circuit? 2. What conclusion can you make about the potential difference (i.e. voltage) in a parallel circuit? Figure 3