Graphic Organizers in Physical ...
advertisement
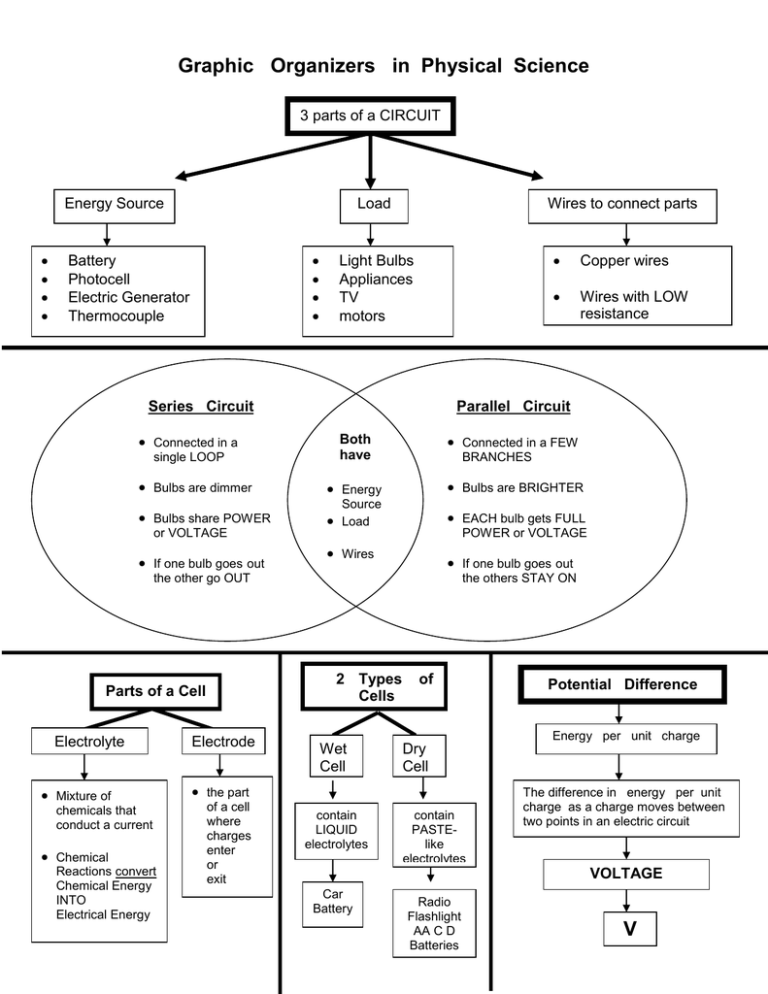
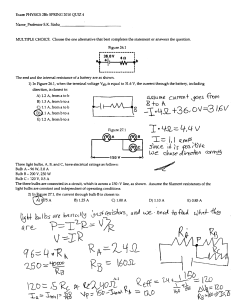
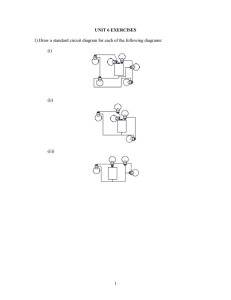
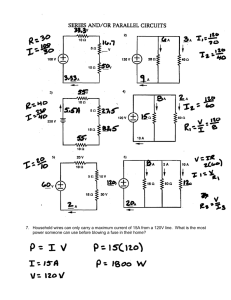
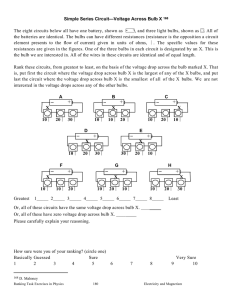
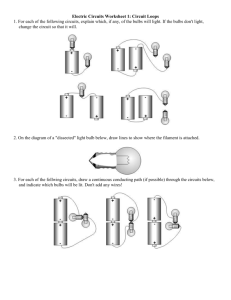
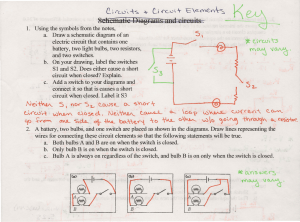
Graphic Organizers in Physical Science 3 parts of a CIRCUIT Energy Source Load Battery Photocell Electric Generator Thermocouple Wires to connect parts Light Bulbs Appliances TV motors Series Circuit or VOLTAGE If one bulb goes out Electrolyte Energy Bulbs are BRIGHTER Source Load EACH bulb gets FULL BRANCHES POWER or VOLTAGE Wires If one bulb goes out Mixture of chemicals that conduct a current Chemical Reactions convert Chemical Energy INTO Electrical Energy the others STAY ON 2 Types Cells Electrode of Potential Difference Energy per unit charge Wet Cell Dry Cell the part of a cell where charges enter or exit Wires with LOW resistance Connected in a FEW the other go OUT Parts of a Cell Both have single LOOP Bulbs share POWER Copper wires Parallel Circuit Connected in a Bulbs are dimmer contain LIQUID electrolytes contain PASTElike electrolytes The difference in energy per unit charge as a charge moves between two points in an electric circuit VOLTAGE Car Battery Radio Flashlight AA C D Batteries V