PC Update
advertisement
Y86 Instruction Set
Lecture 8
Computer Architecture III
Sequential Implementation
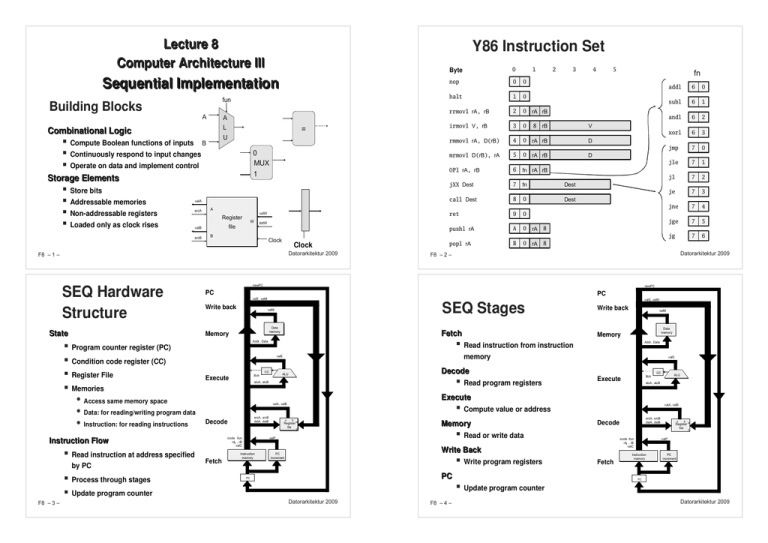
Building Blocks
fun
A
A
L
Combinational Logic
Compute Boolean functions of inputs
=
U
B
Continuously respond to input changes
0
MUX
1
Operate on data and implement control
Storage Elements
Store bits
Addressable memories
valA
Non-addressable registers
srcA
A
valW
Register
Loaded only as clock rises
srcB
W
B
Clock
Clock
Datorarkitektur 2009
F8 – 1 –
SEQ Hardware
Structure
State
valM
CC
CC
Execute
rrmovl rA, rB
2
0
rA rB
irmovl V, rB
3
0
8
rB
V
rmmovl rA, D(rB)
4
0
rA rB
D
mrmovl D(rB), rA
5
0
rA rB
D
OPl rA, rB
6
fn rA rB
jXX Dest
7
fn
Dest
call Dest
8
0
Dest
ret
9
0
pushl rA
A
0
rA
8
popl rA
B
0
rA
8
3
4
5
fn
icode ifun
rA , rB
valC
A
Instruction
Instruction
memory
memory
0
subl
6
1
andl
6
2
xorl
6
3
jmp
7
0
jle
7
1
jl
7
2
je
7
3
jne
7
4
jge
7
5
jg
7
6
Read instruction from instruction
newPC
PC
valE, valM
Write back
valM
Data
Data
memory
memory
Memory
Addr , Data
valE
Execute
Bch
CC
CC
ALU
ALU
aluA , aluB
Execute
Compute value or address
B
M
Register
Register
file
file E
Memory
valA, valB
Decode
Read or write data
valP
,
6
Datorarkitektur 2009
Read program registers
aluA, aluB
srcA, srcB
dstA, dstB
addl
F8 – 2 –
Write program registers
PC
PC
Datorarkitektur 2009
F8 – 4 –
srcA , srcB
dstA , dstB
icode ifun
rA , rB
valC
Fetch
A
B
M
Register
Register
file
file E
valP
,
Write Back
PC
PC
increment
increment
Update program counter
F8 – 3 –
2
Decode
ALU
ALU
Bch
Decode
Fetch
1
memory
valA , valB
Instruction Flow
Process through stages
0
valE
Access same memory space
by PC
1
Fetch
Data
Data
memory
memory
Memories
Read instruction at address specified
halt
Addr , Data
Condition code register (CC)
Instruction: for reading instructions
0
SEQ Stages
valE, valM
Write back
Program counter register (PC)
Data: for reading/writing program data
0
newPC
PC
Memory
Register File
0
nop
dstW
file
valB
Byte
Instruction
Instruction
memory
memory
PC
PC
increment
increment
PC
Update program counter
Datorarkitektur 2009
Instruction Decoding
Executing Arith./Logical Operation
OPl rA, rB
Optional
5
0
rA rB
Optional
Fetch
6 fn rA rB
Memory
Read 2 bytes
D
Do nothing
Decode
icode
ifun
rA
rB
valC
Write back
Read operand registers
Update register
Execute
PC Update
Perform operation
Instruction Format
Increment PC by 2
Set condition codes
Instruction byte
icode:ifun
Optional register byte
rA:rB
Optional constant word valC
Datorarkitektur 2009
F8 – 5 –
Executing rmmovl
Stage Computation: Arith/Log. Ops
OPl rA, rB
rmmovl rA, D(rB)
icode:ifun ← M1 [PC]
rA:rB ← M1 [PC+1]
Read instruction byte
Read register byte
valP ← PC+2
Compute next PC
Decode
valA ← R[rA]
valB ← R[rB]
Read operand A
Read operand B
Execute
valE ← valB OP valA
Set CC
Perform ALU operation
Set condition code register
Write back
R[rB] ← valE
Write back result
PC update
PC ← valP
Update PC
Fetch
Datorarkitektur 2009
F8 – 6 –
4 0 rA rB
Fetch
Memory
Read 6 bytes
Decode
Read operand registers
Execute
Memory
D
Compute effective address
Write to memory
Write back
Do nothing
PC Update
Increment PC by 6
Formulate instruction execution as sequence of simple steps
Use same general form for all instructions
F8 – 7 –
Datorarkitektur 2009
F8 – 8 –
Datorarkitektur 2009
Stage Computation: rmmovl
rmmovl rA, D(rB)
Executing popl
popl rA
icode:ifun ← M1 [PC]
rA:rB ← M1 [PC+1]
valC ← M4[PC+2]
valP ← PC+6
Read instruction byte
Read register byte
Read displacement D
Compute next PC
Decode
valA ← R[rA]
valB ← R[rB]
Read operand A
Read operand B
Execute
valE ← valB + valC
Compute effective address
Memory
M4[valE] ← valA
Write value to memory
Fetch
Fetch
Memory
Read 2 bytes
Read from old stack pointer
Decode
Write back
Read stack pointer
Update stack pointer
Write result to register
Execute
Increment stack pointer by 4
Write back
PC update
b 0 rA 8
PC ← valP
PC Update
Increment PC by 2
Update PC
Use ALU for address computation
Datorarkitektur 2009
F8 – 9 –
Stage Computation: popl
popl rA
icode:ifun ← M1 [PC]
rA:rB ← M1 [PC+1]
Read instruction byte
Read register byte
valP ← PC+2
Compute next PC
Decode
valA ← R[%esp]
valB ← R[%esp]
Read stack pointer
Read stack pointer
Execute
valE ← valB + 4
Increment stack pointer
Fetch
Memory
valM ← M4[valA]
Read from stack
Write back
R[%esp] ← valE
R[rA] ← valM
Update stack pointer
Write back result
PC update
PC ← valP
Executing Jumps
Fetch
7 fn
fall thru:
XX XX
Not taken
target:
XX XX
Taken
Read 5 bytes
Decode
Do nothing
Update PC
Execute
Must update two registers
» Popped value
» New stack pointer
jXX Dest
Increment PC by 5
Use ALU to increment stack pointer
F8 – 11 –
Datorarkitektur 2009
F8 – 10 –
Dest
Memory
Do nothing
Write back
Do nothing
PC Update
Set PC to Dest if branch taken
Determine whether to take
or to incremented PC if not
branch based on jump
branch
condition and condition codes
Datorarkitektur 2009
F8 – 12 –
Datorarkitektur 2009
Stage Computation: Jumps
jXX Dest
Fetch
Executing call
call Dest
icode:ifun ← M1 [PC]
Read instruction byte
valC ← M4[PC+1]
valP ← PC+5
Read destination address
Fall through address
Bch ← Cond(CC,ifun)
Take branch?
Decode
Execute
Write back
PC ← Bch ? valC : valP
Choose based on setting of condition codes and branch condition
Datorarkitektur 2009
F8 – 13 –
Stage Computation: call
Memory
Read 5 bytes
Write incremented PC to new
Increment PC by 5
value of stack pointer
Write back
Update stack pointer
PC Update
Execute
Datorarkitektur 2009
ret
Read instruction byte
valC ← M4[PC+1]
valP ← PC+5
Read destination address
Compute return point
Decode
valB ← R[%esp]
Read stack pointer
Execute
valE ← valB + –4
Decrement stack pointer
9 0
return:
Fetch
M4[valE] ← valP
Write back
R[%esp] ← valE
Update stack pointer
PC update
PC ← valC
Set PC to destination
XX XX
Memory
Read 1 byte
Decode
Memory
Set PC to Dest
Decrement stack pointer by 4
F8 – 14 –
Executing ret
icode:ifun ← M1 [PC]
Fetch
XX XX
Read stack pointer
Compute both addresses
call Dest
target:
Decode
Update PC
Dest
XX XX
Fetch
Memory
PC update
8 0
return:
Read stack pointer
Execute
Increment stack pointer by 4
Read return address from old
stack pointer
Write back
Update stack pointer
PC Update
Set PC to return address
Use ALU to decrement stack pointer
Store incremented PC
F8 – 15 –
Datorarkitektur 2009
F8 – 16 –
Datorarkitektur 2009
Computation Steps
Stage Computation: ret
ret
Fetch
icode:ifun ← M1 [PC]
icode,ifun
Read instruction byte
Decode
valA ← R[%esp]
valB ← R[%esp]
Read operand stack pointer
Read operand stack pointer
Decode
Execute
valE ← valB + 4
Increment stack pointer
Execute
Memory
valM ← M4[valA]
Read return address
Write back
R[%esp] ← valE
Update stack pointer
PC update
PC ← valM
Set PC to return address
Memory
Write back
PC update
Read return address from memory
Datorarkitektur 2009
Stage Computation: A
Computation Steps
Decode
Execute
Memory
Write back
PC update
call Dest
icode:ifun ← M1 [PC]
valC ← M4[PC+1]
valP ← PC+5
valB ← R[%esp]
valE ← valB + –4
M4[valE] ← valP
R[%esp] ← valE
PC ← valC
valB ← R[rB]
valE ← valB OP valA
Set CC
R[rB] ← valE
PC ← valP
Datorarkitektur 2009
F8 – 18 –
Computed Values
Read instruction byte
[Read register byte]
Read constant word
Compute next PC
[Read operand A]
Read operand B
Perform ALU operation
[Set condition code reg.]
Memory read/write
Write back ALU result
[Write back memory result]
Update PC
Fetch
Instruction code
ifun
Instruction function
rA
Instr. Register A
rB
Instr. Register B
valC
Instruction constant
valP
Incremented PC
srcA
Differ in what gets computed on each step
Datorarkitektur 2009
icode
Decode
All instructions follow same general pattern
F8 – 19 –
valP ← PC+2
valA ← R[rA]
Differ in what gets computed on each step
F8 – 17 –
icode,ifun
rA,rB
valC
valP
valA, srcA
valB, srcB
valE
Cond code
valM
dstE
dstM
PC
valC
valP
valA, srcA
valB, srcB
valE
Cond code
valM
dstE
dstM
PC
Read instruction byte
Read register byte
[Read constant word]
Compute next PC
Read operand A
Read operand B
Perform ALU operation
Set condition code register
[Memory read/write]
Write back ALU result
[Write back memory result]
Update PC
All instructions follow same general pattern
Use ALU to increment stack pointer
Fetch
rA,rB
Fetch
OPl rA, rB
icode:ifun ← M1 [PC]
rA:rB ← M1[PC+1]
F8 – 20 –
Execute
valE
ALU result
Bch
Branch flag
Memory
valM Value from memory
Register ID A
srcB
Register ID B
dstE
Destination Register E
dstM
Destination Register M
valA
Register value A
valB
Register value B
Datorarkitektur 2009
SEQ Hardware
Key
Fetch Logic
newPC
New
PC
PC
icode
ifun
rA
rB
valC
valP
Need
valC
valM
data out
Light grey boxes:
read
predesigned hardware
Memory
write
Addr
blocks
Bch
E.g., memories, ALU
Execute
Darker gray boxes:
Instr
valid
Data
Data
memory
memory
Mem.
control
Data
Split
Split
valE
ALU
A
control logic
PC
PC
increment
increment
Align
Align
Byte 0
ALU
fun.
ALU
ALU
CC
CC
Need
regids
Bytes 1 -5
Instruction
Instruction
memory
memory
ALU
B
Describe in HCL
White ovals:
valA
labels for signals
Decode
A
icode
Thin lines:
ifun
Fetch
rB
valC
Instruction
Instruction
memory
memory
4-8 bit values
srcA
srcB
dstE dstM
srcA
srcB
Predefined Blocks
Instruction memory: Read 6 bytes (PC to PC+5)
PC
PC
increment
increment
Split: Divide instruction byte into icode and ifun
Align: Get fields for rA, rB, and valC
1-bit values
Datorarkitektur 2009
Fetch Logic
icode
ifun
rA
rB
valC
valP
Need
valC
Instr
valid
Need
regids
Split
Split
PC
PC
increment
increment
Fetch Control
Logic
Bytes 1 -5
Instruction
Instruction
memory
memory
PC
Control Logic
Datorarkitektur 2009
F8 – 22 –
Align
Align
Byte 0
nop
0
0
halt
1
0
rrmovl rA, rB
2
0 rA rB
irmovl V, rB
3
0
8 rB
V
rmmovl rA, D(rB)
4
0 rA rB
D
mrmovl D(rB), rA
5
0 rA rB
D
OPl rA, rB
6 fn rA rB
jXX Dest
7 fn
Dest
call Dest
8
0
Dest
ret
9
0
pushl rA
A
0 rA 8
popl rA
B
0 rA 8
bool need_regids =
icode in { IRRMOVL, IOPL, IPUSHL, IPOPL,
IIRMOVL, IRMMOVL, IMRMOVL };
Instr. Valid: Is this instruction valid?
Need regids: Does this instruction have a register byte?
bool instr_valid = icode in
{ INOP, IHALT, IRRMOVL, IIRMOVL, IRMMOVL, IMRMOVL,
IOPL, IJXX, ICALL, IRET, IPUSHL, IPOPL };
Need valC: Does this instruction have a constant word?
F8 – 23 –
PC
PC: Register containing PC
Write back
valP
PC
Dotted lines:
F8 – 21 –
rA
dstE dstM
B
Register
Register M
file
file E
Thick lines:
32-bit word values
valB
Datorarkitektur 2009
F8 – 24 –
Datorarkitektur 2009
Decode Logic
A Source
valB
valA
Register File
A
Read ports A, B
B
Register
Register
file
file
Write ports E, M
dstE
Addresses are register IDs
dstM
srcA
dstE dstM srcA
or 8 (no access)
valM
valE
M
icode
rA
Read stack pointer
No operand
Decode
rB
Decode
OPl rA, rB
R[rB] ← valE
Read stack pointer
} : rA;
Datorarkitektur 2009
F8 – 26 –
Execute Logic
Write back result
rmmovl rA, D(rB)
Units
None
popl rA
R[%esp] ← valE
No operand
ret
valA ← R[%esp]
int srcA = [
icode in { IRRMOVL, IRMMOVL, IOPL, IPUSHL
icode in { IPOPL, IRET } : RESP;
1 : RNONE; # Don't need register
];
ALU
Implements 4 required functions
Bch
Update stack pointer
CC
jXX Dest
bcond
bcond
Register with 3 condition code bits
None
call Dest
R[%esp] ← valE
Update stack pointer
Write-back
ret
R[%esp] ← valE
Update stack pointer
Computes branch flag
Set
CC
Control Logic
ALU
fun.
ALU
ALU
CC
CC
bcond
Write-back
valE
Generates condition code values
ALU
A
ALU
B
Set CC: Should condition code
register be loaded?
icode ifun
valC
valA
valB
ALU A: Input A to ALU
int dstE = [
icode in { IRRMOVL, IIRMOVL, IOPL} : rB;
icode in { IPUSHL, IPOPL, ICALL, IRET } : RESP;
1 : RNONE; # Don't need register
];
F8 – 27 –
Decode
Decode
Datorarkitektur 2009
Write-back
Read operand A
popl rA
valA ← R[%esp]
jXX Dest
srcB
F8 – 25 –
Write-back
Decode
srcB
dstE, dstM: write port addresses
Write-back
Read operand A
rmmovl rA, D(rB)
valA ← R[rA]
E
srcA, srcB: read port addresses
Write-back
valA ← R[rA]
call Dest
Control Logic
E Destination
OPl rA, rB
Decode
ALU B: Input B to ALU
ALU fun: What function should ALU
compute?
Datorarkitektur 2009
F8 – 28 –
Datorarkitektur 2009
ALU A Input
Execute
OPl rA, rB
valE ← valB OP valA
Execute
rmmovl rA, D(rB)
valE ← valB + valC
Execute
Execute
Execute
Execute
Perform ALU operation
Execute
Compute effective address
valE ← valB + 4
Compute effective address
Execute
popl rA
valE ← valB + 4
Increment stack pointer
jXX Dest
Execute
valE ← valB + –4
Decrement stack pointer
ret
valE ← valB + 4
Perform ALU operation
valE ← valB + valC
No operation
call Dest
No operation
Execute
call Dest
valE ← valB + –4
Decrement stack pointer
Execute
ret
valE ← valB + 4
Increment stack pointer
Increment stack pointer
int alufun = [
icode == IOPL : ifun;
1 : ALUADD;
];
Datorarkitektur 2009
Memory Logic
Datorarkitektur 2009
F8 – 30 –
Memory Address
Memory
Memory
valM
data out
Reads or writes memory word
Mem.
read
Control Logic
Mem.
write
Memory
read
Data
Data
memory
memory
write
Mem
addr
read?
icode
valE
OPl rA, rB
No operation
rmmovl rA, D(rB)
M4[valE] ← valA
Write value to memory
popl rA
data in
Mem. read: should word be
Mem. write: should word be
valE ← valB OP valA
Execute
Increment stack pointer
jXX Dest
written?
OPl rA, rB
rmmovl rA, D(rB)
popl rA
int aluA = [
icode in { IRRMOVL, IOPL } : valA;
icode in { IIRMOVL, IRMMOVL, IMRMOVL } : valC;
icode in { ICALL, IPUSHL } : -4;
icode in { IRET, IPOPL } : 4;
# Other instructions don't need ALU
F8 – 29 – ];
Mem
data
valA valP
Memory
Memory
Memory
valM ← M4[valA]
Read from stack
jXX Dest
No operation
call Dest
M4[valE] ← valP
Write return value on stack
ret
Mem. addr.: Select address
Memory
Mem. data.: Select data
F8 – 31 –
ALU Operation
Datorarkitektur 2009
valM ← M4[valA]
Read return address
int mem_addr = [
icode in { IRMMOVL, IPUSHL, ICALL, IMRMOVL } : valE;
icode in { IPOPL, IRET } : valA;
# Other instructions don't need address
Datorarkitektur 2009
F8 – 32 – ];
Memory Read
Memory
PC Update Logic
OPl rA, rB
No operation
Memory
rmmovl rA, D(rB)
M4[valE] ← valA
Write value to memory
Memory
popl rA
valM ← M4[valA]
Read from stack
PC
New PC
jXX Dest
Memory
New
PC
Select next value of PC
icode
No operation
Memory
call Dest
M4[valE] ← valP
Write return value on stack
Memory
ret
valM ← M4[valA]
Read return address
Bch
valC
valM
valP
bool mem_read = icode in { IMRMOVL, IPOPL, IRET };
Datorarkitektur 2009
F8 – 33 –
PC
Update
PC update
PC update
PC update
PC update
PC update
PC update
Update PC
SEQ Summary
Update PC
Implementation
OPl rA, rB
PC ← valP
rmmovl rA, D(rB)
PC ← valP
Express every instruction as series of simple steps
popl rA
PC ← valP
Update PC
Follow same general flow for each instruction type
jXX Dest
PC ← Bch ? valC : valP
Assemble registers, memories, predesigned combinational blocks
Update PC
Connect with control logic
call Dest
PC ← valC
Set PC to destination
ret
PC ← valM
Limitations
Too slow to be practical
Set PC to return address
In one cycle, must propagate through instruction memory, register
int new_pc = [
icode == ICALL : valC;
icode == IJXX && Bch : valC;
icode == IRET : valM;
1 : valP;
];
F8 – 35 –
Datorarkitektur 2009
F8 – 34 –
file, ALU, and data memory
Would need to run clock very slowly
Hardware units only active for fraction of clock cycle
Datorarkitektur 2009
F8 – 36 –
Datorarkitektur 2009
![rA:rB ← M1[PC + 1]](http://s2.studylib.net/store/data/018423350_1-599cece974562f293bc03343cf6345d6-300x300.png)