basic electronic devices and circuits
advertisement
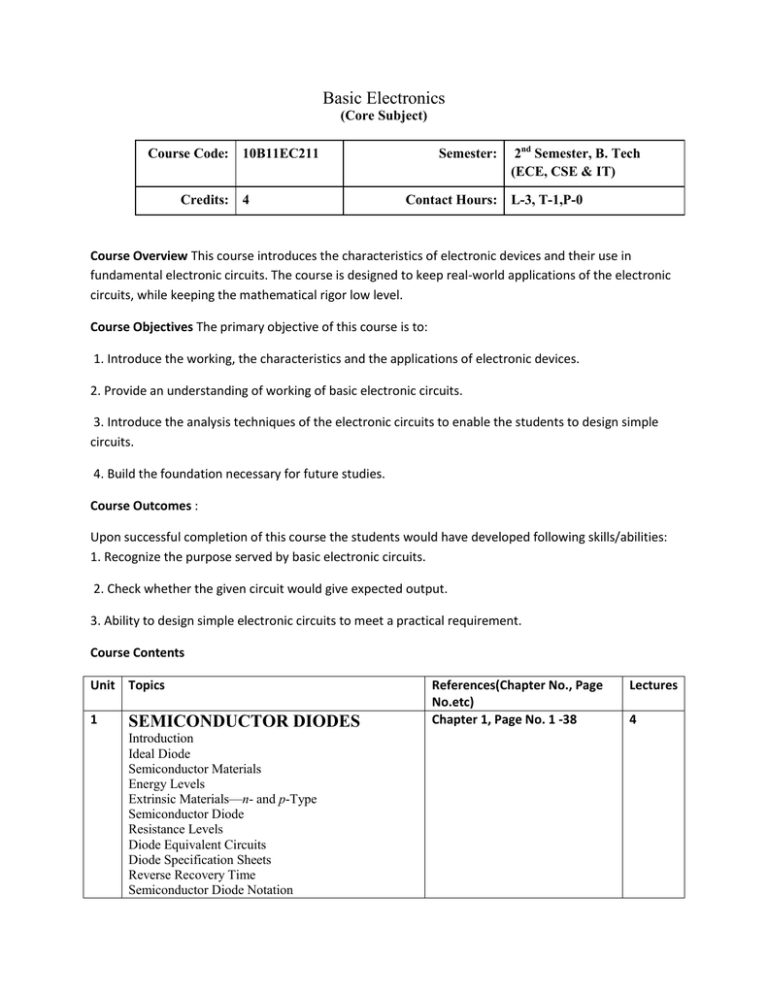
Basic Electronics (Core Subject) Course Code: 10B11EC211 Credits: 4 Semester: 2nd Semester, B. Tech (ECE, CSE & IT) Contact Hours: L-3, T-1,P-0 Course Overview This course introduces the characteristics of electronic devices and their use in fundamental electronic circuits. The course is designed to keep real-world applications of the electronic circuits, while keeping the mathematical rigor low level. Course Objectives The primary objective of this course is to: 1. Introduce the working, the characteristics and the applications of electronic devices. 2. Provide an understanding of working of basic electronic circuits. 3. Introduce the analysis techniques of the electronic circuits to enable the students to design simple circuits. 4. Build the foundation necessary for future studies. Course Outcomes : Upon successful completion of this course the students would have developed following skills/abilities: 1. Recognize the purpose served by basic electronic circuits. 2. Check whether the given circuit would give expected output. 3. Ability to design simple electronic circuits to meet a practical requirement. Course Contents Unit Topics 1 SEMICONDUCTOR DIODES Introduction Ideal Diode Semiconductor Materials Energy Levels Extrinsic Materials—n- and p-Type Semiconductor Diode Resistance Levels Diode Equivalent Circuits Diode Specification Sheets Reverse Recovery Time Semiconductor Diode Notation References(Chapter No., Page No.etc) Chapter 1, Page No. 1 -38 Lectures 4 Zener Diodes Light-Emitting Diodes (LEDs) Diode Arrays— Integrated Circuits 2 DIODE APPLICATIONS Chapter 2, Page 51 -94 6 Chapter 3, Pages 112-130 9 Chapter 4, Pages 114-190 10 Chapter 5, Pages 212 -244 10 Chapter 6, Pages 254-288 7 Introduction Load-Line Analysis Diode Approximations Series Diode Configurations with DC Inputs Parallel and Series-Parallel Configurations AND/OR Gates Sinusoidal Inputs; Half-Wave Rectification Full-Wave Rectification Clippers Clampers Zener Diodes Voltage-Multiplier Circuits 3 BIPOLAR JUNCTION TRANSISTORS Transistor Construction Transistor Operation Common-Base Configuration Transistor Amplifying Action Common-Emitter Configuration Common-Collector Configuration Limits of Operation Transistor Specification Sheet 4 DC BIASING—BJTS Operating Point Fixed-Bias Circuit Emitter-Stabilized Bias Circuit Voltage-Divider Bias DC Bias with Voltage Feedback Miscellaneous Bias Configurations Design Operations Transistor Switching Networks PNP Transistors Bias Stabilization 5 FIELD-EFFECT TRANSISTORS Construction and Characteristics of JFETs Transfer Characteristics Specification Sheets (JFETs) Instrumentation Important Relationships Depletion-Type MOSFET Enhancement-Type MOSFET MOSFET Handling VMOS CMOS 6 FET BIASING Fixed-Bias Configuration Self-Bias Configuration Voltage-Divider Biasing Depletion-Type MOSFETs Enhancement-Type MOSFETs Combination Networks Design P-Channel FETs Universal JFET Bias Curve Total No of Lectures 45 Evaluation Scheme 1. 2. 3. 4. Test 1 :15 marks Test 2 : 25 marks Test 3 : 35 marks Internal Assessment : 25 marks 10 Marks : Class performance, Tutorials & Assignments 10 Marks : Quizzes 5 marks : Attendance Text Books 1. Electronic Devices and Circuit Theory: Robert Boylestad and Louis Nashelsky. 2. Electronic Device: Thomas L Floyd Reference Books 1. Adel S. Sedra, Kenneth C. Smith : University Press, 2004 Microelectronics Circuits, Oxford