The PowerRouter – Battery Basics
advertisement

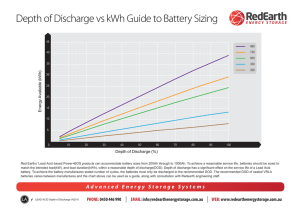
Technical Note battery basics ... Batteries come in a vast number of sizes, chemistries and type. This note will show how connecting batteries effects various things. series connections ... The number of batteries in series determines the battery bank Voltage All voltages are added together. Capacity or amp hour (Ah) will remain the same. All batteries must be the same capacity, age and type or voltage imbalance will occur. Energy storage will also add. Example: Using 2 volt batteries that are 200 Ah which is 400 watt hour (Wh) each in a series configuration of 12. Connecting them in series as shown, the voltage result is 24 volts. The amp hour capacity remains the same, 200 Ah. The calculation of the energy storage in Wh is: 200 ah x 24 V = 4800 Wh or 4.8 kWh. 24V 2 4 6 8 10 12 14 16 18 20 22 200Ah You would use this method to achieve the voltage you require for your system. parallel connections ... 12V In this case the number of batteries in parallel determines the battery bank capacity (in Ah). All capacity (Ah) are added together. Voltage will remain the same. All batteries must be the same voltage, age and type or current imbalance will occur. Energy storage will also add. Example: Using 12 volt batteries that are 100 Ah and 1200 Wh each and connecting them in parallel bank of 4, the voltage result is still 12 volts. The amp hour capacity is now 400 Ah. The calculation of the energy storage in Wh is: 400 ah x 12 V = 4800 Wh or 4.8kWh. You would use this method to increase energy capacity at and keep the voltage constant. www.PowerRouter.com.au PRTN-006-B 300Ah 400Ah 200Ah 100Ah series - parallel connections ... This is a combination of the above techniques. All series battery voltages add together to form a “string”. All strings in parallel determine the battery bank capacity (in Ah). Battery bank voltage is the total of voltage the string. All batteries must be the same voltage, age and type or current imbalance will occur. Energy storage will also add. 24V 12 Example: Using 12 V batteries with 100 Ah capacity and 1200 Wh each. Connecting two in series (forming a striing 24 V 100 Ah), then connecting 2 strings in parallel as shown, the voltage is now 24 V. The capacity has now increased to 200 Ah. The calculation of the energy storage in Wh is: 2 x (100 ah x 24 V) = 4800 Wh or 4.8 kWh. String 2 12 100Ah String 1 You would use this method is used to increase energy capacity at a certain voltage. battery types ... There are many types of batteries, each has it’s own advantages. GEL or Sealed Lead Acid – generally lowest cost initially, manufacturers recommend only using 20% to 50% of capacity to achieve good lifetime if used daily. If used rarely, discharging up to 80% may be OK. Lithium – generally more expensive initially, allow deeper discharge, can use 80% of capacity. Smaller and lighter than equivalent in GEL. Example Battery bank: 400 Ah, 24V (9.6 kWh) average battery usage kW load Hours GEL Hours Lithium Backup Backup 100% DoD 100% DoD Hours GEL Daily 50% DoD Hours Lithium Daily 80% DoD 1 > 8.6 9.5 4.3 7.6 3 > 2.4 3.2 1.2 2.5 5 > 1.2 1.9 0.6 1.5 A 30 kWh/day usage house, would average between 18 kW and 26 kW during the evening period. Battery bank size required based for the two technologies. kWh used GEL (kWh) Lithium (kWh) 20 > 40 25 36 > 72 45 60 > 120 75 www.PowerRouter.com.au PRTN-006-B 200Ah